Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to: ✔️ Linux VMs ✔️ Windows VMs ✔️ Flexible scale sets ✔️ Uniform scale sets.
Trusted Launch is a way to improve the security of Generation 2 virtual machines (VMs). Trusted Launch protects against advanced and persistent attack techniques by combining infrastructure technologies like virtual Trusted Platform Module (vTPM) and secure boot.
Trusted Launch is supported on both x64 and Arm64 Generation 2 VMs where available, including Arm64 marketplace images.
Prerequisites
We recommend that you onboard your subscription to Microsoft Defender for Cloud if it isn't already. Defender for Cloud has a free tier, which offers useful insights for various Azure and hybrid resources. With the absence of Defender for Cloud, Trusted Launch VM users can't monitor boot integrity of VM.
If you have existing Generation 1 VMs, you can upgrade them to Generation 2 with Trusted launch. See Upgrade existing Gen1 VMs to Gen2-Trusted launch.
Assign Azure policy initiatives to your subscription. These policy initiatives need to be assigned only once per subscription. Policies will help deploy and audit for Trusted Launch VMs while automatically installing all required extensions on all supported VMs.
- Configure the Trusted Launch VMs' built-in policy initiative.
- Configure prerequisites to enable Guest Attestation on Trusted Launch-enabled VMs.
- Configure machines to automatically install the Azure Monitor and Azure Security agents on VMs.
Allow the service tag
AzureAttestationin network security group outbound rules to allow traffic for Azure Attestation. For more information, see Virtual network service tags.Make sure that the firewall policies allow access to
*.attest.chinacloudapi.cn.
Note
If you're using a Linux image and anticipate that the VM might have kernel drivers either unsigned or not signed by the Linux distro vendor, you might want to consider turning off secure boot. In the Azure portal, on the Create a virtual machine page for the Security type parameter with Trusted Launch Virtual Machines selected, select Configure security features and clear the Enable secure boot checkbox. In the Azure CLI, PowerShell, or SDK, set the secure boot parameter to false.
Deploy a Trusted Launch VM
Choose one of the deployment methods to create a new Trusted launch VM
