Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this article, you learn how to ingest blobs from your storage account into Azure Data Explorer using an Event Grid data connection. You'll create an Event Grid data connection that sets an Azure Event Grid subscription. The Event Grid subscription routes events from your storage account to Azure Data Explorer via an Azure Event Hubs.
Note
Ingestion supports a maximum file size of 6 GB. The recommendation is to ingest files between 100 MB and 1 GB.
To learn how to create the connection using the Kusto SDKs, see Create an Event Grid data connection with SDKs.
For general information about ingesting into Azure Data Explorer from Event Grid, see Connect to Event Grid.
Note
To achieve the best performance with the Event Grid connection, set the rawSizeBytes ingestion property via the blob metadata. For more information, see ingestion properties.
Prerequisites
- An Azure subscription. Create a Azure account.
- An Azure Data Explorer cluster and database. Create a cluster and database.
- A destination table. Create a table or use an existing table.
- An ingestion mapping for the table.
- A storage account. An Event Grid notification subscription can be set on Azure Storage accounts for
BlobStorage,StorageV2, or Data Lake Storage Gen2. - Have the Event Grid resource provider registered.
Create an Event Grid data connection
In this section, you establish a connection between Event Grid and your Azure Data Explorer table.
Browse to your Azure Data Explorer cluster in the Azure portal.
Under Data, select Databases > TestDatabase.
Under Settings, select Data connections and then select Add data connection > Event Grid (Blob storage).
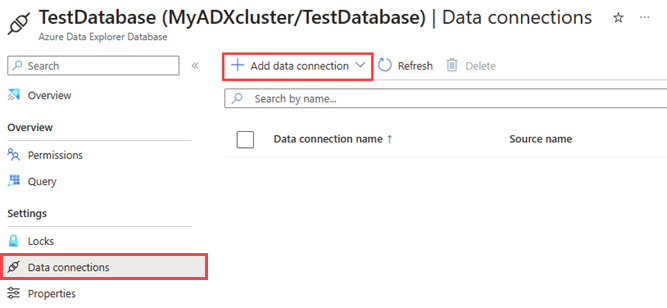
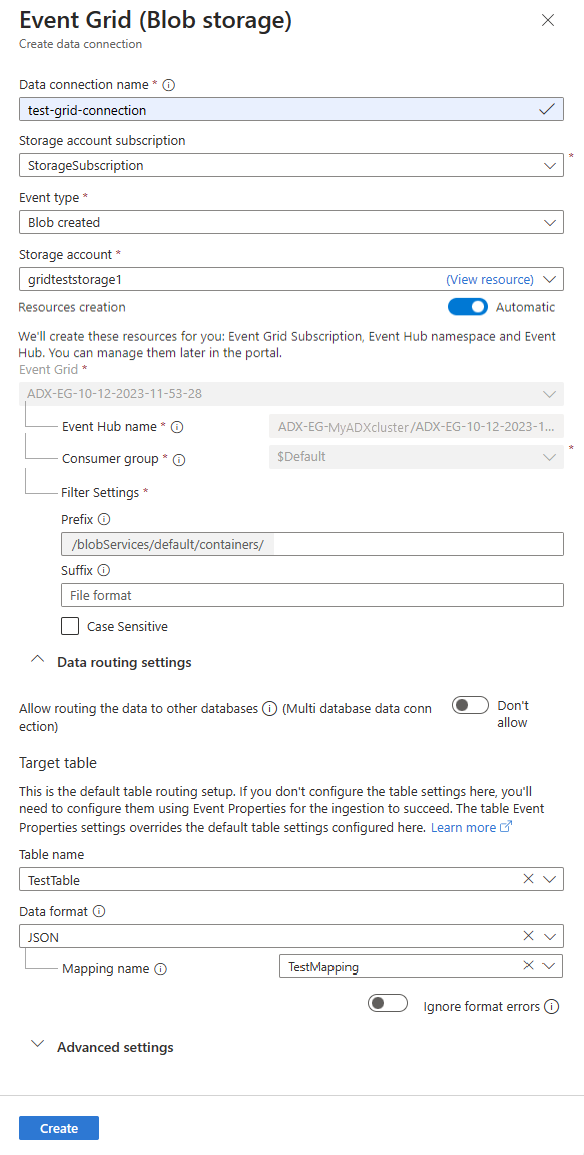
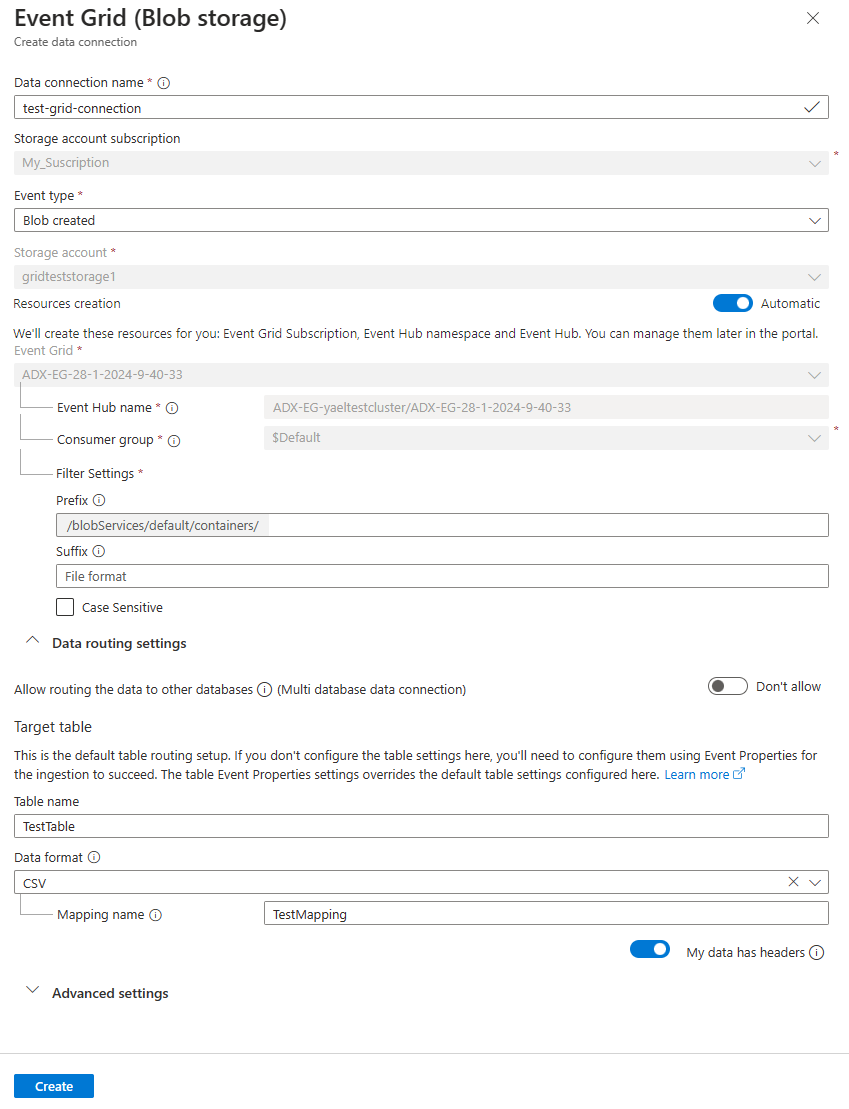
Fill out the Event Grid data connection form with the following information:
Setting Suggested value Field description Data connection name test-grid-connection The name of the connection that you want to create in Azure Data Explorer. Data connection names can contain only alphanumeric, dash and dot characters, and be up to 40 characters in length. Storage account subscription Your subscription ID The subscription ID where your storage account is. Event type Blob created or Blob renamed The type of event that triggers ingestion. Blob renamed is supported only for ADLSv2 storage. To rename a blob, navigate to the blob in Azure portal, right-click on the blob and select Rename. Supported types are: Microsoft.Storage.BlobCreated or Microsoft.Storage.BlobRenamed. Storage account gridteststorage1 The name of the storage account that you created previously. Resources creation Automatic Turning on automatic resource creation means that Azure Data Explorer creates an Event Grid Subscription, an Event Hubs namespace, and an Event Hubs for you. Otherwise, you need to create these resources manually to ensure the creation of the data connection. See Manually create resources for Event Grid ingestion Optionally, you can track specific Event Grid subjects. Set the filters for the notifications as follows:
- Prefix field is the literal prefix of the subject. As the pattern applied is starts with, it can span multiple containers, folders, or blobs. No wildcards are allowed.
- To define a filter on the blob container, the field must be set as follows:
/blobServices/default/containers/[container prefix]. - To define a filter on a blob prefix (or a folder in Azure Data Lake Gen2), the field must be set as follows:
/blobServices/default/containers/[container name]/blobs/[folder/blob prefix].
- To define a filter on the blob container, the field must be set as follows:
- Suffix field is the literal suffix of the blob. No wildcards are allowed.
- Case-Sensitive field indicates whether the prefix and suffix filters are case-sensitive
For more information on filtering events, see Blob storage events.
- Prefix field is the literal prefix of the subject. As the pattern applied is starts with, it can span multiple containers, folders, or blobs. No wildcards are allowed.
Optionally, you can specify the Data routing settings according to the following information. You don't have to specify all Data routing settings. Partial settings are also accepted.
Setting Suggested value Field description Allow routing the data to other databases (Multi database data connection) Don't allow Toggle on this option if you want to override the default target database associated with the data connection. For more information about database routing, see Events routing. Table name TestTable The table you created in TestDatabase. Data format JSON Supported formats are APACHEAVRO, Avro, CSV, JSON, ORC, PARQUET, PSV, RAW, SCSV, SOHSV, TSV, TSVE, TXT, and W3CLOG. Supported compression options are zip and gzip. Mapping name TestTable_mapping The mapping you created in TestDatabase, which maps incoming data to the column names and data types of TestTable. If not specified, an identity data mapping derived from the table's schema is autogenerated. Ignore format errors Ignore Toggle on this option if you want to ignore format errors for JSON data format. Note
Table and mapping names are case-sensitive.
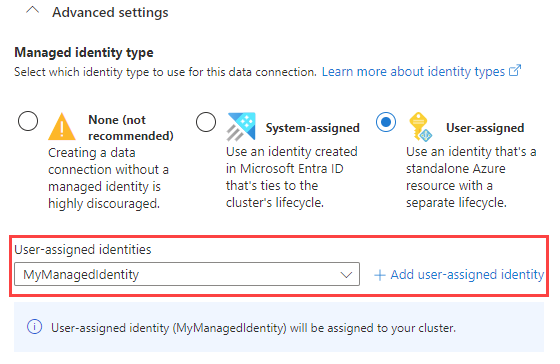
Optionally, under Advanced settings, you can specify the Managed identity type that is used by your data connection. By default, System-assigned is selected.
If you select User-assigned, you need to manually assign a managed identity. If you select a user that isn't assigned to your cluster yet, it will be auto-assigned. For more information, see Configure managed identities for your Azure Data Explorer cluster.
If you select None, the storage account and Event Hub are authenticated via connection strings. This method isn't recommended.
Select Create
Use the Event Grid data connection
This section shows how to trigger ingestion from Azure Blob Storage or Azure Data Lake Gen 2 to your cluster following blob creation or blob renaming.
Select the relevant tab based on the type of storage SDK used to upload blobs.
The following code sample uses the Azure Blob Storage SDK to upload a file to Azure Blob Storage. The upload triggers the Event Grid data connection, which ingests the data into Azure Data Explorer.
var azureStorageAccountConnectionString = <storage_account_connection_string>;
var containerName = <container_name>;
var blobName = <blob_name>;
var localFileName = <file_to_upload>;
var uncompressedSizeInBytes = <uncompressed_size_in_bytes>;
var mapping = <mapping_reference>;
// Create a new container if it not already exists.
var azureStorageAccount = new BlobServiceClient(azureStorageAccountConnectionString);
var container = azureStorageAccount.GetBlobContainerClient(containerName);
container.CreateIfNotExists();
// Define blob metadata and uploading options.
IDictionary<String, String> metadata = new Dictionary<string, string>();
metadata.Add("rawSizeBytes", uncompressedSizeInBytes);
metadata.Add("kustoIngestionMappingReference", mapping);
var uploadOptions = new BlobUploadOptions
{
Metadata = metadata,
};
// Upload the file.
var blob = container.GetBlobClient(blobName);
blob.Upload(localFileName, uploadOptions);
Note
Azure Data Explorer won't delete the blobs post ingestion. Retain the blobs for three to five days by using Azure Blob storage lifecycle to manage blob deletion.
Note
Triggering ingestion following a CopyBlob operation is not supported for storage accounts that have the hierarchical namespace feature enabled on them.
Important
We highly discourage generating Storage Events from custom code and sending them to Event Hubs. If you choose to do so, make sure that the events produced strictly adhere to the appropriate Storage Events schema and JSON format specifications.
Remove an Event Grid data connection
To remove the Event Grid connection from the Azure portal, do the following steps:
- Go to your cluster. From the left menu, select Databases. Then, select the database that contains the target table.
- From the left menu, select Data connections. Then, select the checkbox next to the relevant Event Grid data connection.
- From the top menu bar, select Delete.