Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article explores troubleshooting methods related to connector and format for mapping data flows in Azure Data Factory (ADF).
Azure Blob Storage
Account Storage type (general purpose v1) doesn't support service principal and MI authentication
Symptoms
In data flows, if you use Azure Blob Storage (general purpose v1) with the service principal or MI authentication, you might encounter the following error message:
com.microsoft.dataflow.broker.InvalidOperationException: ServicePrincipal and MI auth are not supported if blob storage kind is Storage (general purpose v1)
Cause
When you use the Azure Blob linked service in data flows, the managed identity or service principal authentication isn't supported when the account kind is empty or Storage. This situation is shown in Image 1 and Image 2 below.
Image 1: The account kind in the Azure Blob Storage linked service
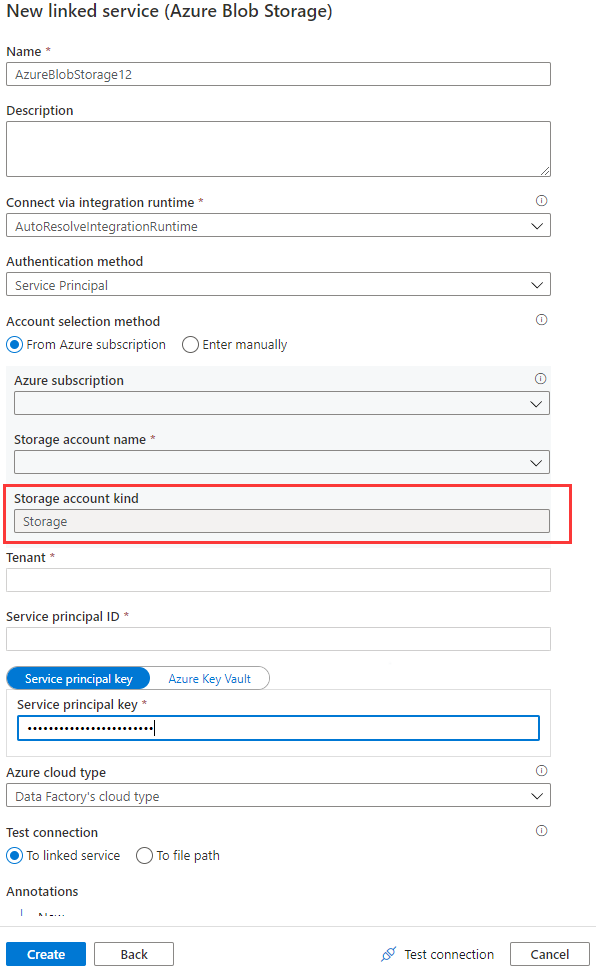
Image 2: Storage account page
Recommendation
To solve this issue, refer to the following recommendations:
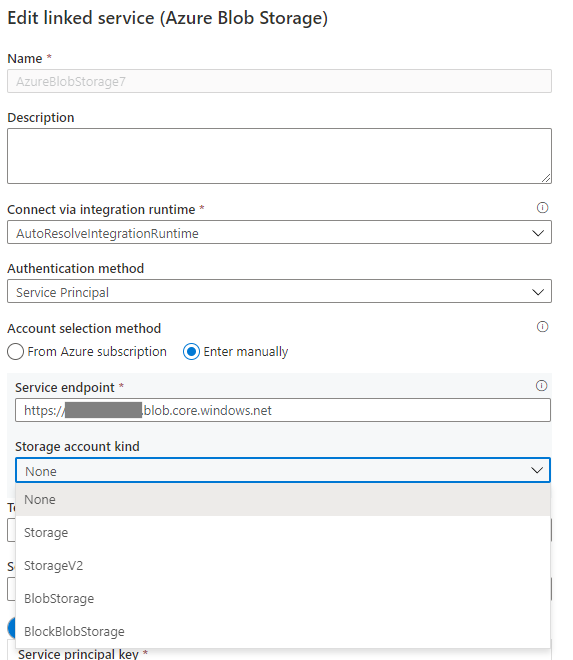
If the storage account kind is None in the Azure Blob linked service, specify the proper account kind, and refer to Image 3 that follows to accomplish it. Furthermore, refer to Image 2 to get the storage account kind, and check and confirm the account kind isn't Storage (general purpose v1).
Image 3: Specify the storage account kind in the Azure Blob Storage linked service
If the account kind is Storage (general purpose v1), upgrade your storage account to the general purpose v2 or choose a different authentication.
Image 4: Upgrade the storage account to general purpose v2
Azure Cosmos DB and JSON format
Support customized schemas in the source
Symptoms
When you want to use the ADF data flow to move or transfer data from Azure Cosmos DB/JSON into other data stores, some columns of the source data might be missed.
Cause
For the schema-free connectors (the column number, column name and column data type of each row can be different when comparing with others), by default, ADF uses sample rows (for example, top 100 or 1,000 rows data) to infer the schema, and the inferred result are used as a schema to read data. So if your data stores have extra columns that don't appear in sample rows, the data of these extra columns aren't read, moved, or transferred into sink data stores.
