Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Before you create an Azure classic file share, you need to answer two questions about how you want to use it:
What are the performance requirements for your file share?
Azure classic file shares offer two different media tiers of storage, SSD (premium) and HDD (standard), which enable you to tailor your file shares to the performance and price requirements of your scenario. SSD file shares provide consistent high performance and low latency, within single-digit milliseconds for most IO operations. HDD file shares provide cost-effective storage for general purpose use.What are the redundancy requirements for your Azure file share?
Azure Files offers locally redundant storage (LRS), zone-redundant storage (ZRS), geo-redundant storage (GRS), and geo-zone-redundant storage (GZRS) options for HDD SMB file shares. SSD file shares are only available for the LRS and ZRS redundancy types. See Azure Files redundancy for more information.
For more information on these choices, see Planning for an Azure Files deployment.
Prerequisites
- This article assumes that you have an Azure subscription. If you don't have an Azure subscription, then create a trial account before you begin.
- If you intend to use Azure PowerShell, install the latest version.
- If you intend to use Azure CLI, install the latest version.
Create a storage account
Azure classic file shares are deployed into storage accounts, which are top-level objects that represent a shared pool of storage. This pool of storage can be used to deploy multiple file shares. If you already have an Azure storage account that you want to use, you can skip this section and proceed to Create a classic file share.
Storage accounts have two properties, kind and SKU, which dictate the billing model, media tier, and redundancy of the file shares that can be deployed in the storage account. For Azure Files, there are three main combinations of kind and SKU to consider:
| Media tier | Billing model | Storage account kind | Storage account SKUs |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSD and HDD | Provisioned v2 | FileStorage |
|
| SSD | Provisioned v1 | FileStorage |
|
| HDD | Pay-as-you-go | StorageV2 |
|
We recommend using the provisioned v2 billing model for all new file share deployments. The provisioned v1 and pay-as-you-go billing models remain fully supported for new and existing deployments. Provisioned v2 file shares are currently available in most regions. See provisioned v2 availability for more information.
To create a storage account via the Azure portal, use the search box at the top of the Azure portal to search for storage accounts and select the matching result.
This shows a list of all existing storage accounts available in your visible subscriptions. Select + Create to create a new storage account.
Basics
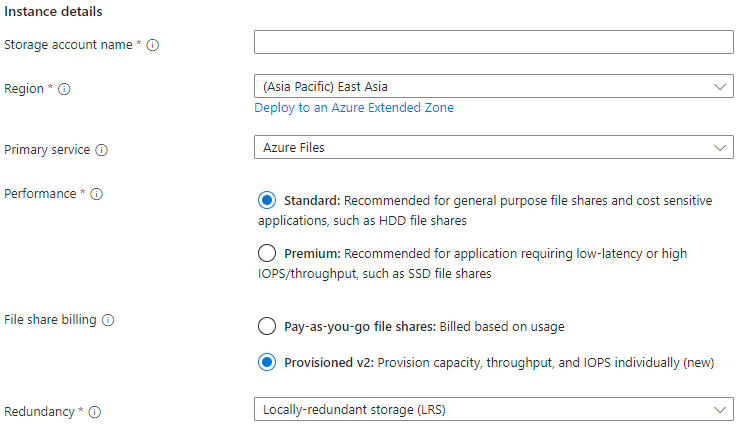
The first tab to complete creating a storage account is labeled Basics, which contains the required fields to create a storage account.
| Field name | Input type | Values | Applicable to Azure Files | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subscription | Drop-down list | Available Azure subscriptions | Yes | The selected subscription in which to deploy the storage account. The number of storage accounts per subscription is limited, so to deploy a new storage account into a selected subscription, it must have fewer storage accounts deployed than the subscription limit. See storage account scale targets for more information. |
| Resource group | Drop-down list | Available resource groups in selected subscription | Yes | The resource group in which to deploy the storage account. A resource group is a logical container for organizing Azure resources, including storage accounts. |
| Storage account name | Text box | -- | Yes | The name of the storage account resource to be created. This name must be globally unique. The storage account name is used as the server name when you mount an Azure file share via SMB. Storage account names must be between 3 and 24 characters in length. They may contain numbers and lowercase letters only. |
| Region | Drop-down list | Available Azure regions | Yes | The region for the storage account to be deployed into. This can be the region associated with the resource group, or any other available region. |
| Primary service | Drop-down list |
|
Only unpopulated and Azure Files | The service for which you're creating the storage account, in this case Azure Files. This field is optional, however, you can't select the provisioned v2 billing model unless you select Azure Files from the list. |
| Performance | Radio button group |
|
Yes | The media tier of the storage account. Select Standard for an HDD storage account and Premium for an SSD storage account. |
| File share billing | Radio button group |
|
Yes | The billing model desired for your scenario. We recommend provisioned v2 for all new deployments, although the provisioned v1 and pay-as-you-go billing models are still supported for SSD and HDD file shares, respectively. |
| Redundancy | Drop-down list |
|
Yes | The redundancy choice for the storage account. See Azure Files redundancy for more information. |
| Make read access to data available in the event of region unavailability | Checkbox | Checked/unchecked | No | This setting only appears if you select the pay-as-you-go billing model with GRS or GZRS redundancy. Azure Files doesn't support read access to data in the secondary region without a failover regardless of the status of this setting. |
Advanced
The Advanced tab is optional, but provides more granular settings for the storage account. The first section relates to Security settings.
