Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
To secure the data stored in your account, Azure Cosmos DB uses a secret-based authorization model with a strong hash-based message authentication code (HMAC). Additionally, Azure Cosmos DB uses IP-based access controls for inbound firewall security. This model is similar to the firewall rules of a traditional database system and adds another layer of security to your account. With firewalls, configure your Azure Cosmos DB account to allow access only from an approved set of machines or cloud services. Access to data stored in your Azure Cosmos DB database from these approved machines and services still requires the caller to present a valid authorization token.
IP access control
By default, your Azure Cosmos DB account is accessible from the internet if the request includes a valid authorization token. To configure IP policy-based access control, the user must provide the set of IP addresses or IP address ranges in CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) form to be included as the allowed list of client IPs to access a given Azure Cosmos DB account. After you apply this configuration, any requests from machines outside this allowed list receive a 403 (Forbidden) response. When you use an IP firewall, some scenarios might require you to enable access from the Azure portal. For more information, see allow requests from the Azure portal. When using data explorer for an API for NoSQL, Gremlin or Table account, you also need to update your firewall settings to add your current IP address to the firewall rules. Firewall changes might take up to 15 minutes to propagate, and the firewall might behave inconsistently during this period.
Combine IP-based firewalls with subnet and virtual network access control. By combining them, you can limit access to any source that has a public IP and/or from a specific subnet within virtual network. To learn more about using subnet and virtual network-based access control see Access Azure Cosmos DB resources from virtual networks.
To summarize, an authorization token is always required to access an Azure Cosmos DB account. If IP firewall and virtual network Access Control List (ACLs) aren't set up, the Azure Cosmos DB account can be accessed with the authorization token. After you set up IP firewall rules or virtual network access lists for your Azure Cosmos DB account, only requests from the allowed sources will work. These requests must also include a valid authorization token to get a response.
You can secure the data stored in your Azure Cosmos DB account by using IP firewalls. Azure Cosmos DB supports IP-based access controls for inbound firewall support. Set an IP firewall on the Azure Cosmos DB account using one of the following methods:
- From the Azure portal
- Declaratively by using an Azure Resource Manager template
- Programmatically through the Azure CLI or Azure PowerShell by updating the ipRangeFilter property
Configure an IP firewall by using the Azure portal
To set the IP access control policy in the Azure portal, go to the Azure Cosmos DB account page and select Networking on the navigation menu. Set the Allow access from value to Selected networks, and then select Save. If you aren't adding any IP addresses yet, you also need to check the box to acknowledge that all VNets and IPs are blocked. If you change the public network access setting, such as turning it off or letting all networks connect, any firewall IP addresses you set before are removed.
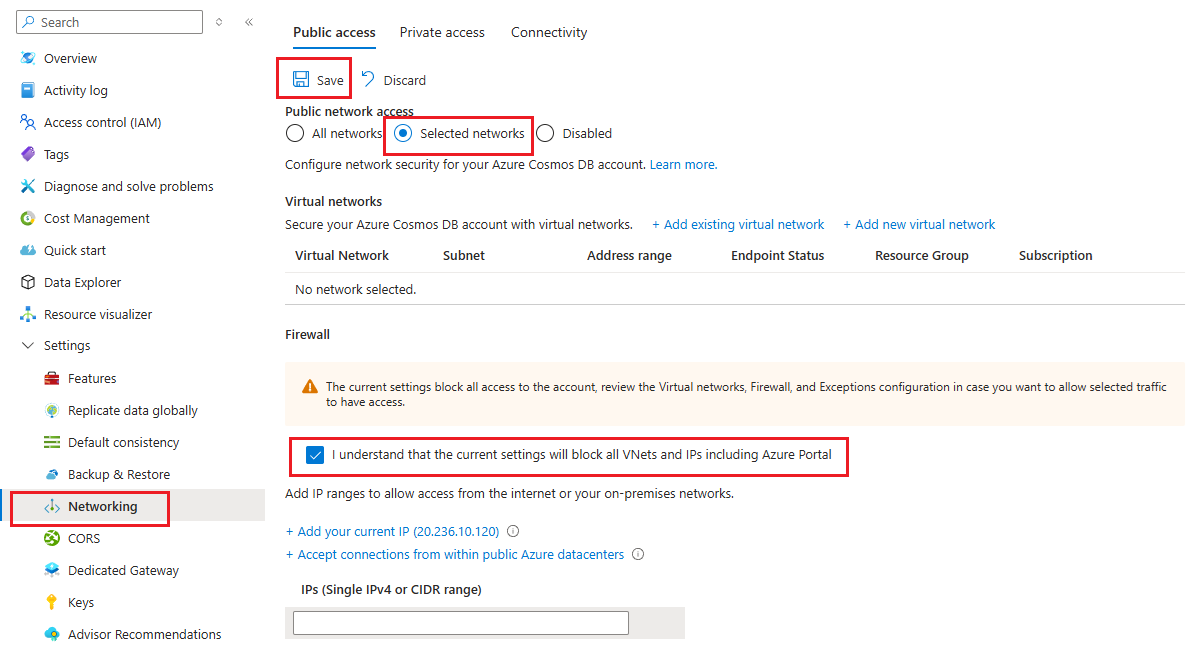
When IP access control is on, the Azure portal lets you specify IP addresses, IP address ranges, and switches. Switches enable access to other Azure services and the Azure portal. The following sections give details about these switches.