Recommendation
To overwrite the default behavior and bring in other fields, ADF provides options for you to customize the source schema. You can specify additional/missing columns that could be missing in schema-infer-result in the data flow source projection to read the data, and you can apply one of the following options to set the customized schema. Usually, Option-1 is more preferred.
Option-1: Compared with the original source data that might be one large file, table, or container that contains millions of rows with complex schemas, you can create a temporary table/container with a few rows that contain all the columns you want to read, and then move on to the following operation:
Use the data flow source Debug Settings to have Import projection with sample files/tables to get the complete schema. You can follow the steps in the following picture:
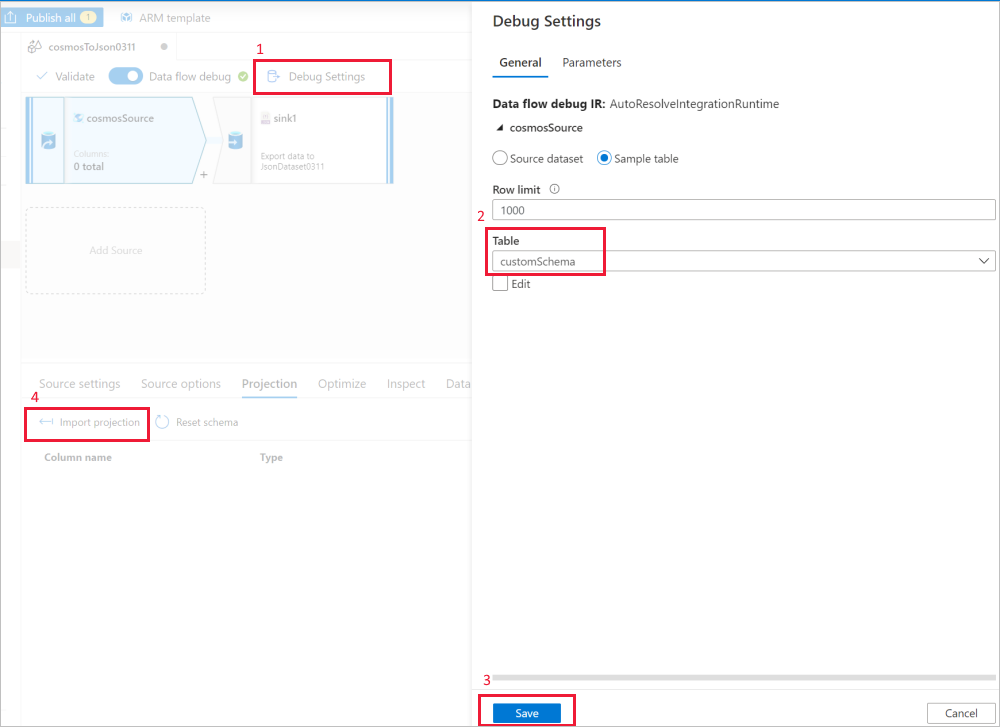
- Select Debug settings in the data flow canvas.
- In the pop-up pane, select Sample table under the cosmosSource tab, and enter the name of your table in the Table block.
- Select Save to save your settings.
- Select Import projection.
Change the Debug Settings back to use the source dataset for the remaining data movement/transformation. You can move on with the steps in the following picture:
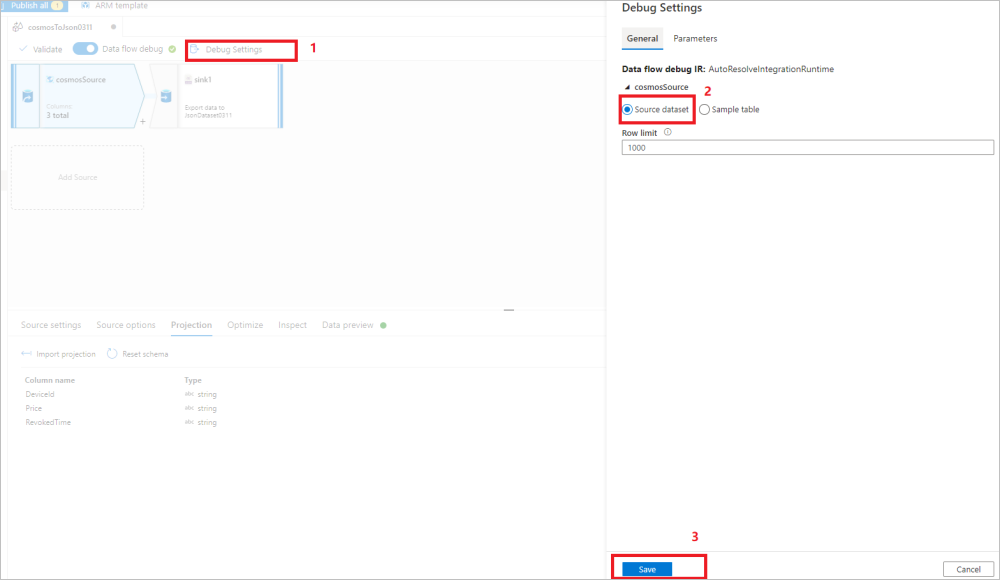
- Select Debug settings in the data flow canvas.
