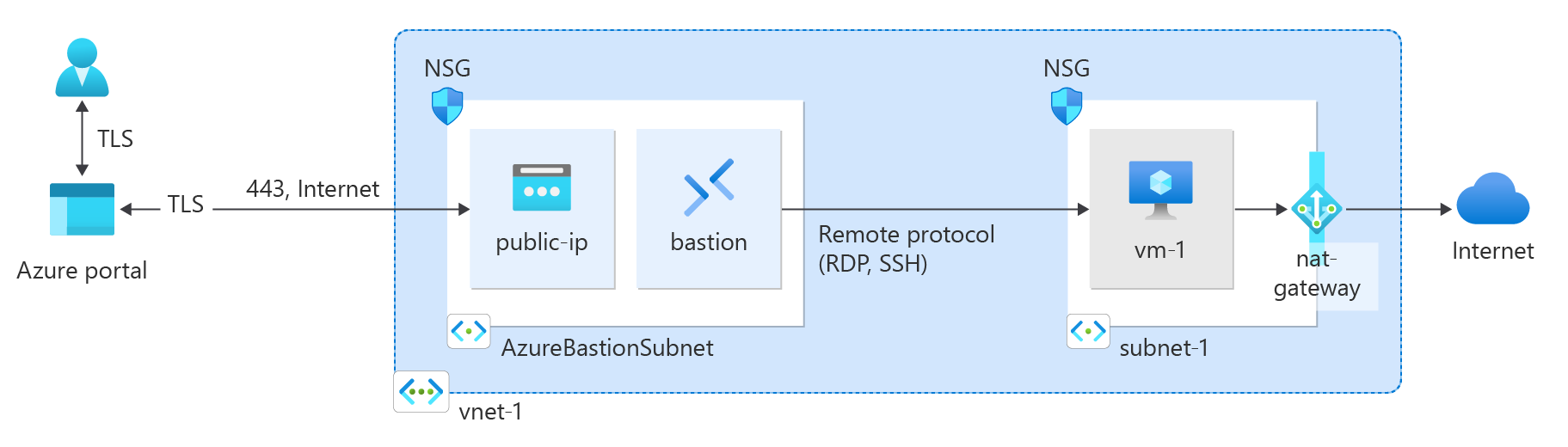
In this quickstart, learn how to create a NAT gateway by using the Azure portal, Azure CLI, PowerShell, Bicep, ARM template and Terraform. The NAT Gateway service provides scalable outbound connectivity for virtual machines in Azure.
Create a NAT gateway
Before you deploy the NAT gateway resource and the other resources, a resource group is required to contain the resources deployed. In the following steps, you create a resource group, NAT gateway resource, and a public IP address. You can use one or more public IP address resources, public IP prefixes, or both.
For information about public IP prefixes and a NAT gateway, see Manage NAT gateway.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter NAT gateway. Select NAT gateways in the search results.
Select + Create.
In Create network address translation (NAT) gateway, enter or select this information in the Basics tab:
| Setting |
Value |
| Project Details |
|
| Subscription |
Select your Azure subscription. |
| Resource Group |
Select Create new.
Enter test-rg.
Select OK. |
| Instance details |
|
| NAT gateway name |
Enter nat-gateway |
| Region |
Select China North 3 |
| Availability Zone |
Select No Zone. |
| TCP idle timeout (minutes) |
Leave the default of 4. |
For information about availability zones and NAT gateway, see NAT gateway and availability zones.
Select the Outbound IP tab, or select the Next: Outbound IP button at the bottom of the page.
In the Outbound IP tab, enter or select the following information:
| Setting |
Value |
| Public IP addresses |
Select Create a new public IP address.
In Name, enter public-ip-nat.
Select OK. |
Select the Review + create tab, or select the blue Review + create button at the bottom of the page.
Select Create.
Create a virtual network and bastion host
The following procedure creates a virtual network with a resource subnet, an Azure Bastion subnet, and an Azure Bastion host.
In the portal, search for and select Virtual networks.
On the Virtual networks page, select + Create.
On the Basics tab of Create virtual network, enter or select the following information:
| Setting |
Value |
| Project details |
|
| Subscription |
Select your subscription. |
| Resource group |
Select test-rg. |
| Instance details |
|
| Name |
Enter vnet-1. |
| Region |
Select China North 3. |
Select Next to proceed to the Security tab.
Select Enable Azure Bastion in the Azure Bastion section of the Security tab.
Azure Bastion uses your browser to connect to VMs in your virtual network over secure shell (SSH) or remote desktop protocol (RDP) by using their private IP addresses. The VMs don't need public IP addresses, client software, or special configuration. For more information about Azure Bastion, see Azure Bastion
Enter or select the following information in Azure Bastion:
| Setting |
Value |
| Azure Bastion host name |
Enter bastion. |
| Azure Bastion public IP address |
Select Create a public IP address.
Enter public-ip-bastion in Name.
Select OK. |
Select Next to proceed to the IP Addresses tab.
In the address space box in Subnets, select the default subnet.
In Edit subnet, enter or select the following information:
| Setting |
Value |
| Subnet purpose |
Leave the default Default. |
| Name |
Enter subnet-1. |
| IPv4 |
|
| IPv4 address range |
Leave the default of 10.0.0.0/16. |
| Starting address |
Leave the default of 10.0.0.0. |
| Size |
Leave the default of /24(256 addresses). |
| Security |
|
| NAT gateway |
Select nat-gateway. |
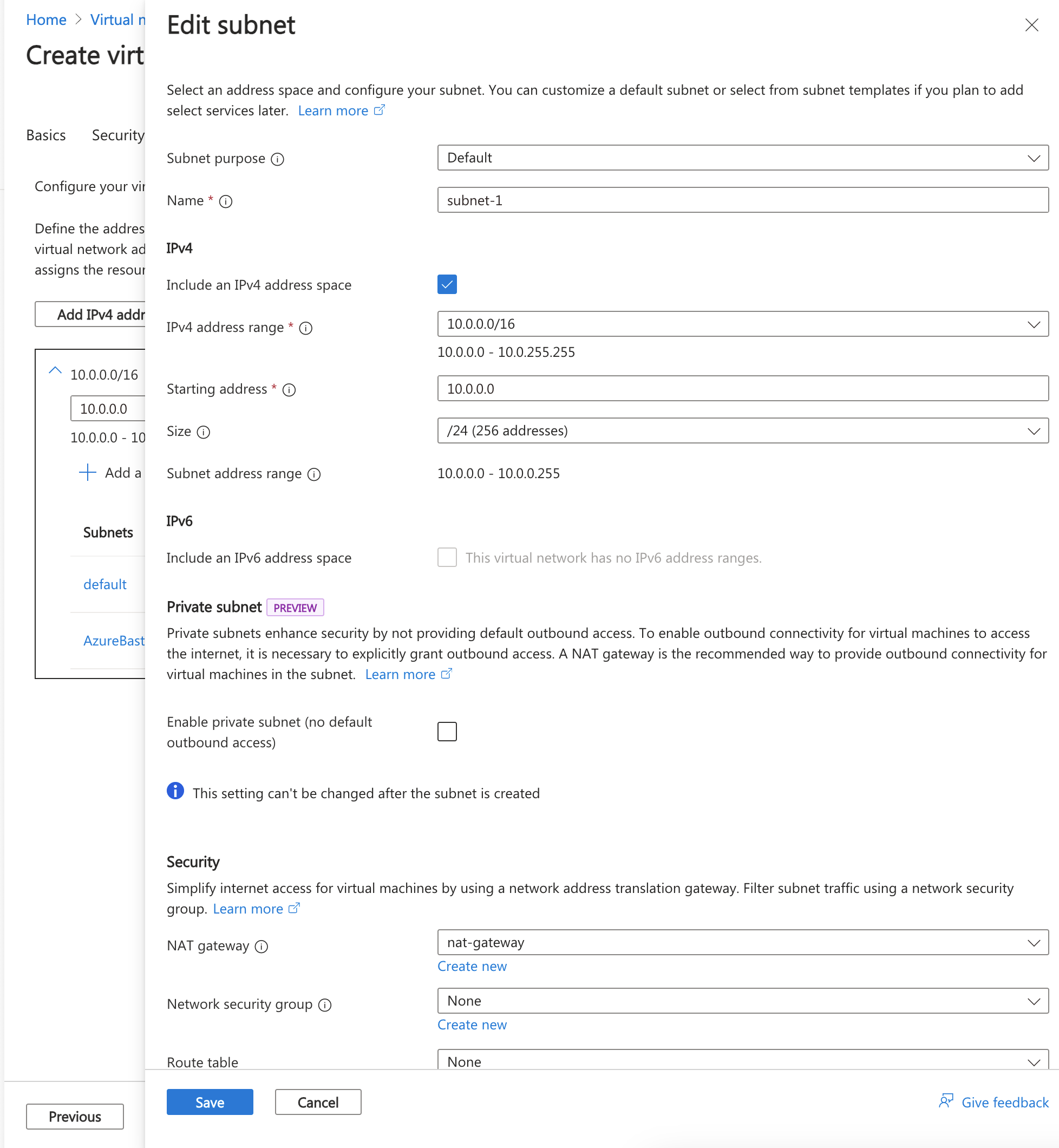
Select Save.
Select Review + create at the bottom of the screen, and when validation passes, select Create.
Create test virtual machine
The following procedure creates a test virtual machine (VM) named vm-1 in the virtual network.
In the portal, search for and select Virtual machines.
In Virtual machines, select + Create.
On the Basics tab of Create a virtual machine, enter or select the following information:
| Setting |
Value |
| Project details |
|
| Subscription |
Select your subscription. |
| Resource group |
Select test-rg. |
| Instance details |
|
| Virtual machine name |
Enter vm-1. |
| Region |
Select (Asia Pacific) China East 2. |
| Availability options |
Select No infrastructure redundancy required. |
| Security type |
Leave the default of Standard. |
| Image |
Select Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS - Gen2. |
| Size |
Select a size. |
| Administrator account |
|
| Authentication type |
Select Password. |
| Username |
Enter azureuser. |
| Password |
Enter a password. |
| Confirm password |
Reenter the password. |
| Inbound port rules |
|
| Public inbound ports |
Select None. |
Select the Networking tab at the top of the page.
Enter or select the following information in the Networking tab:
| Setting |
Value |
| Network interface |
|
| Virtual network |
Select vnet-1. |
| Subnet |
Select subnet-1 (10.0.0.0/24). |
| Public IP |
Select None. |
| NIC network security group |
Select Advanced. |
| Configure network security group |
Select Create new.
Enter nsg-1 for the name.
Leave the rest at the defaults and select OK. |
Leave the rest of the settings at the defaults and select Review + create.
Review the settings and select Create.
Note
Virtual machines in a virtual network with a bastion host don't need public IP addresses. Bastion provides the public IP, and the VMs use private IPs to communicate within the network. You can remove the public IPs from any VMs in bastion hosted virtual networks. For more information, see Dissociate a public IP address from an Azure VM.
Note
Azure provides a default outbound access IP for VMs that either aren't assigned a public IP address or are in the backend pool of an internal basic Azure load balancer. The default outbound access IP mechanism provides an outbound IP address that isn't configurable.
The default outbound access IP is disabled when one of the following events happens:
- A public IP address is assigned to the VM.
- The VM is placed in the backend pool of a standard load balancer, with or without outbound rules.
- An Azure NAT Gateway resource is assigned to the subnet of the VM.
VMs that you create by using virtual machine scale sets in flexible orchestration mode don't have default outbound access.
For more information about outbound connections in Azure, see Default outbound access in Azure and Use Source Network Address Translation (SNAT) for outbound connections.
Create a resource group
Create a resource group with New-AzResourceGroup. An Azure resource group is a logical container into which Azure resources are deployed and managed.
The following example creates a resource group named test-rg in the chinanorth3 location:
$rsg = @{
Name = 'test-rg'
Location = 'chinanorth3'
}
New-AzResourceGroup @rsg
Create the NAT gateway
In this section, create the NAT gateway and supporting resources.
## Create public IP address for NAT gateway ##
$ip = @{
Name = 'public-ip-nat'
ResourceGroupName = 'test-rg'
Location = 'chinanorth3'
Sku = 'Standard'
AllocationMethod = 'Static'
Zone = 1,2,3
}
$publicIP = New-AzPublicIpAddress @ip
## Create NAT gateway resource ##
$nat = @{
ResourceGroupName = 'test-rg'
Name = 'nat-gateway'
IdleTimeoutInMinutes = '10'
Sku = 'Standard'
Location = 'chinanorth3'
PublicIpAddress = $publicIP
}
$natGateway = New-AzNatGateway @nat
## Create subnet config and associate NAT gateway to subnet##
$subnet = @{
Name = 'subnet-1'
AddressPrefix = '10.0.0.0/24'
NatGateway = $natGateway
}
$subnetConfig = New-AzVirtualNetworkSubnetConfig @subnet
## Create Azure Bastion subnet ##
$bastsubnet = @{
Name = 'AzureBastionSubnet'
AddressPrefix = '10.0.1.0/26'
}
$bastsubnetConfig = New-AzVirtualNetworkSubnetConfig @bastsubnet
## Create the virtual network ##
$net = @{
Name = 'vnet-1'
ResourceGroupName = 'test-rg'
Location = 'chinanorth3'
AddressPrefix = '10.0.0.0/16'
Subnet = $subnetConfig,$bastsubnetConfig
}
$vnet = New-AzVirtualNetwork @net
## Create public IP address for bastion host ##
$ip = @{
Name = 'public-ip'
ResourceGroupName = 'test-rg'
Location = 'chinanorth3'
Sku = 'Standard'
AllocationMethod = 'Static'
Zone = 1,2,3
}
$publicip = New-AzPublicIpAddress @ip
## Create bastion host ##
$bastion = @{
Name = 'bastion'
ResourceGroupName = 'test-rg'
PublicIpAddressRgName = 'test-rg'
PublicIpAddressName = 'public-ip'
VirtualNetworkRgName = 'test-rg'
VirtualNetworkName = 'vnet-1'
Sku = 'Basic'
}
New-AzBastion @bastion
The bastion host can take several minutes to deploy. Wait for the bastion host to deploy before moving on to the next section.
Create virtual machine
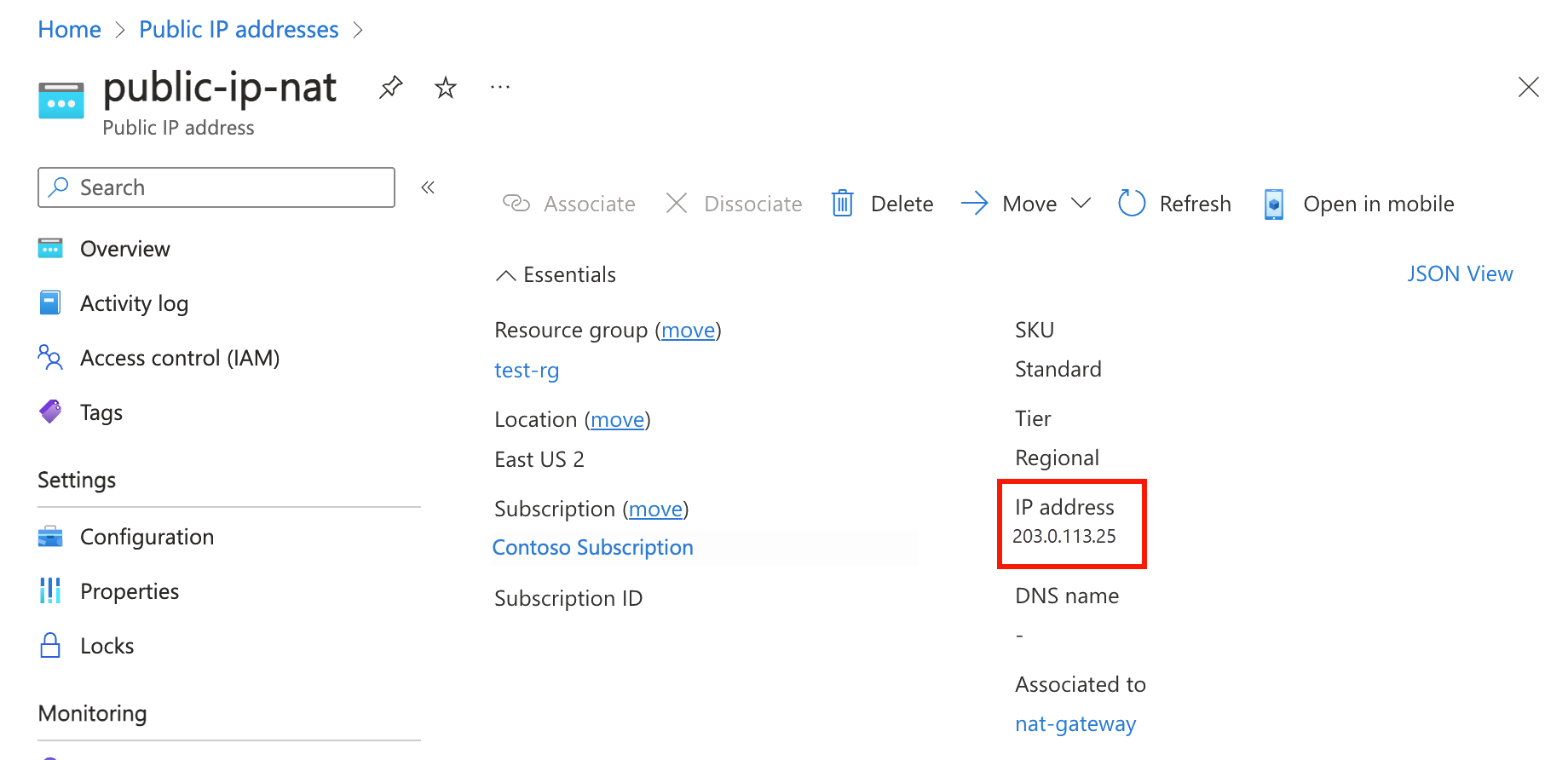
In this section, you create a virtual machine to test the NAT gateway and verify the public IP address of the outbound connection.
# Set the administrator and password for the VM ##
$cred = Get-Credential
## Place the virtual network into a variable ##
$vnet = Get-AzVirtualNetwork -Name 'vnet-1' -ResourceGroupName 'test-rg'
## Create network interface for virtual machine ##
$nic = @{
Name = "nic-1"
ResourceGroupName = 'test-rg'
Location = 'chinanorth3'
Subnet = $vnet.Subnets[0]
}
$nicVM = New-AzNetworkInterface @nic
## Create a virtual machine configuration ##
$vmsz = @{
VMName = 'vm-1'
VMSize = 'Standard_DS1_v2'
}
$vmos = @{
ComputerName = 'vm-1'
Credential = $cred
}
$vmimage = @{
PublisherName = 'Canonical'
Offer = '0001-com-ubuntu-server-jammy'
Skus = '22_04-lts-gen2'
Version = 'latest'
}
$vmConfig = New-AzVMConfig @vmsz `
| Set-AzVMOperatingSystem @vmos -Linux `
| Set-AzVMSourceImage @vmimage `
| Add-AzVMNetworkInterface -Id $nicVM.Id
## Create the virtual machine ##
$vm = @{
ResourceGroupName = 'test-rg'
Location = 'chinanorth3'
VM = $vmConfig
}
New-AzVM @vm
Wait for the virtual machine creation to complete before moving on to the next section.
Create a resource group
Create a resource group with az group create. An Azure resource group is a logical container into which Azure resources are deployed and managed.
az group create \
--name test-rg \
--location chinanorth3
Create the NAT gateway
In this section, create the NAT gateway and supporting resources.
Create public IP address
To access the internet, you need one or more public IP addresses for the NAT gateway. Use az network public-ip create to create a public IP address resource.
az network public-ip create \
--resource-group test-rg \
--name public-ip-nat \
--sku Standard \
--allocation-method Static \
--location chinanorth3 \
--zone 1 2 3
Create NAT gateway resource
Create a NAT gateway resource using az network nat gateway create. The NAT gateway uses the public IP address created in the previous step. The idle time out is set to 10 minutes.
az network nat gateway create \
--resource-group test-rg \
--name nat-gateway \
--public-ip-addresses public-ip-nat \
--idle-timeout 10
Create virtual network and subnet
Create a virtual network named vnet-1 with a subnet named subnet-1 using az network vnet create. The IP address space for the virtual network is 10.0.0.0/16. The subnet within the virtual network is 10.0.0.0/24.
az network vnet create \
--resource-group test-rg \
--name vnet-1 \
--address-prefix 10.0.0.0/16 \
--subnet-name subnet-1 \
--subnet-prefixes 10.0.0.0/24
Create Azure Bastion subnet
Create an Azure Bastion subnet named AzureBastionSubnet using az network vnet subnet create:
az network vnet subnet create \
--name AzureBastionSubnet \
--resource-group test-rg \
--vnet-name vnet-1 \
--address-prefix 10.0.1.0/26
Associate NAT gateway to subnet
Associate the NAT gateway to the subnet using az network vnet subnet update:
az network vnet subnet update \
--resource-group test-rg \
--vnet-name vnet-1 \
--name subnet-1 \
--nat-gateway nat-gateway
Create public IP address for Bastion host
Create a public IP address for the Bastion host using az network public-ip create:
az network public-ip create \
--resource-group test-rg \
--name public-ip \
--sku Standard \
--location chinanorth3 \
--zone 1 2 3
Create Bastion host
Create the Azure Bastion host using az network bastion create:
az network bastion create \
--name bastion \
--public-ip-address public-ip \
--resource-group test-rg \
--vnet-name vnet-1 \
--location chinanorth3
The Bastion host can take several minutes to deploy. Wait for the Bastion host to deploy before moving on to the next section.
Create virtual machine
Create a virtual machine named vm-1 to test the NAT gateway and verify the public IP address of the outbound connection. Use az vm create:
az vm create \
--resource-group test-rg \
--name vm-1 \
--image Ubuntu2204 \
--admin-username azureuser \
--authentication-type password \
--public-ip-address "" \
--subnet subnet-1 \
--vnet-name vnet-1
Wait for the virtual machine creation to complete before moving on to the next section.
This Terraform file deploys a virtual network, a NAT gateway resource, and Ubuntu virtual machine. The Ubuntu virtual machine is deployed to a subnet that is associated with the NAT gateway resource.
The script also generates a random SSH public key and associates it with the virtual machine for secure access. The public key is outputted at the end of the script execution.
The script uses the Random and AzAPI providers in addition to the AzureRM provider. The Random provider is used to generate a unique name for the resource group and the SSH key. The AzAPI provider is used to generate the SSH public key.
As with the public key, the names of the created resource group, virtual network, subnet, and NAT gateway are printed when the script is run.
Terraform enables the definition, preview, and deployment of cloud infrastructure. Using Terraform, you create configuration files using HCL syntax. The HCL syntax allows you to specify the cloud provider - such as Azure - and the elements that make up your cloud infrastructure. After you create your configuration files, you create an execution plan that allows you to preview your infrastructure changes before they're deployed. Once you verify the changes, you apply the execution plan to deploy the infrastructure.
Create a directory in which to test and run the sample Terraform code and make it the current directory.
Create a file named main.tf and insert the following code:
# Resource Group
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "rg" {
location = var.resource_group_location
name = "${random_pet.prefix.id}-rg"
}
# Virtual Network
resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "my_terraform_network" {
name = "${random_pet.prefix.id}-vnet"
address_space = ["10.0.0.0/16"]
location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
}
# Subnet 1
resource "azurerm_subnet" "my_terraform_subnet_1" {
name = "subnet-1"
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
virtual_network_name = azurerm_virtual_network.my_terraform_network.name
address_prefixes = ["10.0.0.0/24"]
}
# Public IP address for NAT gateway
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "my_public_ip" {
name = "public-ip-nat"
location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
allocation_method = "Static"
sku = "Standard"
}
# NAT Gateway
resource "azurerm_nat_gateway" "my_nat_gateway" {
name = "nat-gateway"
location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
}
# Associate NAT Gateway with Public IP
resource "azurerm_nat_gateway_public_ip_association" "example" {
nat_gateway_id = azurerm_nat_gateway.my_nat_gateway.id
public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.my_public_ip.id
}
# Associate NAT Gateway with Subnet
resource "azurerm_subnet_nat_gateway_association" "example" {
subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.my_terraform_subnet_1.id
nat_gateway_id = azurerm_nat_gateway.my_nat_gateway.id
}
# Create public IP for virtual machine
resource "azurerm_public_ip" "my_public_ip_vm" {
name = "public-ip-vm"
location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
allocation_method = "Static"
sku = "Standard"
}
# Create Network Security Group and rule
resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "my_terraform_nsg" {
name = "nsg-1"
location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
security_rule {
name = "SSH"
priority = 1001
direction = "Inbound"
access = "Allow"
protocol = "Tcp"
source_port_range = "*"
destination_port_range = "22"
source_address_prefix = "*"
destination_address_prefix = "*"
}
}
# Create network interface
resource "azurerm_network_interface" "my_terraform_nic" {
name = "nic-1"
location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
ip_configuration {
name = "my_nic_configuration"
subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.my_terraform_subnet_1.id
private_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic"
public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.my_public_ip_vm.id
}
}
# Connect the security group to the network interface
resource "azurerm_network_interface_security_group_association" "example" {
network_interface_id = azurerm_network_interface.my_terraform_nic.id
network_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.my_terraform_nsg.id
}
# Generate random text for a unique storage account name
resource "random_id" "random_id" {
keepers = {
# Generate a new ID only when a new resource group is defined
resource_group = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
}
byte_length = 8
}
# Create storage account for boot diagnostics
resource "azurerm_storage_account" "my_storage_account" {
name = "diag${random_id.random_id.hex}"
location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
account_tier = "Standard"
account_replication_type = "LRS"
}
# Create virtual machine
resource "azurerm_linux_virtual_machine" "my_terraform_vm" {
name = "vm-1"
location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
network_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.my_terraform_nic.id]
size = "Standard_DS1_v2"
os_disk {
name = "myOsDisk"
caching = "ReadWrite"
storage_account_type = "Premium_LRS"
}
source_image_reference {
publisher = "Canonical"
offer = "0001-com-ubuntu-server-jammy"
sku = "22_04-lts-gen2"
version = "latest"
}
computer_name = "hostname"
admin_username = var.username
admin_ssh_key {
username = var.username
public_key = azapi_resource_action.ssh_public_key_gen.output.publicKey
}
boot_diagnostics {
storage_account_uri = azurerm_storage_account.my_storage_account.primary_blob_endpoint
}
}
resource "random_pet" "prefix" {
prefix = var.resource_group_name_prefix
length = 1
}
- Create a file named
outputs.tf and insert the following code:
output "resource_group_name" {
description = "The name of the created resource group."
value = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
}
output "virtual_network_name" {
description = "The name of the created virtual network."
value = azurerm_virtual_network.my_terraform_network.name
}
output "subnet_name_1" {
description = "The name of the created subnet 1."
value = azurerm_subnet.my_terraform_subnet_1.name
}
output "nat_gateway"{
description = "The name of the created NAT gateway."
value = azurerm_nat_gateway.my_nat_gateway.id
}
- Create a file named
providers.tf and insert the following code:
terraform {
required_providers {
azapi = {
source = "azure/azapi"
version = "~>1.5"
}
azurerm = {
source = "hashicorp/azurerm"
version = "~>3.0"
}
random = {
source = "hashicorp/random"
version = "~>3.0"
}
}
}
provider "azurerm" {
features {}
environment = "china"
}
- Create a file named
ssh.tf and insert the following code:
resource "random_pet" "ssh_key_name" {
prefix = "ssh"
separator = ""
}
resource "azapi_resource_action" "ssh_public_key_gen" {
type = "Microsoft.Compute/sshPublicKeys@2022-11-01"
resource_id = azapi_resource.ssh_public_key.id
action = "generateKeyPair"
method = "POST"
response_export_values = ["publicKey", "privateKey"]
}
resource "azapi_resource" "ssh_public_key" {
type = "Microsoft.Compute/sshPublicKeys@2022-11-01"
name = random_pet.ssh_key_name.id
location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location
parent_id = azurerm_resource_group.rg.id
}
output "key_data" {
value = azapi_resource_action.ssh_public_key_gen.output.publicKey
}
- Create a file named
variables.tf and insert the following code:
variable "resource_group_location" {
type = string
default = "chinanorth3"
description = "Location of the resource group."
}
variable "resource_group_name_prefix" {
type = string
default = "rg"
description = "Prefix of the resource group name that's combined with a random ID so name is unique in your Azure subscription."
}
variable "username" {
type = string
description = "The username for the local account that will be created on the new VM."
default = "azureuser"
}
Run terraform init to initialize the Terraform deployment. This command downloads the Azure provider required to manage your Azure resources.
terraform init -upgrade
Key points:
- The
-upgrade parameter upgrades the necessary provider plugins to the newest version that complies with the configuration's version constraints.
Run terraform plan to create an execution plan.
terraform plan -out main.tfplan
Key points:
- The
terraform plan command creates an execution plan, but doesn't execute it. Instead, it determines what actions are necessary to create the configuration specified in your configuration files. This pattern allows you to verify whether the execution plan matches your expectations before making any changes to actual resources.
- The optional
-out parameter allows you to specify an output file for the plan. Using the -out parameter ensures that the plan you reviewed is exactly what is applied.
Run terraform apply to apply the execution plan to your cloud infrastructure.
terraform apply main.tfplan
Key points:
- The example
terraform apply command assumes you previously ran terraform plan -out main.tfplan.
- If you specified a different filename for the
-out parameter, use that same filename in the call to terraform apply.
- If you didn't use the
-out parameter, call terraform apply without any parameters.
Verify the results
Azure CLI
- Get the Azure resource group name.
resource_group_name=$(terraform output -raw resource_group_name)
- Get the NAT gateway ID.
nat_gateway=$(terraform output -raw nat_gateway)
- Run az network nat gateway show to display the details about the NAT gateway.
az network nat gateway show \
--resource-group $resource_group_name \
--ids $nat_gateway
PowerShell
- Get the Azure resource group name.
$resource_group_name=$(terraform output -raw resource_group_name)
- Get the NAT gateway ID.
$nat_gateway=$(terraform output -raw nat_gateway)
- Run Get-AzNatGateway to display the details about the NAT gateway.
$nat = @{
Name = $nat_gateway
ResourceGroupName = $resource_group_name
}
Get-AzNatGateway @nat
In this section, you test the NAT gateway. You first discover the public IP of the NAT gateway. You then connect to the test virtual machine and verify the outbound connection through the NAT gateway public IP.