Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
As with other Azure services, there are limits on certain resources associated with Azure Batch. For example, if your pool doesn't reach your target number of compute nodes, you might have reached the core quota limit for your Batch account. Many limits are default quotas, which Azure applies at the subscription or account level.
Keep these quotas in mind as you design and scale up your Batch workloads. You can run multiple Batch workloads in a single Batch account. Or, you can distribute your workloads among Batch accounts in the same subscription but different Azure regions. If you plan to run production workloads in Batch, you might need to increase one or more of the quotas above the default. To raise a quota, request a quota increase at no charge.
Resource quotas
A quota is a limit, not a capacity guarantee. If you have large-scale capacity needs, contact Azure support.
Also note that quotas aren't guaranteed values. Quotas can vary based on changes from the Batch service or a user request to change a quota value.
| Resource | Default limit | Maximum limit |
|---|---|---|
| Azure Batch accounts per region per subscription | 1-3 | 50 |
| Dedicated cores per Batch account | 0-9001 | Contact support |
| Active jobs and job schedules per Batch account (completed jobs have no limit) | 100-300 | 1,0002 |
| Pools per Batch account | 0-1001 | 5002 |
| Private endpoint connections per Batch account | 100 | 100 |
1 For capacity management purposes, the default quotas for new Batch accounts in some regions and for some subscription types have been reduced from the above range of values. In some cases, these limits have been reduced to zero. When you create a new Batch account, check your quotas and request an appropriate core or service quota increase, if necessary. Alternatively, consider reusing Batch accounts that already have sufficient quota or user subscription pool allocation Batch accounts to maintain core and VM family quota across all Batch accounts on the subscription. Service quotas like active jobs or pools apply to each distinct Batch account even for user subscription pool allocation Batch accounts.
2 To request an increase beyond this limit, contact Azure Support.
Note
Default limits vary depending on the type of subscription you use to create a Batch account. Cores quotas shown are for Batch accounts in Batch service mode. View the quotas in your Batch account.
Core quotas
Core quotas in Batch service mode
Core quotas exist for each virtual machine (VM) series supported by Batch. These core quotas are displayed on the Quotas page in the Azure portal. To update VM series quota limits, open a support request.
- For dedicated nodes, Batch enforces a core quota limit for each VM series, and a total core quota limit for the entire Batch account.
- For Spot nodes, Batch enforces only a total core quota for the Batch account without any distinction between different VM series.
Core quotas in user subscription mode
If you created a Batch account with pool allocation mode set to user subscription, Batch VMs and other resources are created directly in your subscription when a pool is created or resized. The Azure Batch core quotas don't apply and the quotas in your subscription for regional compute cores, per-series compute cores, and other resources are used and enforced.
To learn more about these quotas, see Azure subscription and service limits, quotas, and constraints.
Pool size limits
Pool size limits are set by the Batch service. Unlike resource quotas, these values can't be changed. Only pools with inter-node communication and custom images have restrictions different from the standard quota.
| Resource | Maximum Limit |
|---|---|
| Compute nodes in inter-node communication enabled pool | |
| Batch service pool allocation mode | 100 |
| Batch subscription pool allocation mode | 80 |
| Compute nodes in pool created with a managed image resource1 | |
| Dedicated nodes | 2000 |
1 For pools that aren't inter-node communication enabled.
Other limits
The Batch service sets the following other limits. Unlike resource quotas, it's not possible to change these values.
| Resource | Maximum Limit |
|---|---|
| Concurrent tasks per compute node | 4 x number of node cores |
| Applications per Batch account | 200 |
| Application packages per application | 40 |
| Application packages per pool | 10 |
| Maximum task lifetime | 180 days1 |
| Mounts per compute node | 10 |
| Certificates per pool | 12 |
1 The maximum lifetime of a task, from when it's added to the job to when it completes, is 180 days. By default, data is retained for completed tasks for seven days if the compute node where it ran is still available. Data for tasks not completed within the maximum lifetime isn't accessible. Completed task data retention times are configurable on a per task basis.
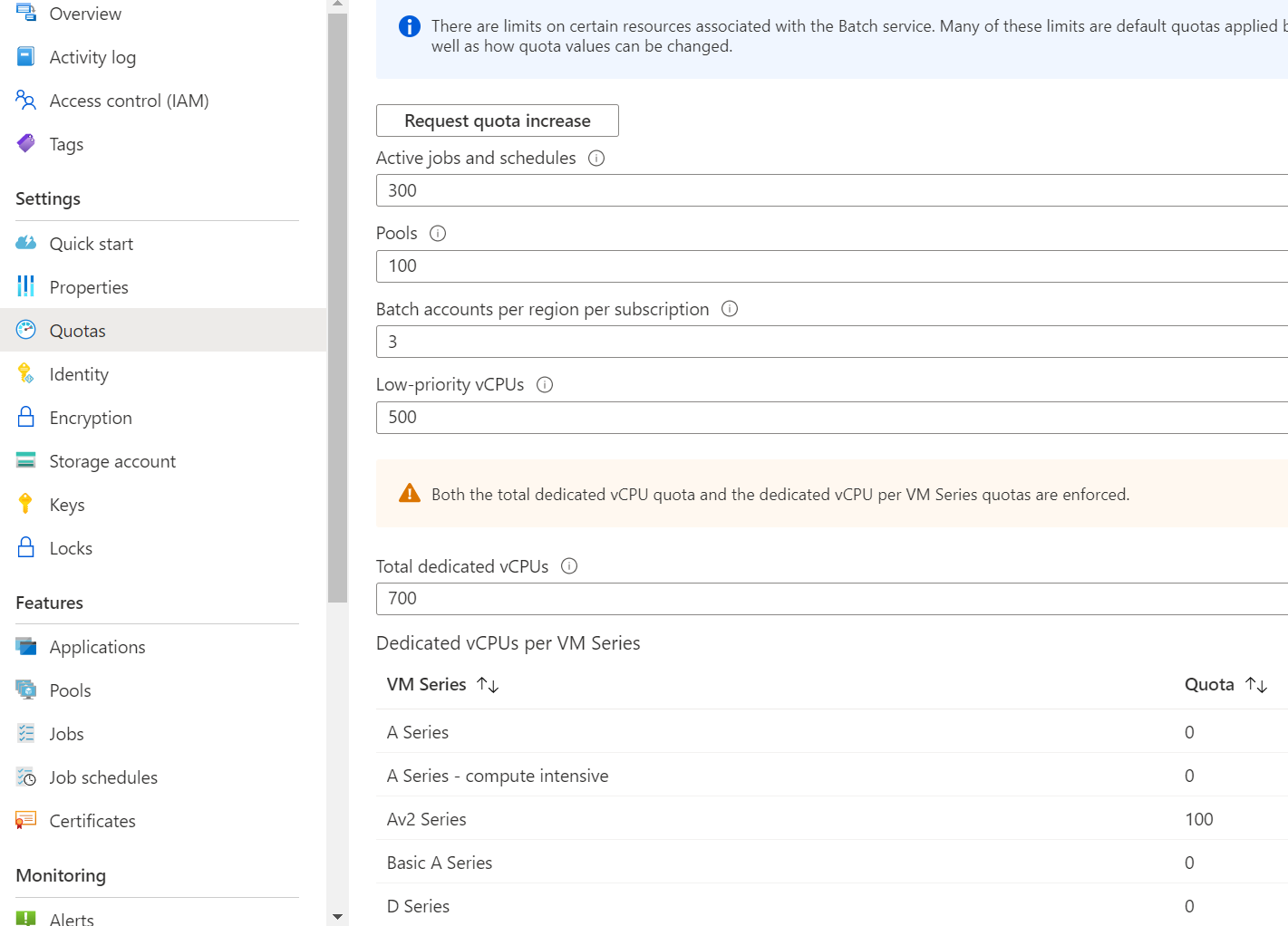
View Batch quotas
To view your Batch account quotas in the Azure portal:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Select or search for Batch accounts.
On the Batch accounts page, select the Batch account that you want to review.
On the Batch account's menu, under Settings, select Quotas.
Review the quotas currently applied to the Batch account.
Increase a quota
You can request a quota increase for your Batch account or your subscription using the Azure portal or by using the Azure Quota REST API.
The type of quota increase depends on the pool allocation mode of your Batch account. To request a quota increase, you must include the VM series for which you would like to increase the quota. When the quota increase is applied, it's applied to all series of VMs.
Once you've submitted your support request, Azure support will contact you. Quota requests may be completed within a few minutes or up to two business days.
Request through Azure Quota REST API
You can use the Azure Quota REST API to request a quota increase at the subscription level or at the Batch account level.
For details and examples, see Request a quota increase using the Azure Support REST API.
Related quotas for VM pools
Batch pools in a VM configuration deployed in an Azure virtual network automatically allocate more Azure networking resources. These resources are created in the subscription that contains the virtual network supplied when creating the Batch pool.
The following resources are created for each 100 pool nodes in a virtual network:
- One network security group
- One public IP address
- One load balancer
These resources are limited by the subscription's resource quotas. If you plan large pool deployments in a virtual network, you may need to request a quota increase for one or more of these resources.
Next steps
- Learn about the Batch service workflow and primary resources such as pools, nodes, jobs, and tasks.
- Learn about Azure subscription and service limits, quotas, and constraints.