- In the pop-up pane, select Source dataset under the cosmosSource tab.
- Select Save to save your settings.
Afterwards, the ADF data flow runtime will honor and use the customized schema to read data from the original data store.
Option-2: If you're familiar with the schema and DSL language of the source data, you can manually update the data flow source script to add additional/missed columns to read the data. An example is shown in the following picture:

Support map type in the source
Symptoms
In ADF data flows, map data type can't be directly supported in Azure Cosmos DB or JSON source, so you can't get the map data type under "Import projection".
Cause
For Azure Cosmos DB and JSON, they're schema-free connectivity and related spark connector uses sample data to infer the schema, and then that schema is used as the Azure Cosmos DB/JSON source schema. When inferring the schema, the Azure Cosmos DB/JSON Spark connector can only infer object data as a struct rather than a map data type, and that's why map type can't be directly supported.
Recommendation
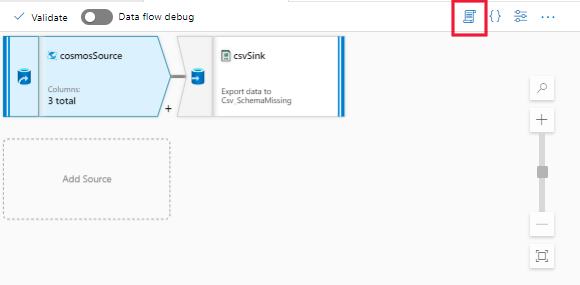
To solve this issue, refer to the following examples and steps to manually update the script (DSL) of the Azure Cosmos DB/JSON source to get the map data type support.
Examples:
Step-1: Open the script of the data flow activity.
Step-2: Update the DSL to get the map type support by referring to the examples above.
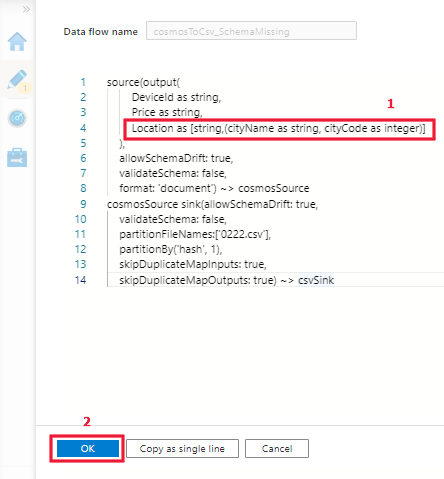
The map type support:
| Type | Is the map type supported? | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Excel, CSV | No | Both are tabular data sources with the primitive type, so there's no need to support the map type. |
| Orc, Avro | Yes | None. |
| JSON | Yes | The map type can't be directly supported. Follow the recommendation part in this section to update the script (DSL) under the source projection. |
| Azure Cosmos DB | Yes | The map type can't be directly supported. Follow the recommendation part in this section to update the script (DSL) under the source projection. |
| Parquet | Yes | Today the complex data type isn't supported on the parquet dataset, so you need to use the "Import projection" under the data flow parquet source to get the map type. |
| XML | No | None. |
Consume JSON files generated by copy activities
Symptoms
If you use the copy activity to generate some JSON files, and then try to read these files in data flows, you fail with the error message: JSON parsing error, unsupported encoding or multiline
Cause
There are following limitations on JSON for copy and data flows respectively:
For Unicode encodings (utf-8, utf-16, utf-32) JSON files, copy activities always generate the JSON files with BOM.
The data flow JSON source with "Single document" enabled doesn't support Unicode encoding with BOM.

So you might experience issues if the following criteria are met:
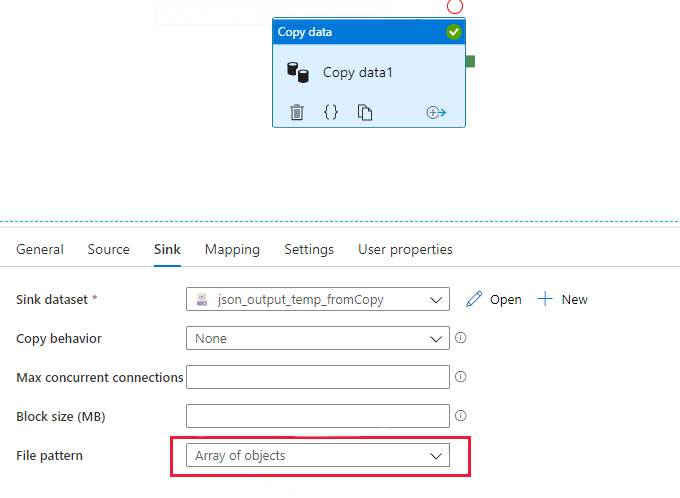
The sink dataset used by the copy activity is set to Unicode encoding (utf-8, utf-16, utf-16be, utf-32, utf-32be) or the default is used.
