Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
When enabled, the Fleet Manager hub cluster serves as the central management point for Kubernetes resource propagation across member clusters using resource placement.
What are Fleet Manager hub clusters?
In Azure Kubernetes Fleet Manager, hub clusters play a crucial role in managing multiple member clusters, but they're optional.
The hub cluster facilitates resource placement and Fleet Managed Namespaces via a managed version of KubeFleet.
In this configuration, a fleet consists of the following components:
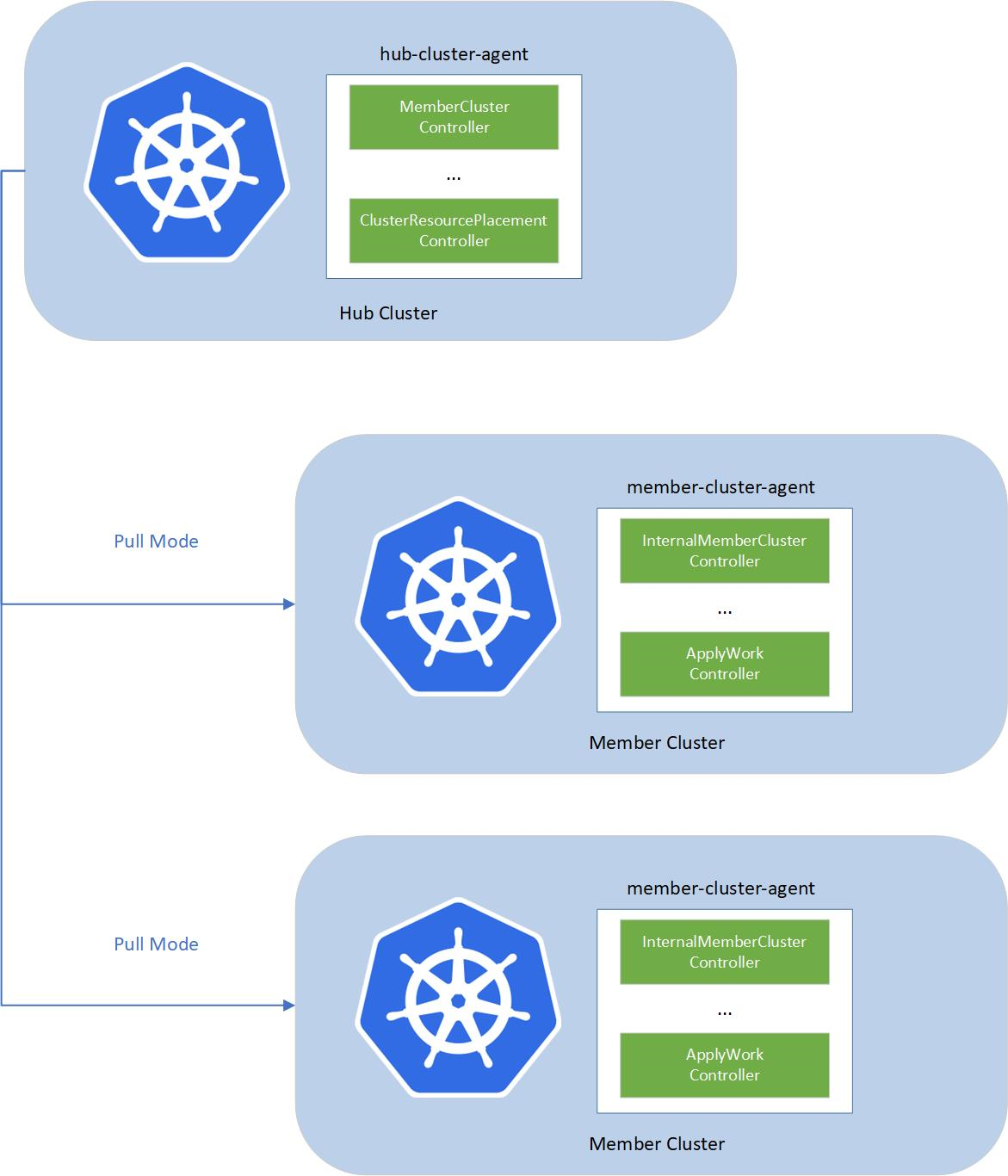
- fleet-hub-agent: A Kubernetes controller that creates and reconciles all the fleet-related custom resources (CRs) in the hub cluster.
- fleet-member-agent: A Kubernetes controller that creates and reconciles all the fleet-related CRs in the member clusters. This controller pulls the latest CRs from the hub cluster and consistently reconciles the member clusters to match the desired state.
Hub cluster configuration
A Fleet Manager hub cluster is a fully managed Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster that has the following properties:
- Cluster name and location: the hub cluster is always named
huband is created in the same Azure region as the Fleet Manager. - Azure Resource Group for hub cluster: the hub cluster AKS resource is created in a managed resource group with the naming format
FL_{fleet_manager_resource_group}_{fleet_manager_name}_{azure_region}. - Azure Resource Group for hub cluster resources: like any AKS cluster, the hub cluster has Azure resources such as an agent node pool virtual machine scale set and virtual network that are created in a managed resource group with the naming format
MC_FL_{fleet_manager_resource_group}_{fleet_manager_name}_{azure_region}. - Hub cluster node: The hub cluster has a node pool with a single node running Azure Linux. The node doesn't run any pods and doesn't affect hub cluster performance. When creating a hub cluster from the Azure CLI, you can choose the node Virtual Machine (VM) SKU type by using the
--vm-sizeparameter. - Network configuration: public hub clusters have a public API server, with an associated public IP address. When configured for private access, the API server is only accessible via an Azure virtual network.
Hub cluster restrictions
The hub cluster has the following restrictions that ensure it functions as required for resource propagation and management:
- Command Invocation Disabled: Using command invocation via the Azure CLI (az aks command invoke) is disabled for hub clusters.
- Local Authentication Disabled: Access via admin
kubeconfigis disabled, ensuring that authentication is exclusively handled through Microsoft Entra ID, enhancing security by centralizing access control. Use az fleet get-credentials to obtain thekubeconfigfor the hub cluster. - Deny Assignments: Changes to the Azure configuration of the hub cluster and associated resources are blocked through Azure Deny Assignments. The following Deny Assignments are used:
FLRG-DenyAssignments-{guid}: Applied on the hub cluster resource group, preventing users from modifying the hub cluster.kubernetes.azure.com/{guid}(optional): This deny assignment prevents users from modifying the hub cluster AKS resources (Virtual Machine Scale Sets, networks), as described in AKS node resource group lockdown.
- Applied Resources not instantiated: The hub cluster doesn't schedule applied Kubernetes resources onto the hub cluster node. Some Kubernetes resources must be applied using an envelope object to avoid side effects on the hub cluster. For more information about envelope objects, see the documentation of Envelope Objects.
Requirements from customers
In order for Fleet Manager to create and keep hub clusters up-to-date with the latest patches, ensure that:
Azure policy doesn't block cluster creation. The hub cluster is a managed AKS cluster. If you can't create AKS clusters you can't create a Fleet Manager hub cluster.
Hub cluster has internet access. Outbound connectivity is required to install updates. Private hubs on networks with user-defined routing (UDR) or firewall rules might block outbound connectivity. For more information on outbound connectivity, see documentation on AKS outbound network.
No need to manage updates to the Fleet Manager hub cluster. Microsoft automatically updates the hub cluster to the latest version of Kubernetes or node image as they become available from AKS. Update releases can be tracked on the AKS Release Tracker.