Note
When you turn on IP access control for your Azure Cosmos DB account, only requests from allowed IP addresses can reach your account. If an IP address isn't on the allowed list, its requests are blocked. You also can't browse your Cosmos DB resources in the Azure portal unless you allow portal access.
Allow requests from the Azure portal
When you enable an IP access control policy programmatically, you might need to add the IP addresses for the Azure portal services to the ipRangeFilter property to keep using some portal functionality.
Portal scenarios that require enabling this option include:
- Specifically for the API for the MongoDB or API for Apache Cassandra, accessing accounts with Data Explorer or https://cosmos.azure.cn
- For all APIs, using the following Azure Cosmos DB sections within the Azure portal:
- Browse Collections
- Power BI
- Azure Synapse
You can enable requests to access the Azure portal by selecting the Add Azure Portal Middleware IPs option, as shown in the following screenshot:
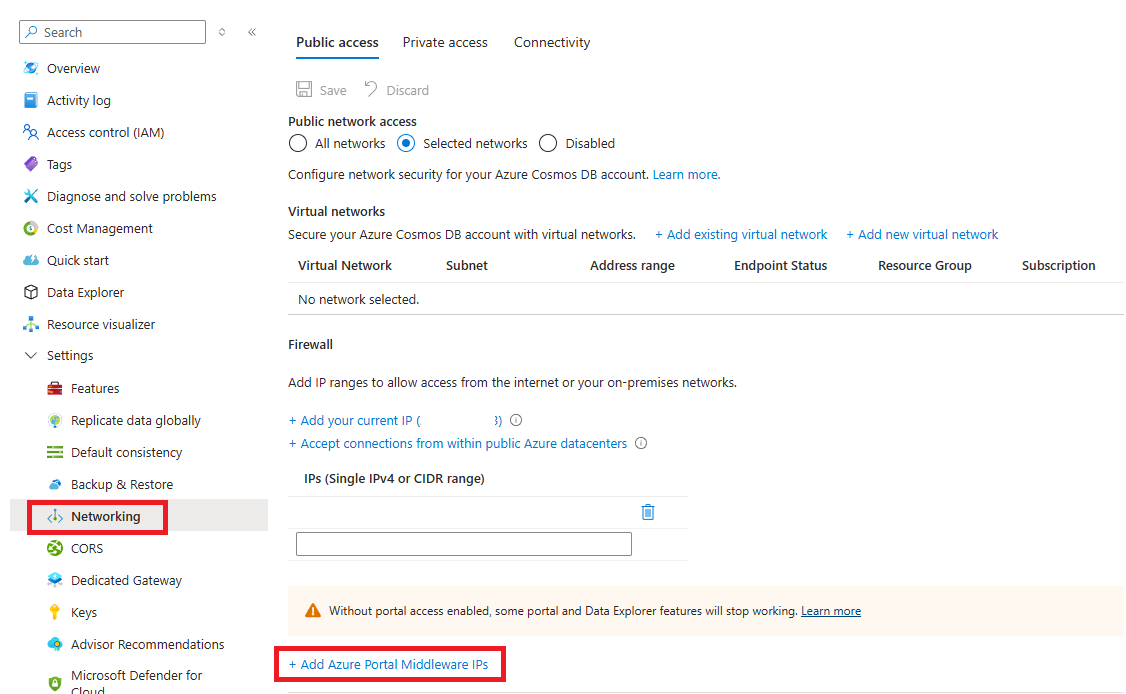
The Azure portal Middleware IP addresses are added to a separate list, as shown in the following screenshot. Select Save to add these addresses to your database account. More details on the Middleware IP addresses can be found further in this article.
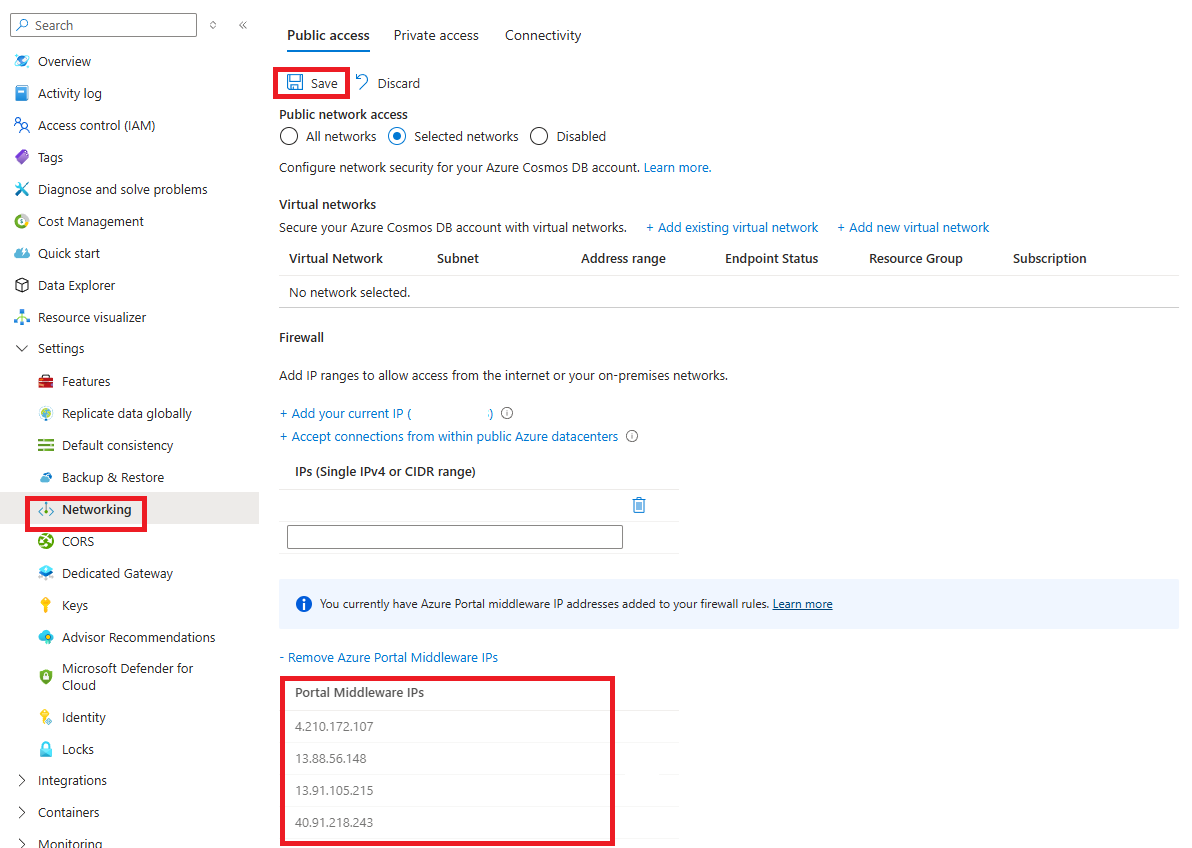
The Azure portal Middleware IP addresses can be removed by selecting the Remove Azure Portal Middleware IPs option and then selecting Save.
Azure portal Middleware IP Addresses
The Azure portal Middleware IP addresses are listed here. Some IP addresses are only required for specific Database Account APIs. When you add the Middleware IP Addresses in the portal, as described previously, only the IP addresses required for your account are added.
For example:
- For an API for NoSQL account, the IP addresses from the All category are added.
- For an API for MongoDB account, the IP addresses from the All and MongoDB only categories are added.
Azure operated by 21Vianet
| Database Account API | IP addresses |
|---|---|
| All | 163.228.137.6, 143.64.170.142 |
| MongoDB only | 52.131.240.99, 143.64.61.130 |
| Apache Cassandra only | 40.73.99.146, 143.64.62.47 |
Legacy Middleware IP Addresses
The Cosmos DB portal services recently transitioned to new infrastructure that required new Middleware IP addresses. With the completion of that transition, the legacy IP addresses used by the old infrastructure can now be safely removed. If your account has legacy Middleware IP addresses present in the firewall rules, the Remove Azure Portal Legacy Middleware IPs option is displayed. Select that option and then Save to remove the legacy IP addresses.
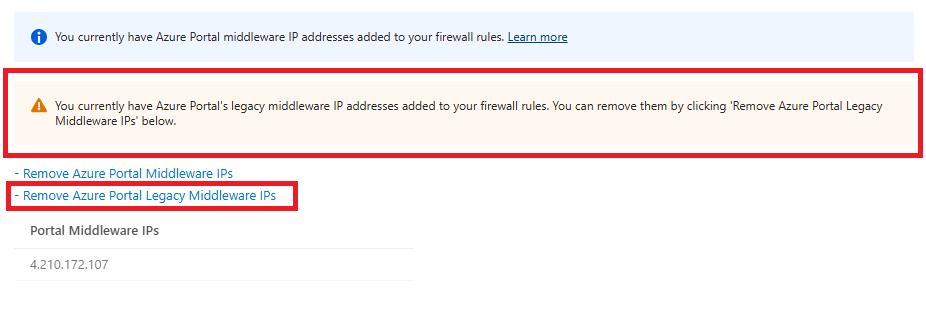
The legacy IP addresses are dependent on cloud environment:
| Azure Environment | IP Addresses |
|---|---|
| Azure Public | 104.42.195.92, 40.76.54.131, 52.176.6.30, 52.169.50.45, 52.187.184.26 |
| Azure operated by 21Vianet | 139.217.8.252, 52.176.6.30, 52.169.50.45, 52.187.184.26 |
| Azure US Government | 52.244.48.71, 52.176.6.30, 52.169.50.45, 52.187.184.26 |
Note
If you're experiencing challenges connecting to your Azure Cosmos DB account from the Data Explorer, review the Data Explorer troubleshooting guide.
Allow requests from multiple-regional Azure datacenters or other sources within Azure
Some Azure services, like Azure Stream Analytics and Azure Functions, don't use a fixed IP address. You can still use the IP firewall to control access for these services. To allow access from other Azure resources, choose the Accept connections from within Azure datacenters option. This option lets services running in Azure connect to your Cosmos DB account.
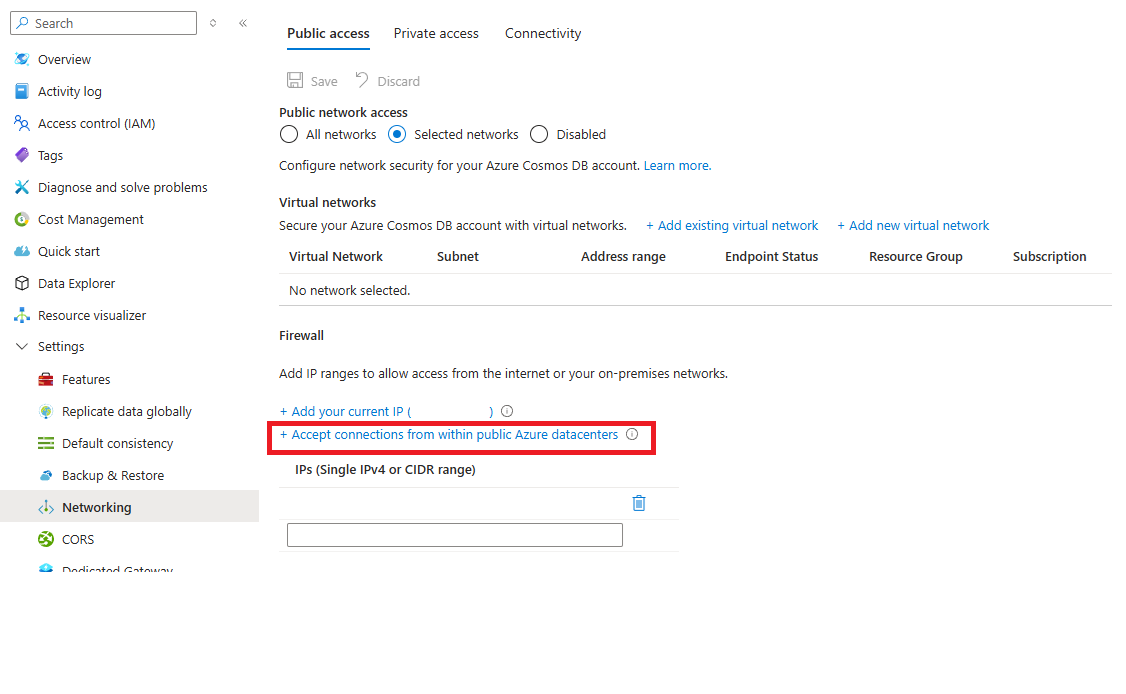
When you enable this option, the IP address 0.0.0.0 is added to the list of allowed IP addresses. The 0.0.0.0 IP address restricts requests to your Azure Cosmos DB account from Azure datacenter IP range. This setting doesn't allow access for any other IP ranges to your Azure Cosmos DB account.
Note
Setting publicNetworkAccess to Disabled takes precedence over the Accept connection from within Azure datacenters option. See blocking-public-network-access-during-account-creation
Note
This option configures the firewall to allow all requests from Azure, including requests from the subscriptions of other customers deployed in Azure. The list of IPs allowed by this option is wide, so it limits the effectiveness of a firewall policy. Use this option only if your requests don’t originate from static IPs or subnets in virtual networks. Choosing this option automatically allows access from the Azure portal because the Azure portal is deployed in Azure.
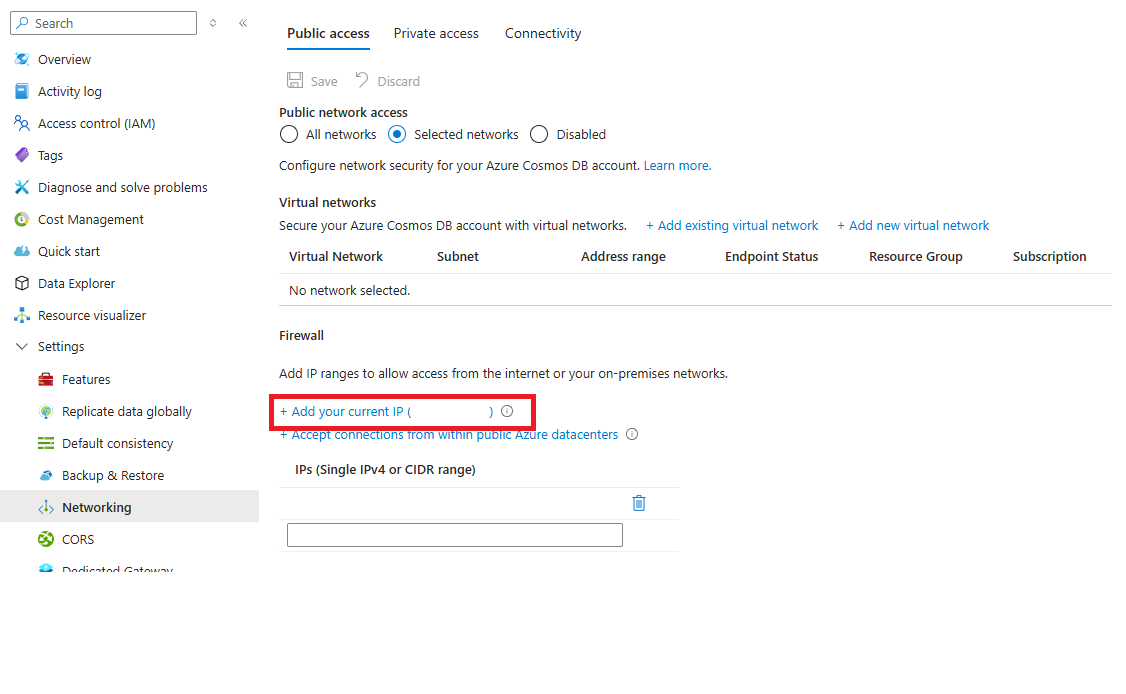
Requests from your current IP
To simplify development, the Azure portal helps identify and add the IP of your client machine to the allowed list. Apps running your machine can then access your Azure Cosmos DB account.
The portal automatically detects the client IP address. It might be the client IP address of your machine, or the IP address of your network gateway. Make sure to remove this IP address before you take your workloads to production.
To add your current IP to the list of IPs, select Add your current IP. Then select Save.
Requests from cloud services
In Azure, cloud services are a common way for hosting middle-tier service logic by using Azure Cosmos DB. To let a cloud service connect to your Azure Cosmos DB account, add the public IP address of the cloud service to your allowed IP list. You can perform this operation by updating the IP access control policy in the Azure portal. This step ensures that all role instances of cloud services have access to your Azure Cosmos DB account.
You can retrieve IP addresses for your cloud services in the Azure portal, as shown in the following screenshot:
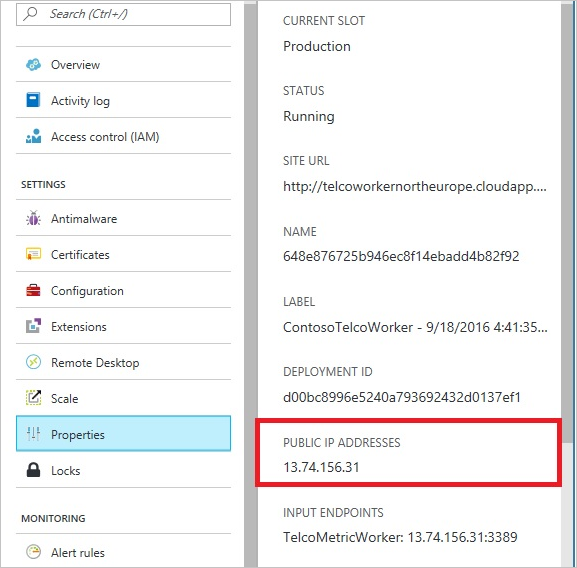 When you scale out your cloud service by adding role instances, the new instances automatically have access to the Azure Cosmos DB account because they're part of the same cloud service.
When you scale out your cloud service by adding role instances, the new instances automatically have access to the Azure Cosmos DB account because they're part of the same cloud service.
Requests from virtual machines
You can also use virtual machines or virtual machine scale sets to host middle-tier services by using Azure Cosmos DB. To let a virtual machine connect to your Azure Cosmos DB account, add its public IP address to the allowed list. You can perform this step by updating the IP access control policy. This configuration also works for virtual machine scale sets. Once you add the public IP address, the virtual machine can access your Cosmos DB account.
You can retrieve IP addresses for virtual machines in the Azure portal, as shown in the following screenshot:
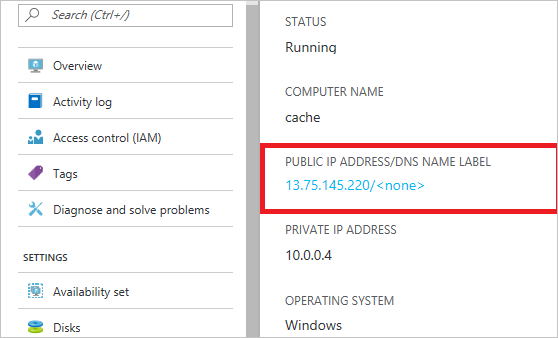
When you add virtual machine instances to the group, they automatically receive access to your Azure Cosmos DB account.
Requests from the internet
To connect to your Azure Cosmos DB account from a computer on the internet, add that computer’s IP address or IP range to the allowed list. Only computers you add to this list can reach your Cosmos DB account.
Add outbound rules to the firewall
To get a current list of outbound IP ranges to add to your firewall settings, see Download Azure IP Ranges and Service Tags.
To automate the list, see Use the Service Tag Discovery API.
Configure an IP firewall by using a Resource Manager template
To set up access control for your Azure Cosmos DB account, ensure that the Resource Manager template specifies the ipRules property with an array of allowed IP ranges. If setting up IP Firewall for an already deployed Azure Cosmos DB account, ensure the locations array matches the current deployment. You can't modify the locations array and other properties at the same time. For more information and samples of Azure Resource Manager templates for Azure Cosmos DB, see Azure Resource Manager templates for Azure Cosmos DB.
Important
The ipRules property is introduced with API version 2020-04-01. Earlier versions use an ipRangeFilter property instead, which is a list of comma-separated IP addresses.
The example shows how the ipRules property is exposed in API version 2020-04-01 or later:
{
"type": "Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts",
"name": "[variables('accountName')]",
"apiVersion": "2020-04-01",
"location": "[parameters('location')]",
"kind": "GlobalDocumentDB",
"properties": {
"consistencyPolicy": "[variables('consistencyPolicy')[parameters('defaultConsistencyLevel')]]",
"locations": "[variables('locations')]",
"databaseAccountOfferType": "Standard",
"enableAutomaticFailover": "[parameters('automaticFailover')]",
"ipRules": [
{
"ipAddressOrRange": "13.91.105.215"
},
{
"ipAddressOrRange": "4.210.172.107"
},
{
"ipAddressOrRange": "13.88.56.148"
},
{
"ipAddressOrRange": "40.91.218.243"
}
]
}
}
Here's the same example for any API version earlier than 2020-04-01:
{
"type": "Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts",
"name": "[variables('accountName')]",
"apiVersion": "2019-08-01",
"location": "[parameters('location')]",
"kind": "GlobalDocumentDB",
"properties": {
"consistencyPolicy": "[variables('consistencyPolicy')[parameters('defaultConsistencyLevel')]]",
"locations": "[variables('locations')]",
"databaseAccountOfferType": "Standard",
"enableAutomaticFailover": "[parameters('automaticFailover')]",
"ipRangeFilter":"139.217.8.252"
}
}
Configure an IP access control policy using the Azure CLI
The following command shows how to create an Azure Cosmos DB account with IP access control:
# Create an Azure Cosmos DB account with default values and IP firewall enabled
resourceGroupName='MyResourceGroup'
accountName='mycosmosaccount'
ipRangeFilter='192.168.221.17,183.240.196.255,139.217.8.252'
# Ensure there are no spaces in the comma-delimited list of IP addresses or CIDR ranges.
az cosmosdb create \
-n $accountName \
-g $resourceGroupName \
--locations regionName='China North 2' failoverPriority=0 isZoneRedundant=False \
--locations regionName='China East 2' failoverPriority=1 isZoneRedundant=False \
--ip-range-filter $ipRangeFilter
Configure an IP access control policy using PowerShell
The following script shows how to create an Azure Cosmos DB account with IP access control:
# Create an Azure Cosmos DB account with default values and IP Firewall enabled
$resourceGroupName = "myResourceGroup"
$accountName = "mycosmosaccount"
$ipRules = @("192.168.221.17","183.240.196.255","139.217.8.252")
$locations = @(
@{ "locationName"="China North 2"; "failoverPriority"=0; "isZoneRedundant"=False },
@{ "locationName"="China East 2"; "failoverPriority"=1, "isZoneRedundant"=False }
)
# Make sure there are no spaces in the comma-delimited list of IP addresses or CIDR ranges.
$CosmosDBProperties = @{
"databaseAccountOfferType"="Standard";
"locations"=$locations;
"ipRules"=$ipRules
}
New-AzResource -ResourceType "Microsoft.DocumentDb/databaseAccounts" `
-ApiVersion "2020-04-01" -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName `
-Name $accountName -PropertyObject $CosmosDBProperties
Troubleshoot issues with IP access control policies
You can troubleshoot issues with an IP access control policy by using the following options:
Azure portal
Enabling an IP access control policy for your Azure Cosmos DB account blocks all requests from machines outside the allowed list of IP address ranges. To enable portal data-plane operations like browsing containers and querying documents, explicitly allow Azure portal access by using the Firewall pane in the portal.
Software development kits
When you access Azure Cosmos DB resources by using software development kits (SDKs) from machines that aren't in the allowed list, a generic 403 Forbidden response is returned with no extra details. Check the allowed IP list for your account, and ensure the correct policy configuration is applied to your Azure Cosmos DB account.
Source IPs in blocked requests
View each request and response by enabling diagnostic logging on your Azure Cosmos DB account. The firewall-related messages are logged with a 403 return code. By filtering these messages, you can see the source IPs for the blocked requests. See Azure Cosmos DB diagnostic logging.
Requests from a subnet with a service endpoint for Azure Cosmos DB enabled
Requests from a subnet in a virtual network with a service endpoint for Azure Cosmos DB enabled send the virtual network and subnet identity to Azure Cosmos DB accounts. These requests don't have the public IP of the source, so IP filters reject them. To allow access from specific subnets in virtual networks, add an access control list as outlined in How to configure virtual network and subnet-based access for your Azure Cosmos DB account. It can take up to 15 minutes for firewall rules to apply and the firewall could exhibit an inconsistent behavior during this period.
Private IP addresses in list of allowed addresses
Creating or updating an Azure Cosmos DB account with a list of allowed addresses containing private IP addresses fails. Make sure that no private IP address is specified in the list.