The copy sink is set to use "Array of objects" file pattern as shown in the following picture, no matter whether "Single document" is enabled or not in the data flow JSON source.
Recommendation
- Always use the default file pattern or explicit "Set of objects" pattern in the copy sink if the generated files are used in data flows.
- Disable the "Single document" option in the data flow JSON source.
Note
Using "Set of objects" is also the recommended practice from the performance perspective. As the "Single document" JSON in the data flow can't enable parallel reading for single large files, this recommendation does not have any negative impact.
The query with parameters doesn't work
Symptoms
Mapping data flows in Azure Data Factory supports the use of parameters. The parameter values are set by the calling pipeline via the Execute Data Flow activity, and using parameters is a good way to make your data flow general-purpose, flexible, and reusable. You can parameterize data flow settings and expressions with these parameters: Parameterizing mapping data flows.
After setting parameters and using them in the query of data flow source, they do not take effective.
Cause
You encounter this error due to your wrong configuration.
Recommendation
Use the following rules to set parameters in the query, and for more detailed information, refer to Build expressions in mapping data flow.
- Apply double quotes at the beginning of the SQL statement.
- Use single quotes around the parameter.
- Use lowercase letters for all CLAUSE statements.
For example:

Common Data Model format
Model.json files with special characters
Symptoms
You might encounter an issue that the final name of the model.json file contains special characters.
Error message
at Source 'source1': java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: java.net.URISyntaxException: Relative path in absolute URI: PPDFTable1.csv@snapshot=2020-10-21T18:00:36.9469086Z.
Recommendation
Replace the special chars in the file name, which works in the synapse but not in ADF.
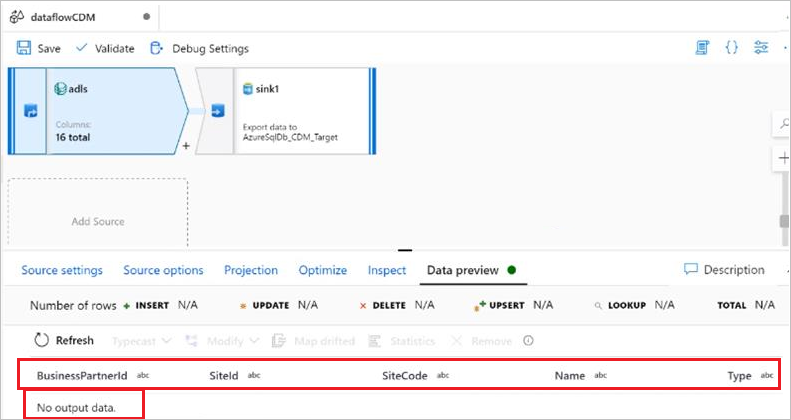
No data output in the data preview or after running pipelines
Symptoms
When you use the manifest.json for CDM, no data is shown in the data preview or shown after running a pipeline. Only headers are shown. You can see this issue in the picture below.
Cause
The manifest document describes the CDM folder, for example, what entities that you have in the folder, references of those entities and the data that corresponds to this instance. Your manifest document misses the dataPartitions information that indicates ADF where to read the data, and since it's empty, it returns zero data.
Recommendation
Update your manifest document to have the dataPartitions information, and you can refer to this example manifest document to update your document: Common Data Model metadata: Introducing manifest-Example manifest document.
JSON array attributes are inferred as separate columns
Symptoms
You might encounter an issue where one attribute (string type) of the CDM entity has a JSON array as data. When this data is encountered, ADF infers the data as separate columns incorrectly. As you can see from the following pictures, a single attribute presented in the source (msfp_otherproperties) is inferred as a separate column in the CDM connector's preview.
In the CSV source data (refer to the second column):

In the CDM source data preview:
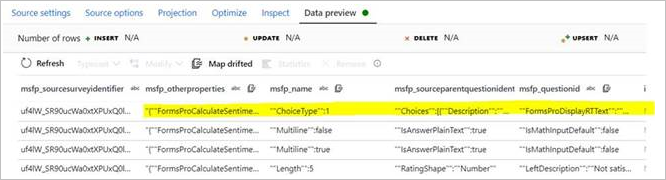
You might also try to map drifted columns and use the data flow expression to transform this attribute as an array. But since this attribute is read as a separate column when reading, transforming to an array does not work.
Cause
This issue is likely caused by the commas within your JSON object value for that column. Since your data file is expected to be a CSV file, the comma indicates that it's the end of a column's value.
Recommendation
To solve this problem, you need to double quote your JSON column and avoid any of the inner quotes with a backslash (\). In this way, the contents of that column's value can be read in as a single column entirely.
Note
The CDM doesn't inform that the data type of the column value is JSON, yet it informs that it is a string and parsed as such.
Unable to fetch data in the data flow preview
Symptoms
You use CDM with model.json generated by Power BI. When you preview the CDM data using the data flow preview, you encounter an error: No output data.
Cause
The following code exists in the partitions in the model.json file generated by the Power BI data flow.
"partitions": [
{
"name": "Part001",
"refreshTime": "2020-10-02T13:26:10.7624605+00:00",
"location": "https://datalakegen2.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn/powerbi/salesEntities/salesPerfByYear.csv @snapshot=2020-10-02T13:26:10.6681248Z"
}
For this model.json file, the issue is the naming schema of the data partition file has special characters, and supporting file paths with '@' do not exist currently.
Recommendation
Remove the @snapshot=2020-10-02T13:26:10.6681248Z part from the data partition file name and the model.json file, and then try again.
The corpus path is null or empty
Symptoms
When you use CDM in the data flow with the model format, you can't preview the data, and you encounter the error: DF-CDM_005 The corpus path is null or empty. The error is shown in the following picture:
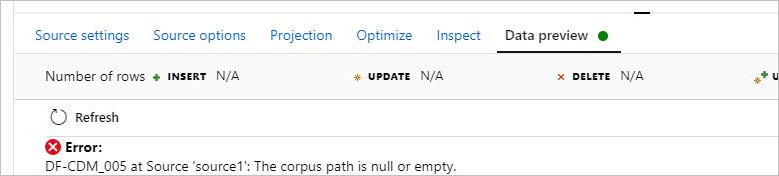
Cause
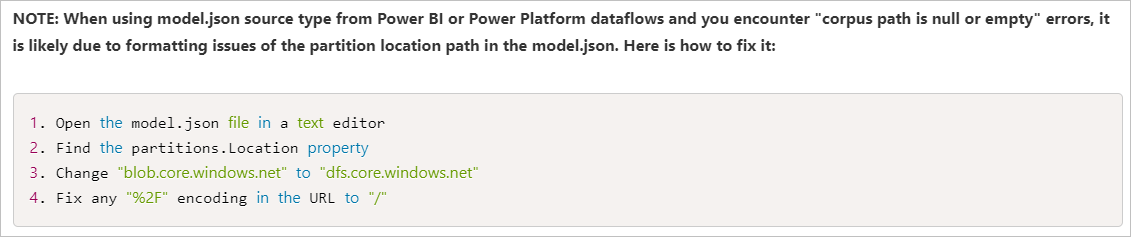
Your data partition path in the model.json is pointing to a blob storage location and not your data lake. The location should have the base URL of .dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn for the ADLS Gen2.
Recommendation
To solve this issue, you can refer to this article: ADF Adds Support for Inline Datasets and Common Data Model to Data Flows, and the following picture shows the way to fix the corpus path error in this article.
Unable to read CSV data files
Symptoms
You use the inline dataset as the common data model with manifest as a source, and you provided the entry manifest file, root path, entity name, and path. In the manifest, you have the data partitions with the CSV file location. Meanwhile, the entity schema and csv schema are identical, and all validations were successful. However, in the data preview, only the schema rather than the data gets loaded and the data is invisible, which is shown in the following picture:
Cause
Your CDM folder isn't separated into logical and physical models, and only physical models exist in the CDM folder. The following two articles describe the difference: Logical definitions and Resolving a logical entity definition.
Recommendation
For the data flow using CDM as a source, try to use a logical model as your entity reference, and use the manifest that describes the location of the physical resolved entities and the data partition locations. You can see some samples of logical entity definitions within the public CDM GitHub repository: CDM-schemaDocuments
A good starting point to forming your corpus is to copy the files within the schema documents folder (just that level inside the GitHub repository), and put those files into a folder. Afterwards, you can use one of the predefined logical entities within the repository (as a starting or reference point) to create your logical model.
Once the corpus is set up, you're recommended to use CDM as a sink within data flows, so that a well-formed CDM folder can be properly created. You can use your CSV dataset as a source and then sink it to your CDM model that you created.
CSV and Excel format
Set the quote character to 'no quote char' isn't supported in the CSV
Symptoms
There are several issues that aren't supported in the CSV when the quote character is set to 'no quote char':
- When the quote character is set to 'no quote char', multi-char column delimiter can't start and end with the same letters.
- When the quote character is set to 'no quote char', multi-char column delimiter can't contain the escape character:
\. - When the quote character is set to 'no quote char', column value can't contain row delimiter.
- The quote character and the escape character can't both be empty (no quote and no escape) if the column value contains a column delimiter.
Cause
Causes of the symptoms are stated below with examples respectively:
Start and end with the same letters.
column delimiter: $*^$*
column value: abc$*^ def
csv sink: abc$*^$*^$*def
will be read as "abc" and "^&*def"The multi-char delimiter contains escape characters.
column delimiter: \x
escape char:\
column value: "abc\\xdef"
The escape character either escapes the column delimiter or the escape the character.The column value contains the row delimiter.
We need quote character to tell if row delimiter is inside column value or not.The quote character and the escape character both be empty and the column value contains column delimiters.
Column delimiter: \t
column value: 111\t222\t33\t3
It will be ambiguous if it contains 3 columns 111,222,33\t3 or 4 columns 111,222,33,3.
Recommendation
The first symptom and the second symptom can't be solved currently. For the third and fourth symptoms, you can apply the following methods:
- For Symptom 3, don't use the 'no quote char' for a multiline csv file.
- For Symptom 4, set either the quote character or the escape character as nonempty, or you can remove all column delimiters inside your data.
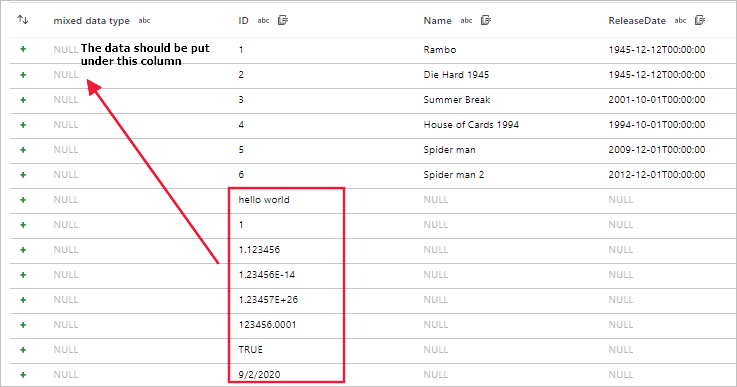
Read files with different schemas error
Symptoms
When you use data flows to read files such as CSV and Excel files with different schemas, the data flow debug, sandbox, or activity run fails.
For CSV, the data misalignment exists when the schema of files is different.
For Excel, an error occurs when the schema of the file is different.
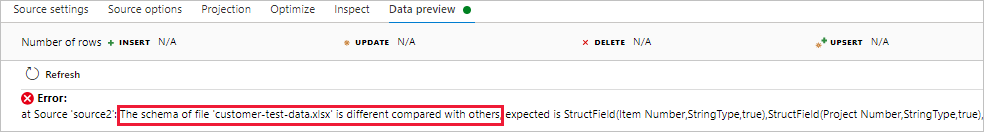
Cause
Reading files with different schemas in the data flow isn't supported.
Recommendation
If you still want to transfer files such as CSV and Excel files with different schemas in the data flow, you can use these ways to work around:
For CSV, you need to manually merge the schema of different files to get the full schema. For example, file_1 has columns
c_1,c_2,c_3while file_2 has columnsc_3,c_4, ...c_10, so the merged and the full schema isc_1,c_2, ...c_10. Then make other files also have the same full schema even though it doesn't have data, for example, file_x only has columnsc_1,c_2,c_3,c_4, add columnsc_5,c_6, ...c_10in the file to make them consistent with the other files.For Excel, you can solve this issue by applying one of the following options:
- Option-1: You need to manually merge the schema of different files to get the full schema. For example, file_1 has columns
c_1,c_2,c_3while file_2 has columnsc_3,c_4, ...c_10, so the merged and full schema isc_1,c_2, ...c_10. Then make other files also have the same schema even though it doesn't have data, for example, file_x with sheet "SHEET_1" only has columnsc_1,c_2,c_3,c_4, please add columnsc_5,c_6, ...c_10in the sheet too, and then it can work. - Option-2: Use range (for example, A1:G100) + firstRowAsHeader=false, and then it can load data from all Excel files even though the column name and count is different.
- Option-1: You need to manually merge the schema of different files to get the full schema. For example, file_1 has columns
Snowflake
Unable to connect to the Snowflake linked service
Symptoms
You encounter the following error when you create the Snowflake linked service in the public network, and you use the autoresolve integration runtime.
ERROR [HY000] [Microsoft][Snowflake] (4) REST request for URL https://XXXXXXXX.china-east-2.azure.snowflakecomputing.com.snowflakecomputing.com:443/session/v1/login-request?requestId=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX&request_guid=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
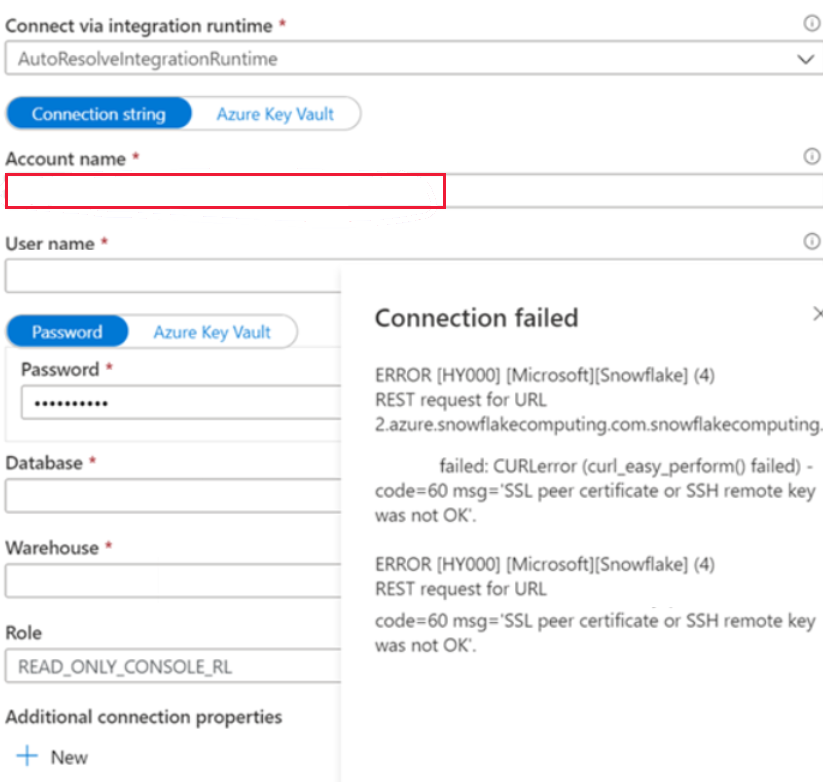
Cause
You haven't applied the account name in the format that is given in the Snowflake account document (including extra segments that identify the region and cloud platform), for example, XXXXXXXX.china-east-2.azure. You can refer to this document: Linked service properties for more information.
Recommendation
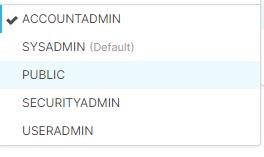
To solve the issue, change the account name format. The role should be one of the roles shown in the following picture, but the default one is Public.
SQL access control error: "Insufficient privileges to operate on schema"
Symptoms
When you try to use "import projection", "data preview", etc. in the Snowflake source of data flows, you meet errors like net.snowflake.client.jdbc.SnowflakeSQLException: SQL access control error: Insufficient privileges to operate on schema.
Cause
You meet this error because of the wrong configuration. When you use the data flow to read Snowflake data, the runtime Azure Databricks (ADB) isn't directly select the query to Snowflake. Instead, a temporary stage are created, and data are pulled from tables to the stage and then compressed and pulled by ADB. This process is shown in the picture below.
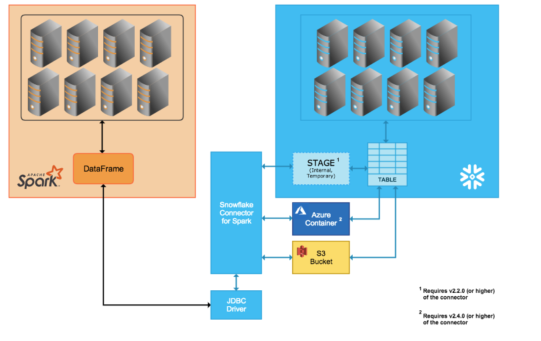
So the user/role used in ADB should have necessary permission to do this in the Snowflake. But usually the user/role don't have the permission since the database is created on the share.
Recommendation
To solve this issue, you can create different database and create views on the top of the shared DB to access it from ADB. For more details, please refer to Snowflake.
Failed with an error: "SnowflakeSQLException: IP x.x.x.x isn't allowed to access Snowflake. Contact your local security administrator"
Symptoms
When you use snowflake in Azure Data Factory, you can successfully use test-connection in the Snowflake linked service, preview-data/import-schema on Snowflake dataset and run copy/lookup/get-metadata or other activities with it. But when you use Snowflake in the data flow activity, you might see an error like SnowflakeSQLException: IP 13.66.58.164 is not allowed to access Snowflake. Contact your local security administrator.
Cause
The Azure Data Factory data flow doesn't support the use of fixed IP ranges. For more information, see Azure Integration Runtime IP addresses.
Recommendation
To solve this issue, you can change the Snowflake account firewall settings with the following steps:
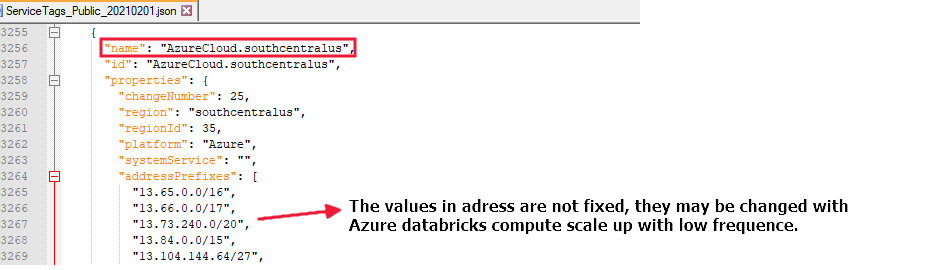
You can get the IP range list of service tags from the "service tags IP range download link": Discover service tags by using downloadable JSON files.

If you run a data flow in the "chinaeast2" region, you need to allow the access from all addresses with name "AzureCloud.chinaeast2", for example:
Queries in the source doesn't work
Symptoms
When you try to read data from Snowflake with query, you might see an error like these:
SQL compilation error: error line 1 at position 7 invalid identifier 'xxx'SQL compilation error: Object 'xxx' does not exist or not authorized.
Cause
You encounter this error because of your wrong configuration.
Recommendation
For Snowflake, it applies the following rules for storing identifiers at creation/definition time and resolving them in queries and other SQL statements:
When an identifier (table name, schema name, column name, etc.) is unquoted, it's stored and resolved in uppercase by default, and it's case-in-sensitive. For example:
Because it's case-in-sensitive, so you can feel free to use following query to read snowflake data while the result is the same:
Select MovieID, title from Public.TestQuotedTable2Select movieId, title from Public.TESTQUOTEDTABLE2Select movieID, TITLE from PUBLIC.TESTQUOTEDTABLE2
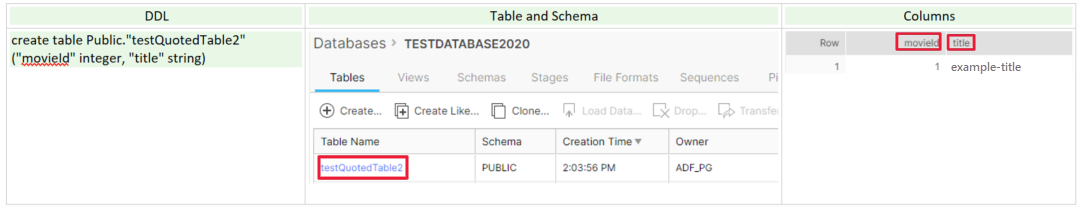
When an identifier (table name, schema name, column name, etc.) is double-quoted, it's stored and resolved exactly as entered, including case as it is case-sensitive, and you can see an example in the following picture. For more details, please refer to this document: Identifier Requirements.
Because the case-sensitive identifier (table name, schema name, column name, etc.) has lowercase character, you must quote the identifier during data reading with the query, for example:
- Select "movieId", "title" from Public."testQuotedTable2"
If you meet up error with the Snowflake query, check whether some identifiers (table name, schema name, column name, etc.) are case-sensitive with the following steps:
Sign in to the Snowflake server (
https://{accountName}.azure.snowflakecomputing.com/, replace {accountName} with your account name) to check the identifier (table name, schema name, column name, etc.).Create worksheets to test and validate the query:
- Run
Use database {databaseName}, replace {databaseName} with your database name. - Run a query with table, for example:
select "movieId", "title" from Public."testQuotedTable2"
- Run
After the SQL query of Snowflake is tested and validated, you can use it in the data flow Snowflake source directly.
The expression type doesn't match the column data type, expecting VARIANT but got VARCHAR
Symptoms
When you try to write data into the Snowflake table, you might meet the following error:
java.sql.BatchUpdateException: SQL compilation error: Expression type does not match column data type, expecting VARIANT but got VARCHAR
Cause
The column type of input data is string, which is different from the VARIANT type of the related column in the Snowflake sink.
When you store data with complex schemas (array/map/struct) in a new Snowflake table, the data flow type is automatically converted into its physical type VARIANT.
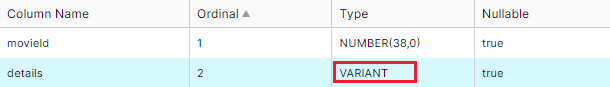
The related values are stored as JSON strings, showing in the picture below.

Recommendation
For the Snowflake VARIANT, it can only accept the data flow value that is struct or map or array type. If the value of your input data column is JSON or XML or other strings, use one of the following options to solve this issue:
Option-1: Use parse transformation before using Snowflake as a sink to covert the input data column value into struct or map or array type, for example:
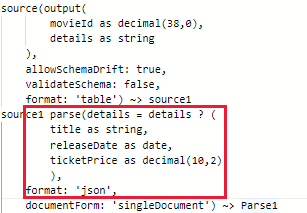
Note
The value of the Snowflake column with VARIANT type is read as string in Spark by default.
Option-2: Sign in to your Snowflake server (
https://{accountName}.azure.snowflakecomputing.com/, replace {accountName} with your account name) to change the schema of your Snowflake target table. Apply the following steps by running the query under each step.Create one new column with VARCHAR to store the values.
alter table tablename add newcolumnname varchar;Copy the value of VARIANT into the new column.
update tablename t1 set newcolumnname = t1."details"Delete the unused VARIANT column.
alter table tablename drop column "details";Rename the new column to the old name.
alter table tablename rename column newcolumnname to "details";
Related content
For more help with troubleshooting, see these resources: