本文包含用于配置 Lakeflow 作业计算的建议和资源。
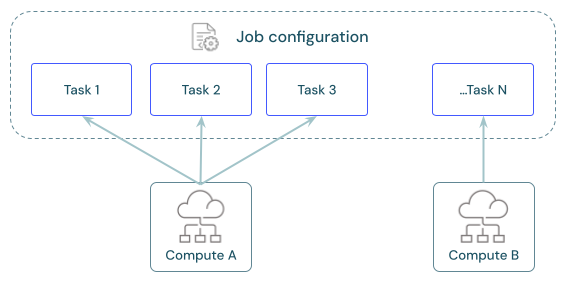
每个作业可以有一个或多个任务。 需要定义每个任务的计算资源。 为同一作业定义的多个任务可以使用同一计算资源。
什么是对每个任务的建议的计算?
下表列车了对于每个任务类型建议和支持的计算类型。
注释
作业的无服务器计算具有限制,不支持所有工作负载。 请参阅无服务器计算限制。
| 任务 | 建议的计算 | 支持的计算 |
|---|---|---|
| Notebooks | 无服务器作业 | 无服务器作业、经典作业、经典通用作业 |
| Python 脚本 | 无服务器作业 | 无服务器作业、经典作业、经典通用作业 |
| Python轮子 | 无服务器作业 | 无服务器作业、经典作业、经典通用作业 |
| SQL | 无服务器 SQL 仓库 | 无服务器 SQL 仓库、Pro SQL 仓库 |
| Lakeflow Spark 声明性管道 | 无服务器管道 | 无服务器管道、经典管道 |
| dbt | 无服务器 SQL 仓库 | 无服务器 SQL 仓库、Pro SQL 仓库 |
| dbt CLI 命令 | 无服务器作业 | 无服务器作业、经典作业、经典通用作业 |
| JAR | 经典作业 | 经典作业,经典通用 |
| Spark 提交 | 经典作业 | 经典作业 |
Lakeflow 作业的定价与运行任务所用的计算资源挂钩。 有关详细信息,请参阅 Databricks 定价。
如何为作业配置计算?
经典作业计算直接从 Lakeflow 作业 UI 进行配置,这些配置是作业定义的一部分。 所有其他可用的计算类型会将配置与其他工作区资产一起存储。 下表提供了更多详细信息:
| 计算类型 | 详细信息 |
|---|---|
| 经典作业计算 | 可以使用适用于通用计算的相同用户界面和设置来配置经典作业的计算。 请参阅计算配置参考。 |
| 作业的无服务器计算 | 对于支持无服务器计算的所有任务,作业的无服务器计算是默认选择。 Databricks 负责管理无服务器计算的计算设置。 请参阅 使用适用于工作流的无服务器计算运行 Lakeflow 作业。 |
| SQL 仓库 | 无服务器和 Pro SQL 仓库可由工作区管理员或具有不受限制群集创建权限的用户配置。 可将任务配置为针对现有 SQL 仓库运行。 请参阅连接到 SQL 仓库。 |
| Lakeflow Spark 声明式流水线计算 | 您在管道配置过程中配置 Lakeflow Spark 声明性管道的计算设置。 请参阅 管道的经典计算配置。 Azure Databricks 管理无服务器 Lakeflow Spark 声明性管道的计算资源。 请参阅 配置无服务器管道。 |
| 通用计算 | 可以选择使用经典通用计算来配置任务。 Databricks 不建议将此配置用于生产作业。 请参阅计算配置参考和是否应将通用计算用于作业? |
跨任务共享计算
将任务配置为使用相同的作业计算资源来优化协调多个任务的作业的资源使用情况。 跨任务共享计算可以减少与启动时间有关的延迟。
可以使用单个作业计算资源来运行属于该作业的所有任务,也可使用针对特定工作负载优化的多个作业资源。 配置为作业一部分的任何作业计算都可用于作业中的所有其他任务。
下表重点介绍了为单个任务配置的作业计算与在任务之间共享的作业计算之间的区别:
| 单个任务 | 跨任务共享 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动 | 任务运行开始时。 | 第一个配置为使用计算资源的任务运行开始时。 |
| 终止 | 任务运行后。 | 在配置为使用计算资源的最终任务运行之后。 |
| 闲置计算资源 | 不适用。 | 当任务不使用计算资源运行时,计算将保持打开但空闲的状态。 |
共享作业集群仅限于单个作业运行,不能被其他作业或同一作业的其他运行使用。
不能在共享作业群集配置中声明库。 必须在任务设置中添加依赖库。
查看、配置和交换作业计算
“作业详细信息”面板中的“计算”部分会列出为当前作业中的任务配置的所有计算。
将鼠标悬停在计算规范上时,将在任务图中突出显示配置为使用计算资源的任务。
通过使用交换按钮,可以更改与计算资源相关的所有任务的计算。
经典作业计算资源具有“配置”选项。 其他计算资源提供了查看和修改计算配置详细信息的选项。
详细信息
有关配置 Azure Databricks 经典作业的其他详细信息,请参阅 有关配置经典 Lakeflow 作业的最佳做法。