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Search for Virtual Machines.
Under Services, select Virtual machines.
On the Virtual machines page, select Add, and then select Virtual machine.
Under Project details, make sure the correct subscription is selected.
Under Resource group, select Create new. Enter a name for your resource group or select an existing resource group from the dropdown list.
Under Instance details, enter a name for the VM name and choose a region that supports Trusted Launch.
For Security type, select Trusted launch virtual machines. When the options Secure boot, vTPM, and Integrity Monitoring appear, select the appropriate options for your deployment. For more information, see Trusted Launch-enabled security features.
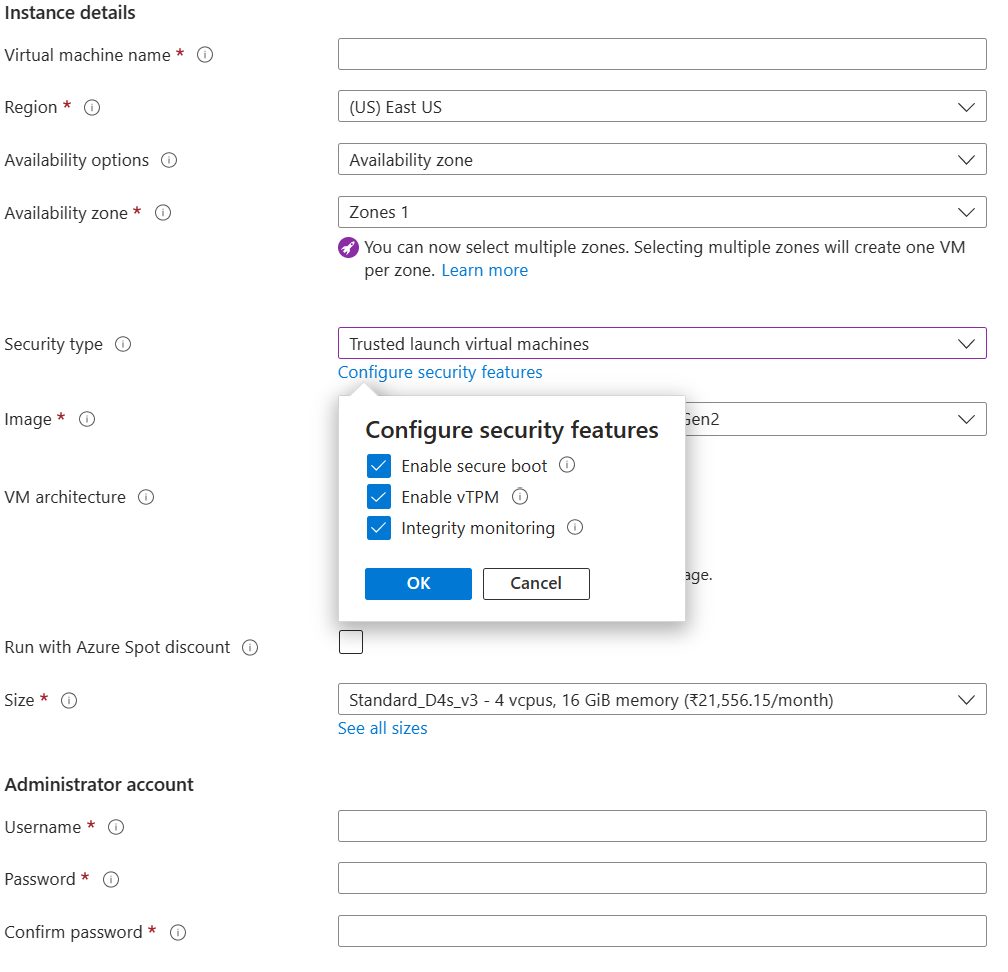
Under Image, select an image from Recommended Gen 2 images compatible with Trusted launch. Arm64 Gen2 images that support Trusted Launch are available in the Azure Marketplace. For a list, see Trusted Launch.
Tip
If you don't see the Gen2 version of the image that you want in the dropdown list, select See all images. Then change the Security type filter to Trusted Launch.
Select a VM size that supports Trusted Launch. For more information, see the list of supported sizes.
Fill in the Administrator account information and then Inbound port rules.
At the bottom of the page, select Review + Create.
On the Create a virtual machine page, you can see the information about the VM you're about to deploy. After validation shows as passed, select Create.
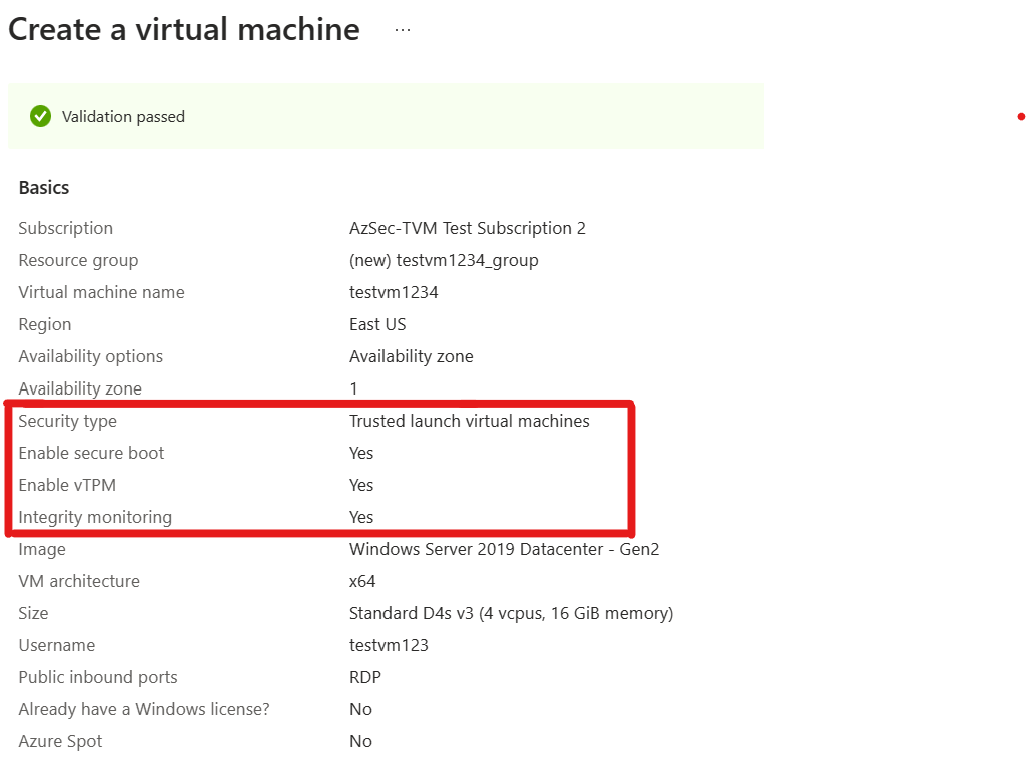
It takes a few minutes for your VM to be deployed.
Deploy a Trusted Launch VM from an Azure Compute Gallery image
Azure Trusted Launch VMs support the creation and sharing of custom images by using Azure Compute Gallery. There are two types of images that you can create, based on the security types of the image:
- Recommended: Trusted Launch VM supported (
TrustedLaunchSupported) images are images where the source doesn't have VM Guest state information and can be used to create either Generation 2 VMs or Trusted Launch VMs. - Trusted Launch VM (
TrustedLaunch) images are images where the source usually has VM Guest State information and can be used to create only Trusted Launch VMs.
Arm64 Gen2 images are supported. Ensure the image architecture matches the intended Arm64 VM size when creating Trusted Launch VMs.
Trusted Launch VM supported images
For the following image sources, the security type on the image definition should be set to TrustedLaunchsupported:
- Gen2 operating system (OS) disk VHD
- Gen2 Managed Image
- Gen2 Gallery Image version
No VM Guest State information can be included in the image source.
You can use the resulting image version to create either Azure Gen2 VMs or Trusted Launch VMs.
Note
The OS disk VHD, Managed Image, or Gallery Image version should be created from a Gen2 image that's compatible with Trusted Launch VMs.
- Sign in to the Azure portal.
- Search for and select VM image versions in the search bar.
- On the VM image versions page, select Create.
- On the Create VM image version page, on the Basics tab:
- Select the Azure subscription.
- Select an existing resource group or create a new resource group.
- Select the Azure region.
- Enter an image version number.
- For Source, select either Storage Blobs (VHD) or Managed Image or another VM Image Version.
- If you selected Storage Blobs (VHD), enter an OS disk VHD (without the VM Guest state). Make sure to use a Gen2 VHD.
- If you selected Managed Image, select an existing managed image of a Gen2 VM.
- If you selected VM Image Version, select an existing Gallery Image version of a Gen2 VM.
- For Target Azure compute gallery, select or create a gallery to share the image.
- For Operating system state, select either Generalized or Specialized depending on your use case. If you're using a managed image as the source, always select Generalized. If you're using a storage blob (VHD) and want to select Generalized, follow the steps to generalize a Linux VHD or generalize a Windows VHD before you continue. If you're using an existing VM image version, select either Generalized or Specialized based on what's used in the source VM image definition.
- For Target VM Image Definition, select Create new.
- On the Create a VM image definition pane, enter a name for the definition. Make sure the security type is set to Trustedlaunch Supported. Enter the publisher, offer, and SKU information. Then select OK.
- On the Replication tab, enter the replica count and target regions for image replication, if necessary.
- On the Encryption tab, enter SSE encryption-related information, if necessary.
- Select Review + Create.
- After the configuration is successfully validated, select Create to finish creating the image.
- After the image version is created, select Create VM.
- On the Create a virtual machine page, under Resource group, select Create new. Enter a name for your resource group or select an existing resource group from the dropdown list.
- Under Instance details, enter a name for the VM name and choose a region that supports Trusted Launch.
- For Security type, select Trusted launch virtual machines. The Secure Boot and vTPM checkboxes are enabled by default.
- Fill in the Administrator account information and then Inbound port rules.
- On the validation page, review the details of the VM.
- After the validation succeeds, select Create to finish creating the VM.
Trusted Launch VM images
The security type on the image definition should be set to TrustedLaunchfor the following image sources:
- Trusted Launch VM capture
- Managed OS disk
- Managed OS disk snapshot
You can use the resulting image version to create Azure Trusted Launch VMs only.
- Sign in to the Azure portal.
- To create an Azure Compute Gallery Image from a VM, open an existing Trusted Launch VM and select Capture.
- On the Create an Image page, allow the image to be shared to the gallery as a VM image version. Creation of managed images isn't supported for Trusted Launch VMs.
- Create a new target Azure Compute Gallery or select an existing gallery.
- Select the Operating system state as either Generalized or Specialized. If you want to create a generalized image, ensure that you generalize the VM to remove machine-specific information before you select this option. If Bitlocker-based encryption is enabled on your Trusted Launch Windows VM, you might not be able to generalize the same.
- Create a new image definition by providing a name, publisher, offer, and SKU details. Security type for the image definition should already be set to Trusted launch.
- Provide a version number for the image version.
- Modify replication options, if necessary.
- At the bottom of the Create an Image page, select Review + Create. After validation shows as passed, select Create.
- After the image version is created, go to the image version directly. Alternatively, you can go to the required image version through the image definition.
- On the VM image version page, select + Create VM to go to the Create a virtual machine page.
- On the Create a virtual machine page, under Resource group, select Create new. Enter a name for your resource group or select an existing resource group from the dropdown list.
- Under Instance details, enter a name for the VM name and choose a region that supports Trusted Launch.
- The image and the security type are already populated based on the selected image version. The Secure Boot and vTPM checkboxes are enabled by default.
- Fill in the Administrator account information and then Inbound port rules.
- At the bottom of the page, select Review + Create.
- On the validation page, review the details of the VM.
- After the validation succeeds, select Create to finish creating the VM.
If you want to use either a managed disk or a managed disk snapshot as a source of the image version (instead of a Trusted Launch VM), follow these steps.
- Sign in to the Azure portal.
- Search for VM Image Versions and select Create.
- Provide the subscription, resource group, region, and image version number.
- Select the source as Disks and/or Snapshots.
- Select the OS disk as a managed disk or a managed disk snapshot from the dropdown list.
- Select a Target Azure Compute Gallery to create and share the image. If no gallery exists, create a new gallery.
- Select the Operating system state as either Generalized or Specialized. If you want to create a generalized image, ensure that you generalize the disk or snapshot to remove machine-specific information.
- For the Target VM Image Definition select Create new. In the window that opens, select an image definition name and ensure that Security type is set to Trusted launch. Provide the publisher, offer, and SKU information and select OK.
- The Replication tab can be used to set the replica count and target regions for image replication, if required.
- The Encryption tab can also be used to provide SSE encryption-related information, if required.
- Select Create on the Review + create tab to create the image.
- After the image version is successfully created, select + Create VM to go to the Create a virtual machine page.
- Follow steps 12 to 18 as mentioned earlier to create a Trusted Launch VM by using this image version.
Trusted Launch built-in policies
To help users adopt Trusted Launch, Azure policies are available to help resource owners adopt Trusted Launch. The main objective is to help upgrade Generation 1 and 2 VMs that are Trusted launch capable.
The Virtual machine should have Trusted launch enabled single policy checks if the VM is currently enabled with Trusted Launch security configurations. The Disks and OS supported for Trusted launch policy checks if previously created VMs have the capable Generation 2 OS and VM size to deploy a Trusted Launch VM.
These two policies come together to make the Trusted Launch policy initiative. This initiative enables you to group several related policy definitions to simplify assignments and management resources to include Trusted Launch configuration.
To learn more and start deploying, see Trusted Launch built-in policies.
Verify or update your settings
For VMs created with Trusted Launch enabled, you can view the Trusted Launch configuration by going to the Overview page for the VM in the Azure portal. The Properties tab shows the status of Trusted Launch features.

To change the Trusted Launch configuration, on the left menu, under Settings, select Configuration. In the Security type section, you can enable or disable Secure Boot, vTPM, and Integrity monitoring. Select Save at the top of the page when you're finished.
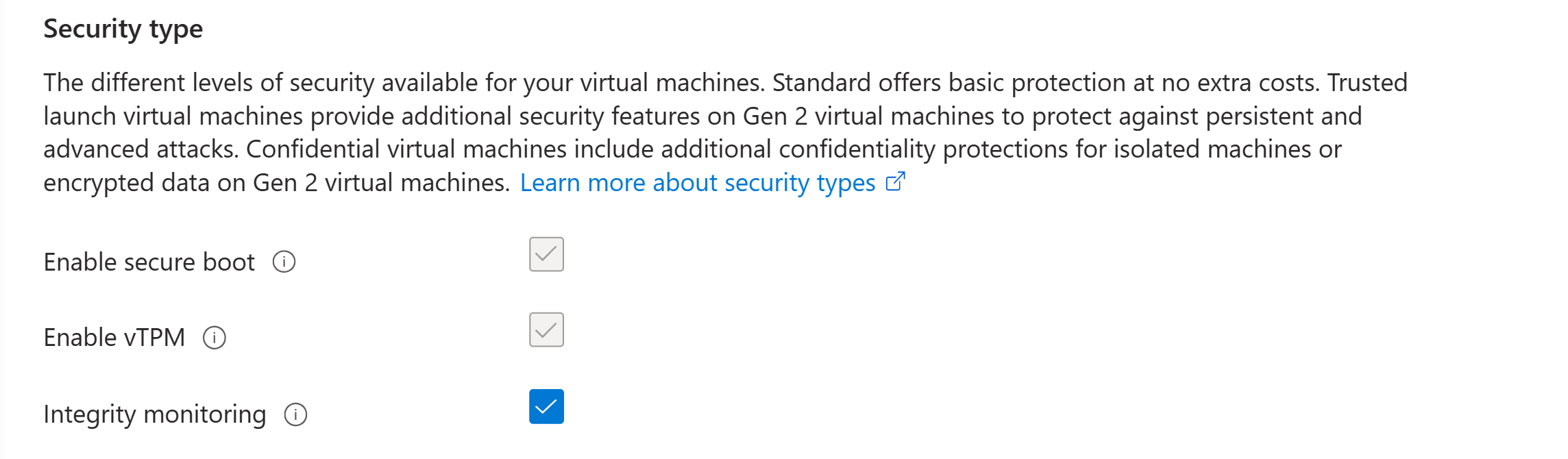
If the VM is running, you receive a message that the VM will restart. Select Yes and then wait for the VM to restart for changes to take effect.
Related content
- Learn more about Trusted Launch and boot integrity monitoring VMs.
- If you have existing VMs or VM scale sets, you can upgrade them to Gen2-Trusted launch. For more information, see Upgrade existing Gen1 VMs to Gen2-Trusted launch, Upgrade existing Gen2 VMs to Gen2-Trusted launch, Upgrade existing Gen1 or Gen2 VM scale sets to Gen2-Trusted launch