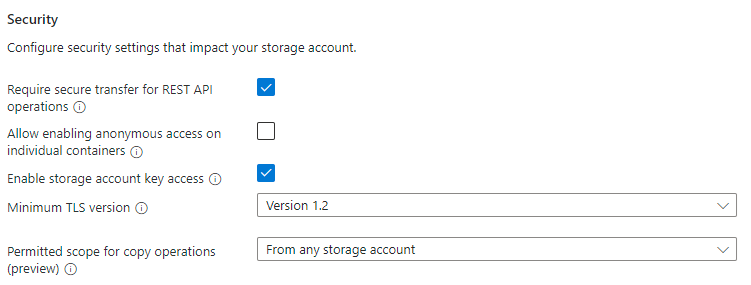
| Field name | Input type | Values | Applicable to Azure Files | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Require secure transfer for REST API operations | Checkbox | Checked/unchecked | Yes | This setting indicates that this applies to REST API operations, but it applies to SMB and NFS for Azure Files as well. If you plan to deploy NFS file shares in your storage account, or you have clients that need access to unencrypted SMB (such as SMB 2.1), uncheck this checkbox. |
| Allow enabling anonymous access on individual containers | Checkbox | Checked/unchecked | No | This setting controls whether Azure Blob storage containers are allowed to be accessed with anonymous access. This setting doesn't apply to Azure Files. This setting is available for FileStorage storage accounts containing provisioned v1 or provisioned v2 file shares even though it isn't possible to create Azure Blob storage containers in FileStorage storage accounts. |
| Enable storage account key access | Checkbox | Checked/unchecked | Yes | This setting controls whether the storage account keys (also referred to as shared keys) are enabled. When enabled, storage account keys can be used to mount the file share using SMB or to access the share using the FileREST API. |
| Minimum TLS version | Drop-down list | Supported TLS versions | Yes | This setting controls the minimum allowed TLS version that's used for protocols which use TLS. For Azure Files, only the FileREST protocol uses TLS (as part of HTTPS). |
| Permitted scope for copy operations | Drop-down list | Scopes for copy operations | Yes | This setting controls the scope of storage account to storage account copy operations using the FileREST API, usually facilitated through tools like AzCopy. |
The Hierarchical Namespace section applies only to Azure Blob storage, even in FileStorage storage accounts using the provisioned v1 or provisioned v2 billing models which can only contain Azure file shares. Azure file shares support a hierarchical namespace regardless of the value of these settings.
| Field name | Input type | Values | Applicable to Azure Files | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enable hierarchical namespace | Checkbox | Checked/unchecked | No | This is an Azure Blob storage only setting. This setting is disabled for FileStorage storage accounts, but is active for storage accounts using the pay-as-you-go model, even if Azure Files is selected as the primary service. |
The Access protocols section applies only to Azure Blob storage, even in FileStorage storage accounts using the provisioned v1 or provisioned v2 billing models which can only contain Azure file shares.
| Field name | Input type | Values | Applicable to Azure Files | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enable SFTP | Checkbox | Checked/unchecked | No | This is an Azure Blob storage only setting. This setting is disabled for FileStorage storage accounts, but is active for storage accounts using the pay-as-you-go model, even if Azure Files is selected as the primary service. |
| Enable network file system v3 | Checkbox | Checked/unchecked | No | This is an Azure Blob storage only setting. This setting is disabled for FileStorage storage accounts, but is active for storage accounts using the pay-as-you-go model. SSD storage accounts can create NFSv4.1 file shares even though this setting is unchecked; in Azure Files, the file share's protocol is selected on the file share, not the storage account. |
The Blob storage section applies only to Azure Blob storage use, even in FileStorage storage accounts using the provisioned v1 or provisioned v2 models which can only contain Azure file shares.
| Field name | Input type | Values | Applicable to Azure Files | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allow cross-tenant replication | Checkbox | Checked/unchecked | No | This is an Azure Blob storage only setting. This setting is always available, even for FileStorage storage accounts which can't contain Azure Blob storage. Checking this checkbox has no impact on Azure Files. |
| Access tier | Radio button group | Blob storage access tiers | No | This is an Azure Blob storage only setting. This setting is always available, even for FileStorage storage accounts which can't contain Azure Blob storage. Selecting an option has no impact on Azure Files. |
Networking
The networking section allows you to configure networking options. These settings are optional for the creation of the storage account and can be configured later if desired. For more information on these options, see Azure Files networking considerations.
Data protection
The Data protection tab allows you to enable or disable soft-delete. The soft-delete option for Azure Files is under the Recovery section.
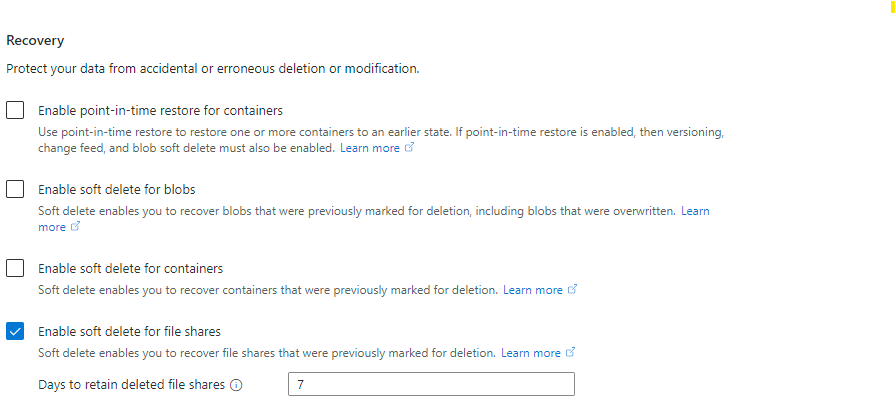
| Field name | Input type | Values | Applicable to Azure Files | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enable point-in-time restore for containers | Checkbox | Checked/unchecked | No | This is an Azure Blob storage only setting. This setting is always available, even for FileStorage storage accounts which can't contain Azure Blob storage, although checking this box for FileStorage storage accounts does result in a validation error message. For pay-as-you-go storage accounts, the selection for this setting doesn't apply to Azure Files. |
| Maximum restore point (days ago) | Textbox | Days (number) | No | When Enable point-in-time restore for containers is selected, this textbox is available. The value chosen doesn't apply to Azure Files. |
| Enable soft delete for blobs | Checkbox | Checked/unchecked | No | This is an Azure Blob storage only setting. This setting is always available, even for FileStorage storage accounts which can't contain Azure Blob storage, although checking this box for FileStorage storage accounts does result in a validation error message. For pay-as-you-go storage accounts, the selection for this setting doesn't apply to Azure Files. |
| Days to retain deleted blobs | Textbox | Days (number) | No | When Enable soft delete for blobs is selected, this textbox is available. The value chosen doesn't apply to Azure Files. |
| Enable soft delete for containers | Checkbox | Checked/unchecked | No | This is an Azure Blob storage only setting. This setting is always available, even for FileStorage storage accounts which can't contain Azure Blob storage, although checking this box for FileStorage storage account does result in a validation error message. For pay-as-you-go storage accounts, the selection for this setting doesn't apply to Azure Files. |
| Days to retain deleted containers | Textbox | Days (number) | No | When Enable soft delete for containers is selected, this textbox is available. The value chosen doesn't apply to Azure Files. |
| Enable soft delete for file shares | Checkbox | Checked/unchecked | Yes | Enable the soft delete feature to protect against the accidental deletion of file shares. Soft delete is enabled by default, but you may choose to disable this setting if shares are frequently created and deleted as part of a business workflow. Soft-deleted file shares are billed for their used capacity, even in provisioned models. |
| Days to retain deleted file shares | Textbox | Days (number) | Yes | When Enable soft delete for file shares is selected, this textbox is available. By default, file shares are retained for 7 days before being purged, however you may choose to increase or decrease this number depending on your requirements. Soft-deleted file shares are billed for their used capacity, even in provisioned file shares, so retaining for a longer period of time can result in greater expenses due to soft-delete. |
The Tracking section applies only to Azure Blob storage use, even in FileStorage storage accounts using the provisioned v1 or provisioned v2 billing models which can only contain Azure file shares.
| Field name | Input type | Values | Applicable to Azure Files | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enable versioning for blobs | Checkbox | Checked/unchecked | No | This is an Azure Blob storage only setting. This setting is always available, even for FileStorage storage accounts which can't contain Azure Blob storage, although checking this box for FileStorage storage accounts does result in a validation error message. For pay-as-you-go storage accounts, the selection for this setting doesn't apply to Azure Files. |
| Enable blob change feed | Checkbox | Checked/unchecked | No | This is an Azure Blob storage only setting. This setting is always available, even for FileStorage storage accounts which can't contain Azure Blob storage, although checking this box for FileStorage storage accounts does result in a validation error message. For pay-as-you-go storage accounts, the selection for this setting doesn't apply to Azure Files. |
The Access control section applies only to Azure Blob storage use, even in FileStorage storage accounts using the provisioned v1 or provisioned v2 billing models which can only contain Azure file shares.
| Field name | Input type | Values | Applicable to Azure Files | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enable version-level immutability support | Checkbox | Checked/unchecked | No | This is an Azure Blob storage only setting. This setting is always available, even for FileStorage storage accounts which can't contain Azure Blob storage, although checking this box for FileStorage storage accounts does result in a validation error message. For pay-as-you-go storage accounts, the selection for this setting doesn't apply to Azure Files. |
Encryption
The Encryption tab controls settings related to encryption at rest.
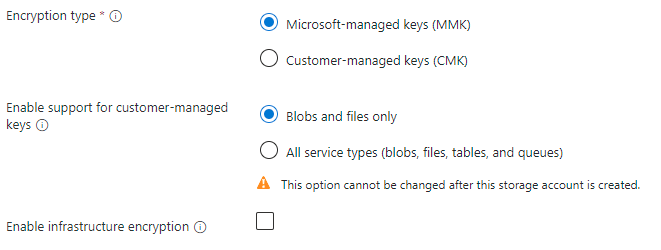
| Field name | Input type | Values | Applicable to Azure Files | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Encryption type | Radio button group |
|
Yes | This setting controls who holds the encryption key for the data placed in this storage account. See Encryption for data at rest for more information. |
| Enable support for customer-managed keys | Radio button group |
|
No | All kind/SKU combinations for Azure Files support customer-managed keys regardless of this setting. |
| Enable infrastructure encryption | Checkbox | Checked/unchecked | Yes | Storage accounts can optionally use a secondary layer of encryption for data stored in the system to guard against one of the keys being compromised. See Enable infrastructure encryption. |
Tags
Tags are name/value pairs that enable you to categorize resources and view consolidated billing by applying the same tag to multiple resources and resource groups. These are optional and can be applied after storage account creation.
Review + create
The final step to create the storage account is to select the Create button on the Review + create tab. This button isn't available until all the required fields for a storage account are completed.
Create a classic file share
After you create a storage account, you can create a classic file share. This process is different depending on whether you created a provisioned v2, provisioned v1, or pay-as-you-go storage account. Provisioned file shares require a FileStorage storage account kind, and pay-as-you-go file shares (HDD only) require a StorageV2 (general purpose v2) storage account kind.
Create a provisioned v2 classic file share
When you create a classic file share using the provisioned v2 billing model, you specify how much storage, IOPS, and throughput your file share needs. The amount of each quantity that you provision determines your total bill. We provide a recommendation for how many IOPS and how much throughput you need based on the amount of provisioned storage you specify. Depending on your requirements, you might find that you require more or less IOPS or throughput than our recommendations, and can optionally override these recommendations with your own values as desired. To learn more, see Understanding the provisioned v2 billing model.
Important
Before you create a provisioned v2 classic file share, make sure the storage account you intend to use is of the FileStorage storage account kind. To check the account kind, navigate to the storage account and look under Essentials. If you created your storage account using the Azure portal, you must have selected Provisioned v2 for File share billing.
Follow these instructions to create a provisioned v2 classic file share using the Azure portal.
Go to your storage account. From the service menu, under Data storage, select File shares.
In the file share listing, you should see any previously created file shares in this storage account or an empty table if no file shares exist. Select + File share to create a new file share.
Complete the field in the Basics tab of the new file share blade:
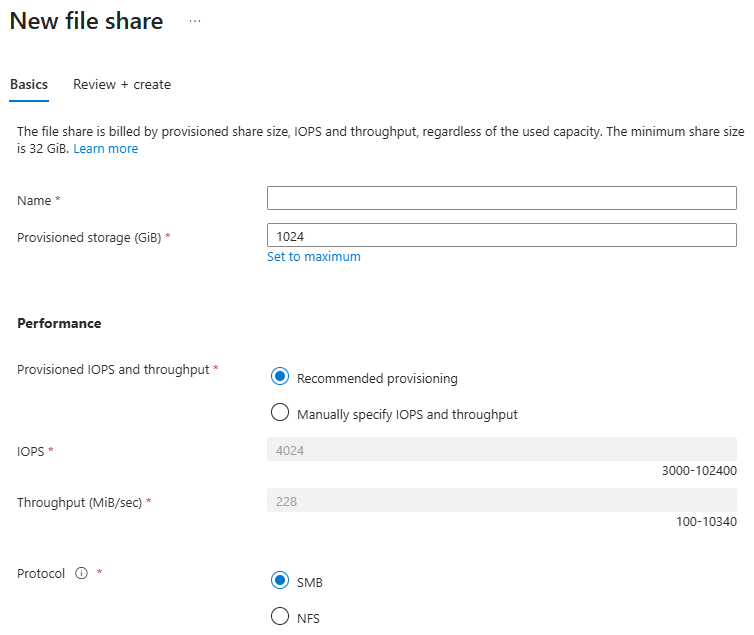
Name: The name of the file share to be created. The name of your file share must be all lower-case letters, numbers, and single hyphens, and must begin and end with a lower-case letter or number. The name can't contain two consecutive hyphens. For details about naming file shares and files, see Naming and referencing shares, directories, files, and metadata.
Provisioned storage (GiB): The amount of storage to provision on the share. The actual provisioned storage capacity is the amount that you're billed for regardless of actual usage.
Provisioned IOPS and throughput: A radio button group that lets you select between Recommended provisioning and Manually specify IOPS and throughput. The IOPS and throughput recommendations are based on typical customer usage for that amount of provisioned storage for that media tier, so if you don't know specifically what your IOPS and throughput requirements are, we recommend you stick with the recommendations and adjust later as needed.
IOPS: If you select Manually specify IOPS and throughput, this textbox enables you to enter the amount of IOPS you want to provision on this file share.
Throughput (MiB/sec): If you select Manually specify IOPS and throughput, this textbox enables you to enter the amount of throughput you want to provision on this file share.
Protocol: The file sharing protocol to use on the share. By default, new shares use the SMB protocol. Select the NFS protocol to create an NFSv4.1 share.
Select the Backup tab. By default, backup is enabled when you create a classic file share using the Azure portal. If you want to disable backup for the file share, uncheck the Enable backup checkbox. If you want backup enabled, you can either leave the defaults or create a new Recovery Services Vault in the same region and subscription as the storage account. To create a new backup policy, select Create a new policy.
Select Review + create and then Create to create the file share.
Create an SSD provisioned v1 classic file share
When you create a classic file share using the provisioned v1 billing model, which only supports SSD file shares, you specify how much storage your share needs. IOPS and throughput capacity are then computed for you based on how much storage you provisioned. Depending on your individual file share requirements, you might find that you require more IOPS or throughput than our recommendations. In this case, you need to provision more storage to get the required IOPS or throughput. To learn more, see Understanding the provisioned v1 billing model.
Important
Before you create a provisioned v1 classic file share, make sure the storage account you intend to use is of the FileStorage storage account kind. To check the account kind, navigate to the storage account and look under Essentials. If you created your storage account using the Azure portal, you must have selected Provisioned v1 for File share billing.
Follow these instructions to create an SSD provisioned v1 classic file share using the Azure portal.
Go to your storage account. From the service menu, under Data storage, select File shares.

In the file share listing, you should see any previously created file shares in this storage account or an empty table if no file shares exist. Select + File share to create a new file share.
Complete the fields in the Basics tab of new file share blade:
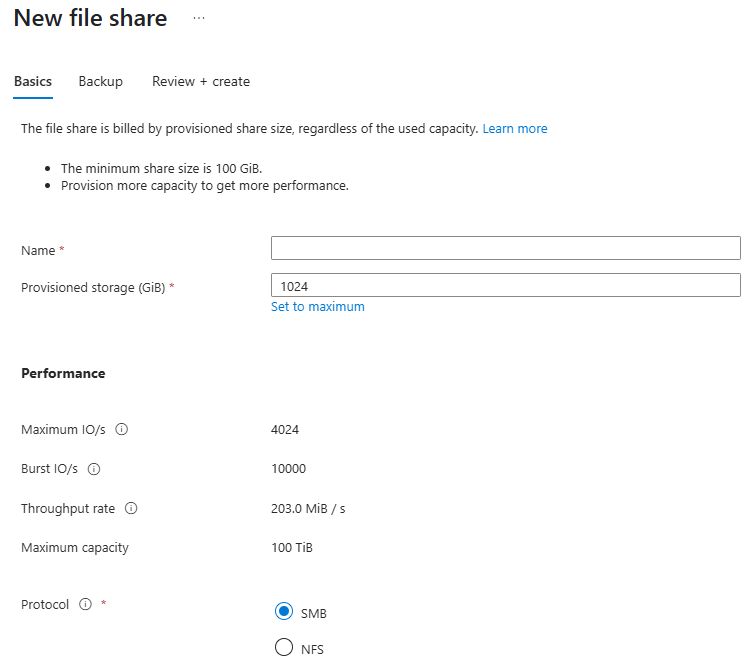
Name: The name of the file share to be created. The name of your file share must be all lower-case letters, numbers, and single hyphens, and must begin and end with a lower-case letter or number. The name can't contain two consecutive hyphens. For details about naming file shares and files, see Naming and referencing shares, directories, files, and metadata.
Provisioned storage (GiB): The amount of storage to provision on the share. The provisioned storage capacity is the amount that you're billed for regardless of actual usage.
Protocol: The file sharing protocol to use on the share. By default, new shares use the SMB protocol. Select the NFS protocol to create an NFSv4.1 share.
Select Review + create and then Create to create the Azure file share.
Create an HDD pay-as-you-go classic file share
Pay-as-you-go file shares (SMB only) have a property called access tier. All three access tiers are stored on the exact same HDD storage hardware. The main difference for these three access tiers is their data at-rest storage prices, which are lower in cooler tiers, and the transaction prices, which are higher in the cooler tiers. To learn more about the differences between tiers, see differences in access tiers.
Important
Before you create a pay-as-you-go classic file share, make sure the storage account you intend to use is of the StorageV2 (general purpose v2) storage account kind. To check the account kind, navigate to the storage account and look under Essentials. If you created your storage account using the Azure portal, you must have selected Pay-as-you-go file shares for File share billing.
Follow these instructions to create a new HDD pay-as-you-go classic file share using the Azure portal.
Go to your storage account. From the service menu, under Data storage, select File shares.
In the file share listing, you should see any previously created file shares in this storage account or an empty table if no file shares exist. Select + File share to create a new file share.
Complete the fields in the Basics tab of new file share blade:
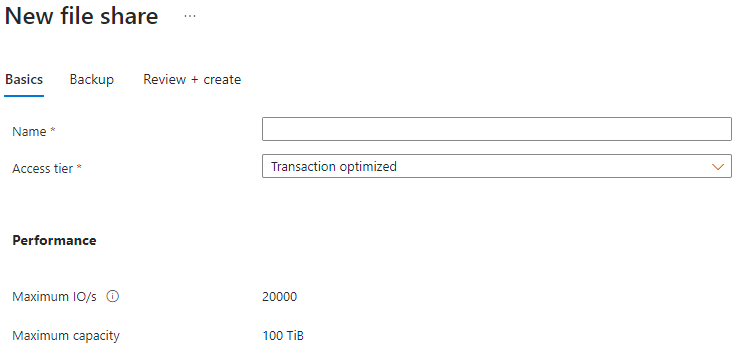
Name: The name of the file share to be created. The name of your file share must be all lower-case letters, numbers, and single hyphens, and must begin and end with a lower-case letter or number. The name can't contain two consecutive hyphens. For details about naming file shares and files, see Naming and referencing shares, directories, files, and metadata.
Access tier: The selected access tier for a pay-as-you-go file share. We recommend picking the transaction optimized access tier during a migration to minimize transaction expenses, and then switching to a lower tier if desired after the migration is complete.
Select Review + create and then Create to create the Azure file share.
Set up networking
If you're using an SMB file share, networking configuration isn't required. However, we still recommend you take it into consideration. If you're using an NFS file share, networking configuration is required.
Important
The NFSv4.1 protocol runs on port 2049. If you're connecting from an on-premises network, make sure that your client allows outgoing communication through port 2049. If you grant access to specific virtual networks, make sure that any network security groups associated with those virtual networks don't contain security rules that block incoming communication through port 2049.
Set up a private endpoint or service endpoint
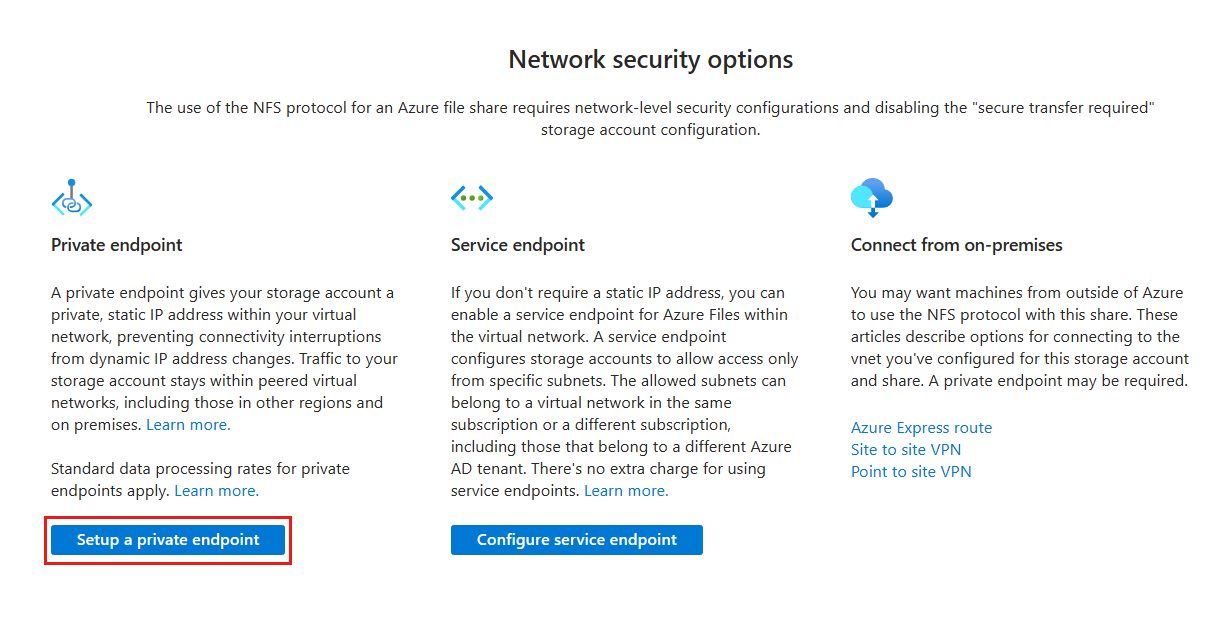
NFS file shares require network-level security configurations. Currently there are two options for establishing networking-level security configurations: Private endpoint and service endpoint. Private endpoint gives your file share a private, static IP address within your virtual network, preventing connectivity interruptions from dynamic IP address changes. Traffic to your file share stays within peered virtual networks, including those in other regions and on premises. Standard data processing rates for private endpoints apply. See What is a private endpoint to learn more.
If you don't require a static IP address, you can enable a service endpoint for Azure Files within the virtual network. A service endpoint configures file share to allow access only from specific subnets. The allowed subnets can belong to a virtual network in the same subscription or a different subscription, including those that belong to a different Microsoft Entra tenant. There's no extra charge for using service endpoints. See Azure virtual network service endpoints to learn more.
Steps 1 to 3 show an NFS file share scenario. You can also modify the networking settings at the storage account level for SMB file shares. Go to the storage account, choose Security + networking, and configure the required endpoints.
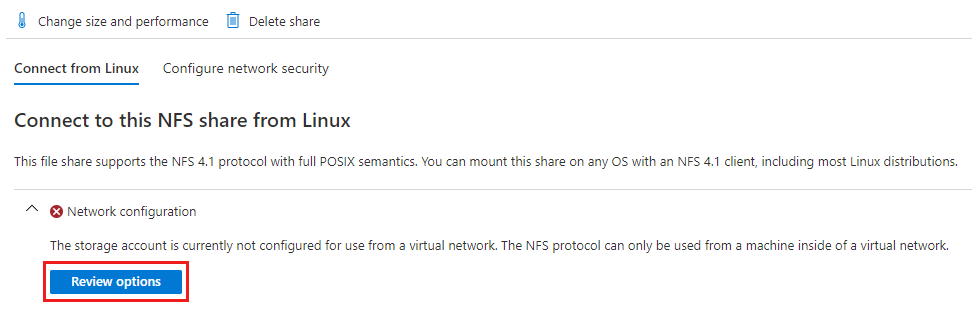
Select the NFS file share you created. You should see a dialog that says Connect to this NFS share from Linux. Under Network configuration, select Review options
Next, select Setup a private endpoint.
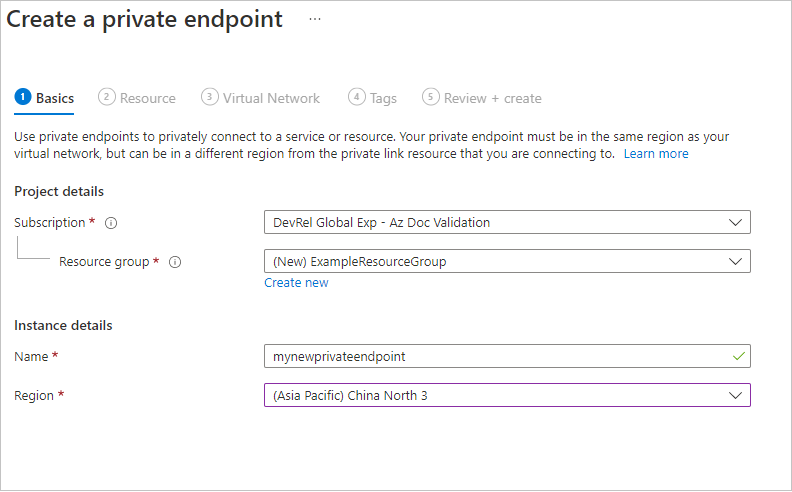
Select + Private endpoint.
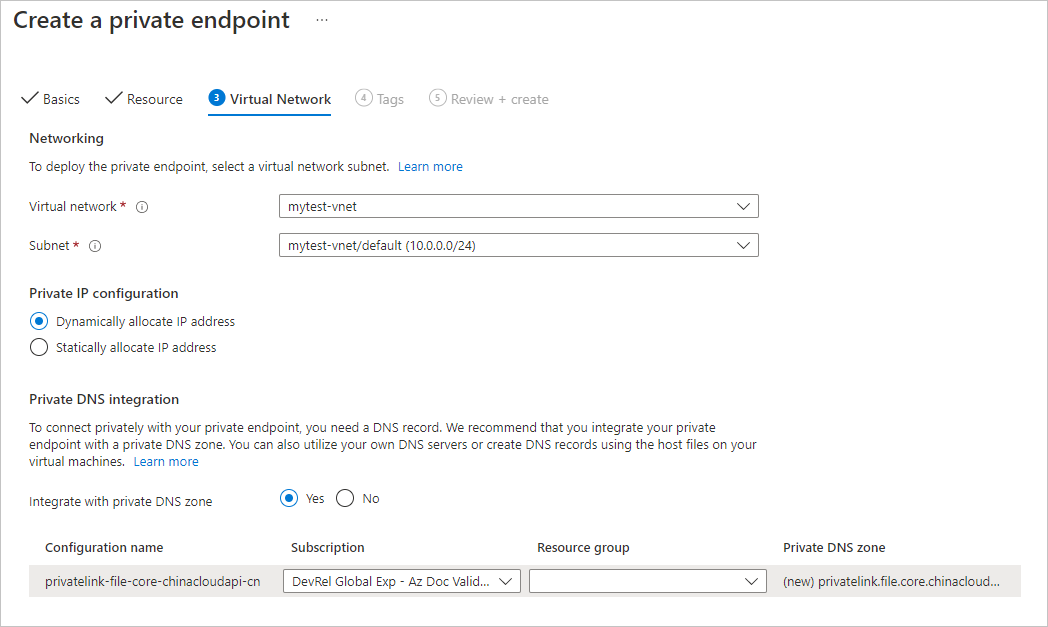
Leave Subscription and Resource group the same. Under Instance, provide a name and select a region for the new private endpoint. Your private endpoint must be in the same region as your virtual network, so use the same region as you specified when creating the VM. When all the fields are complete, select Next: Resource.
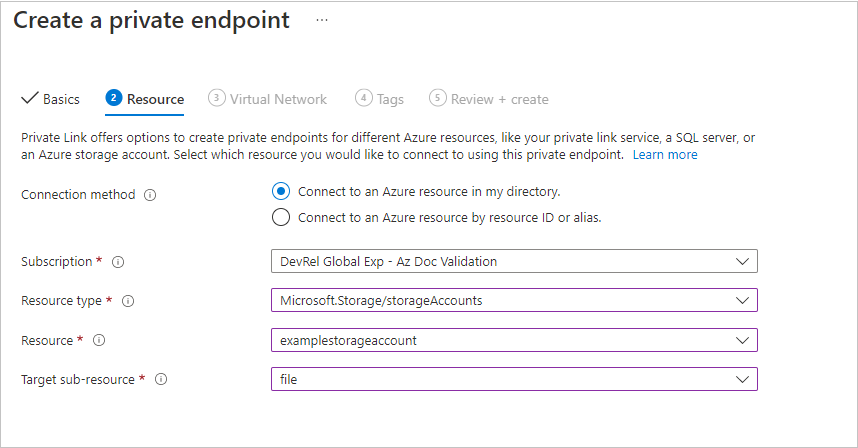
Confirm that the Subscription, Resource type and Resource are correct, and select File from the Target sub-resource drop-down. Then select Next: Virtual Network.
Under Networking, select the virtual network associated with your VM and leave the default subnet. Under Private IP configuration, leave Dynamically allocate IP address selected. Select Yes for Integrate with private DNS zone. Make sure the correct subscription and resource group are selected, and then select Next: Tags.
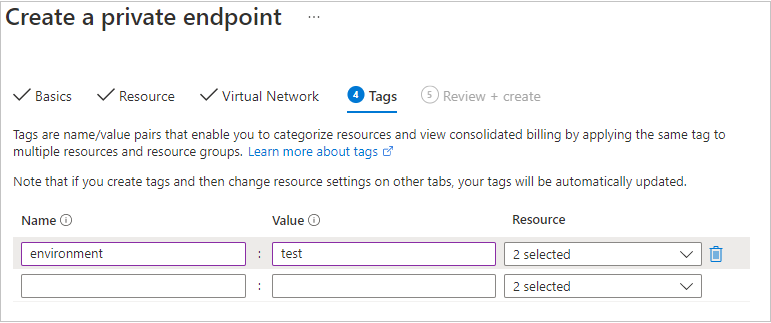
You can optionally apply tags to categorize your resources, such as applying the name Environment and the value Test to all testing resources. Enter name/value pairs if desired, and then select Next: Review + create.
Azure will attempt to validate the private endpoint. When validation is complete, select Create. You'll see a notification that deployment is in progress. After a few minutes, you should see a notification that deployment is complete.
Enable hybrid access through VPN or ExpressRoute (optional)
To enable hybrid access to an NFS Azure file share, use one of the following networking solutions: