Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO: Developer | Premium
You can deploy Azure API Management inside an Azure virtual network to access backend services within the network. For virtual network connectivity options, requirements, and considerations, see:
- Using a virtual network with Azure API Management
- Network resource requirements for API Management injection into a virtual network
This article explains how to set up virtual network connectivity for your API Management Developer tier or Premium tier instance in the external mode. In this mode, the developer portal, API gateway, and other API Management endpoints are accessible from the public internet, and backend services can be located in the network.
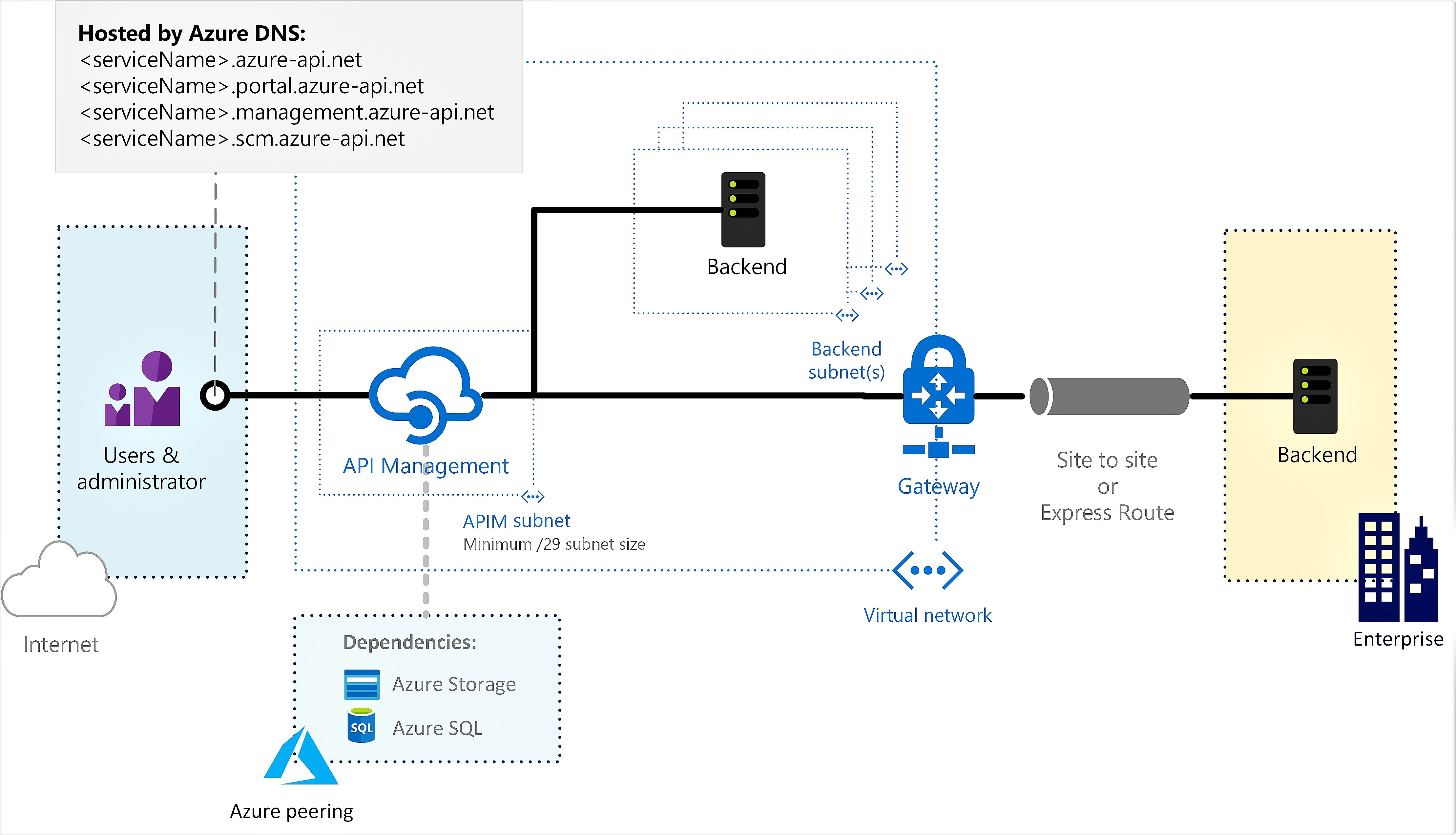
For configurations specific to the internal mode, where the endpoints are accessible only within the virtual network, see Deploy your Azure API Management instance to a virtual network - internal mode.
Note
We recommend that you use the Azure Az PowerShell module to interact with Azure. See Install Azure PowerShell to get started. To learn how to migrate to the Az PowerShell module, see Migrate Azure PowerShell from AzureRM to Az.
Important
Changes to your API Management service's infrastructure (such as configuring custom domains, adding CA certificates, scaling, virtual network configuration, availability zone changes, and region additions) can take 15 minutes or longer to complete, depending on the service tier and the size of the deployment. Expect longer times for an instance with a greater number of scale units or multi-region configuration. Rolling changes to API Management are executed carefully to preserve capacity and availability.
While the service is updating, other service infrastructure changes can't be made. However, you can configure APIs, products, policies, and user settings. The service will not experience gateway downtime, and API Management will continue to service API requests without interruption (except in the Developer tier).
Prerequisites
Review the network resource requirements for API Management injection into a virtual network before you begin.
- An API Management instance. For more information, see Create an Azure API Management instance.
A virtual network and subnet in the same region and subscription as your API Management instance.
- The subnet used to connect to the API Management instance may contain other Azure resource types.
- The subnet shouldn't have any delegations enabled. The Delegate subnet to a service setting for the subnet should be set to None.
A network security group attached to the subnet above. A network security group (NSG) is required to explicitly allow inbound connectivity, because the load balancer used internally by API Management is secure by default and rejects all inbound traffic. For specific configuration, see Configure NSG rules, later in this article.
For certain scenarios, enable service endpoints in the subnet to dependent services such as Azure Storage or Azure SQL. For more information, see Force tunnel traffic to on-premises firewall using ExpressRoute or network virtual appliance, later in this article.
(Optional) A Standard SKU public IPv4 address.
Important
- Starting May 2024, a public IP address resource is no longer needed when deploying (injecting) an API Management instance in a VNet in internal mode or migrating the internal VNet configuration to a new subnet. In external VNet mode, specifying a public IP address is optional; if you don't provide one, an Azure-managed public IP address is automatically configured and used for runtime API traffic. Only provide the public IP address if you want to own and control the public IP address used for inbound or outbound communication to the internet.
If provided, the IP address must be in the same region and subscription as the API Management instance and the virtual network.
When creating a public IP address resource, ensure you assign a DNS name label to it. In general, you should use the same DNS name as your API Management instance. If you change it, redeploy your instance so that the new DNS label is applied.
For best network performance, it's recommended to use the default Routing preference: Microsoft network.
The value of the IP address is assigned as the virtual public IPv4 address of the API Management instance in that region.
For multi-region API Management deployments, configure virtual network resources separately for each location.
Enable virtual network connection
Enable virtual network connectivity by using the Azure portal
Go to the Azure portal to find your API management instance. Search for and select API Management services.
Select your API Management instance.
In the sidebar menu, under Deployment + infrastructure, select Network.
Select the External access type.
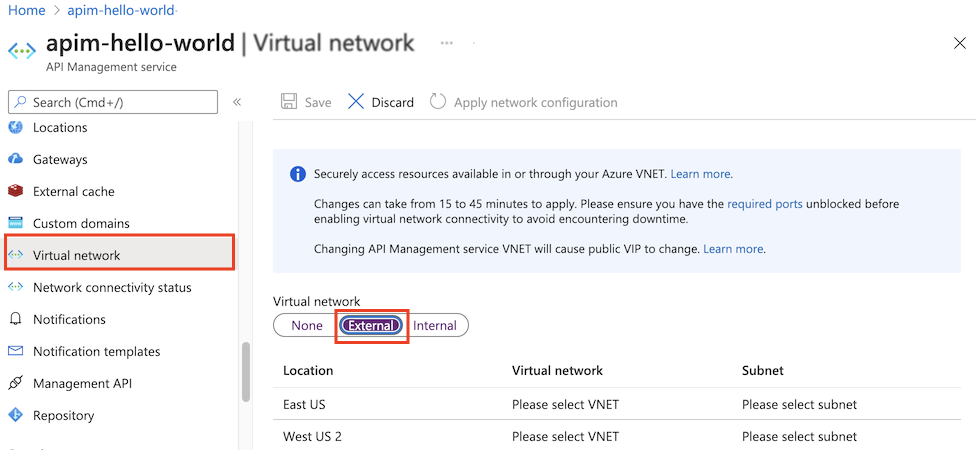
In the list of locations (regions) where your API Management service is provisioned:
- Choose a Location.
- Select Virtual network, Subnet, and (optionally) Public IP address.
The virtual network list is populated with virtual networks available in your Azure subscriptions, set up in the region you're configuring.
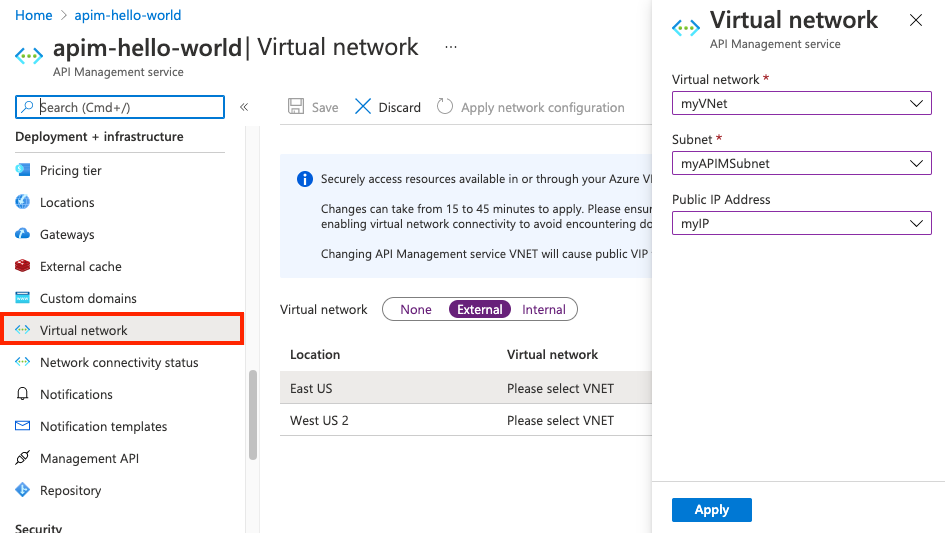
Select Apply. The Network page of your API Management instance is updated with your new virtual network and subnet choices.
Select Verify to confirm that the prerequisites are met and the API Management service can successfully update.
Continue configuring virtual network settings for the remaining locations of your API Management instance.
In the top navigation bar, select Save.
Enable connectivity by using a Resource Manager template
Azure Resource Manager template (API version 2021-08-01)
Configure NSG rules
Configure custom network security rules in the API Management subnet to filter traffic to and from your API Management instance. We recommend the following minimum NSG rules to ensure proper operation and access to your instance. Review your environment carefully to determine more rules that might be needed.
Important
Depending on your use of caching and other features, you may need to configure additional NSG rules beyond the minimum rules in the following table. For detailed settings, see Virtual network configuration reference.
- For most scenarios, use the indicated service tags instead of service IP addresses to specify network sources and destinations.
- Set the priority of these rules higher than that of the default rules.
| Direction | Source service tag | Source port ranges | Destination service tag | Destination port ranges | Protocol | Action | Purpose | VNet type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inbound | Internet | * | VirtualNetwork | [80], 443 | TCP | Allow | Client communication to API Management | External only |
| Inbound | ApiManagement | * | VirtualNetwork | 3443 | TCP | Allow | Management endpoint for Azure portal and PowerShell | External & Internal |
| Inbound | AzureLoadBalancer | * | VirtualNetwork | 6390 | TCP | Allow | Azure Infrastructure Load Balancer | External & Internal |
| Inbound | AzureTrafficManager | * | VirtualNetwork | 443 | TCP | Allow | Azure Traffic Manager routing for multi-region deployment | External only |
| Outbound | VirtualNetwork | * | Internet | 80 | TCP | Allow | Validation and management of Microsoft-managed and customer-managed certificates | External & Internal |
| Outbound | VirtualNetwork | * | Storage | 443 | TCP | Allow | Dependency on Azure Storage for core service functionality | External & Internal |
| Outbound | VirtualNetwork | * | SQL | 1433 | TCP | Allow | Access to Azure SQL endpoints for core service functionality | External & Internal |
| Outbound | VirtualNetwork | * | AzureKeyVault | 443 | TCP | Allow | Access to Azure Key Vault for core service functionality | External & Internal |
| Outbound | VirtualNetwork | * | AzureMonitor | 1886, 443 | TCP | Allow | Publish Diagnostics Logs and Metrics, Resource Health, and Application Insights | External & Internal |
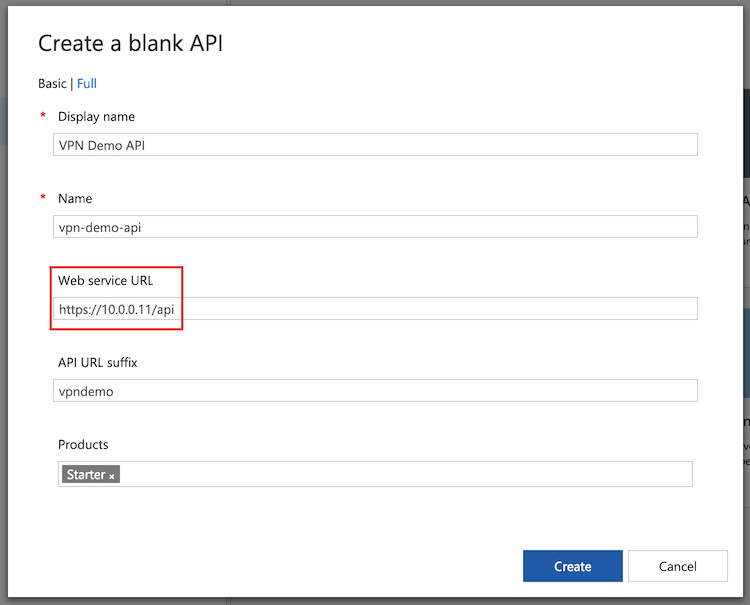
Connect to a web service hosted within a virtual network
After you connect your API Management service to the virtual network, you can access backend services within the virtual network just as you do public services. When creating or editing an API, type the local IP address or the host name (if a DNS server is configured for the virtual network) of your web service into the Web service URL field.
Custom DNS server setup
In external virtual network mode, Azure manages the DNS by default. You can optionally configure a custom DNS server.
The API Management service depends on several Azure services. When API Management is hosted in a virtual network with a custom DNS server, it needs to resolve the hostnames of those Azure services.
- For guidance on custom DNS setup, including forwarding for Azure-provided hostnames, see Name resolution for resources in Azure virtual networks.
- Outbound network access on port
53is required for communication with DNS servers. For more settings, see Virtual network configuration reference.
Important
If you plan to use custom DNS servers for the virtual network, set them up before deploying an API Management service into the virtual network. Otherwise, you need to update the API Management service each time you change the DNS servers by running the Apply Network Configuration Operation. You can also apply a network configuration on the Network/Network status blade in the Azure portal.
Routing
- A load-balanced public IP address (VIP) is reserved to provide access to the API Management endpoints and resources outside the virtual network.
- You can find the public VIP on the Overview/Essentials blade in the Azure portal.
For more information and considerations, see IP addresses of Azure API Management.
VIP and DIP addresses
Dynamic IP (DIP) addresses will be assigned to each underlying virtual machine in the service and used to access endpoints and resources in the VNet and in peered VNets. The API Management service's public virtual IP (VIP) address will be used to access public-facing resources.
If IP restriction lists secure resources within the VNet or peered VNets, we recommend specifying the entire subnet range where the API Management service is deployed to grant or restrict access from the service.
Learn more about the recommended subnet size.
Force tunnel traffic to on-premises firewall using ExpressRoute or network virtual appliance
Forced tunneling lets you redirect or "force" all internet-bound traffic from your subnet back to on-premises for inspection and auditing. Commonly, you configure and define your own default route (0.0.0.0/0), forcing all traffic from the API Management subnet to flow through an on-premises firewall or to a network virtual appliance. This traffic flow breaks connectivity with API Management, since outbound traffic is either blocked on-premises, or NAT'd to an unrecognizable set of addresses that no longer work with various Azure endpoints. You can solve this issue via the following methods:
Enable service endpoints on the subnet in which the API Management service is deployed for:
- Azure SQL (required only in the primary region if the API Management service is deployed to multiple regions)
- Azure Storage
- Azure Event Hubs
- Azure Key Vault
By enabling endpoints directly from the API Management subnet to these services, you can use the Azure backbone network, providing optimal routing for service traffic. If you use service endpoints with a force tunneled API Management, traffic for the preceding Azure services isn't force tunneled. However, the other API Management service dependency traffic remains force tunneled. Ensure that your firewall or virtual appliance doesn't block this traffic, or the API Management service may not function properly.
Note
We strongly recommend enabling service endpoints directly from the API Management subnet to dependent services such as Azure SQL and Azure Storage that support them. However, some organizations may have requirements to force tunnel all traffic from the API Management subnet. In this case, ensure that you configure your firewall or virtual appliance to allow this traffic. You will need to allow the complete IP address range of each dependent service, and keep this configuration up to date when the Azure infrastructure changes. Your API Management service may also experience latency or unexpected timeouts because of the force tunneling of this network traffic.
All the control plane traffic from the internet to the management endpoint of your API Management service is routed through a specific set of inbound IPs, hosted by API Management, encompassed by the ApiManagement service tag. When the traffic is force tunneled, the responses won't symmetrically map back to these inbound source IPs and connectivity to the management endpoint is lost. To overcome this limitation, configure a user-defined route (UDR) for the ApiManagement service tag with next hop type set to "Internet", to steer traffic back to Azure.
Note
Allowing API Management management traffic to bypass an on-premises firewall or network virtual appliance isn't considered a significant security risk. The recommended configuration for your API Management subnet allows inbound management traffic on port 3443 only from the set of Azure IP addresses encompassed by the ApiManagement service tag. The recommended UDR configuration is only for the return path of this Azure traffic.
(External VNet mode) Data plane traffic for clients attempting to reach the API Management gateway and developer portal from the internet will also be dropped by default because of asymmetric routing introduced by forced tunneling. For each client that requires access, configure an explicit UDR with next hop type "Internet" to bypass the firewall or virtual network appliance.
For other force tunneled API Management service dependencies, resolve the hostname and reach out to the endpoint. These include:
- Metrics and Health Monitoring
- Azure portal diagnostics
- SMTP relay
- Developer portal CAPTCHA
- Azure KMS server
For more information, see Virtual network configuration reference.
Common network configuration issues
This section has moved. See Virtual network configuration reference.
Troubleshooting
Unsuccessful initial deployment of API Management service into a subnet
- Deploy a virtual machine into the same subnet.
- Connect to the virtual machine and validate connectivity to one of each of the following resources in your Azure subscription:
- Azure Storage blob
- Azure SQL Database
- Azure Storage Table
- Azure Key Vault
Important
After validating the connectivity, remove all the resources in the subnet before deploying API Management into the subnet.
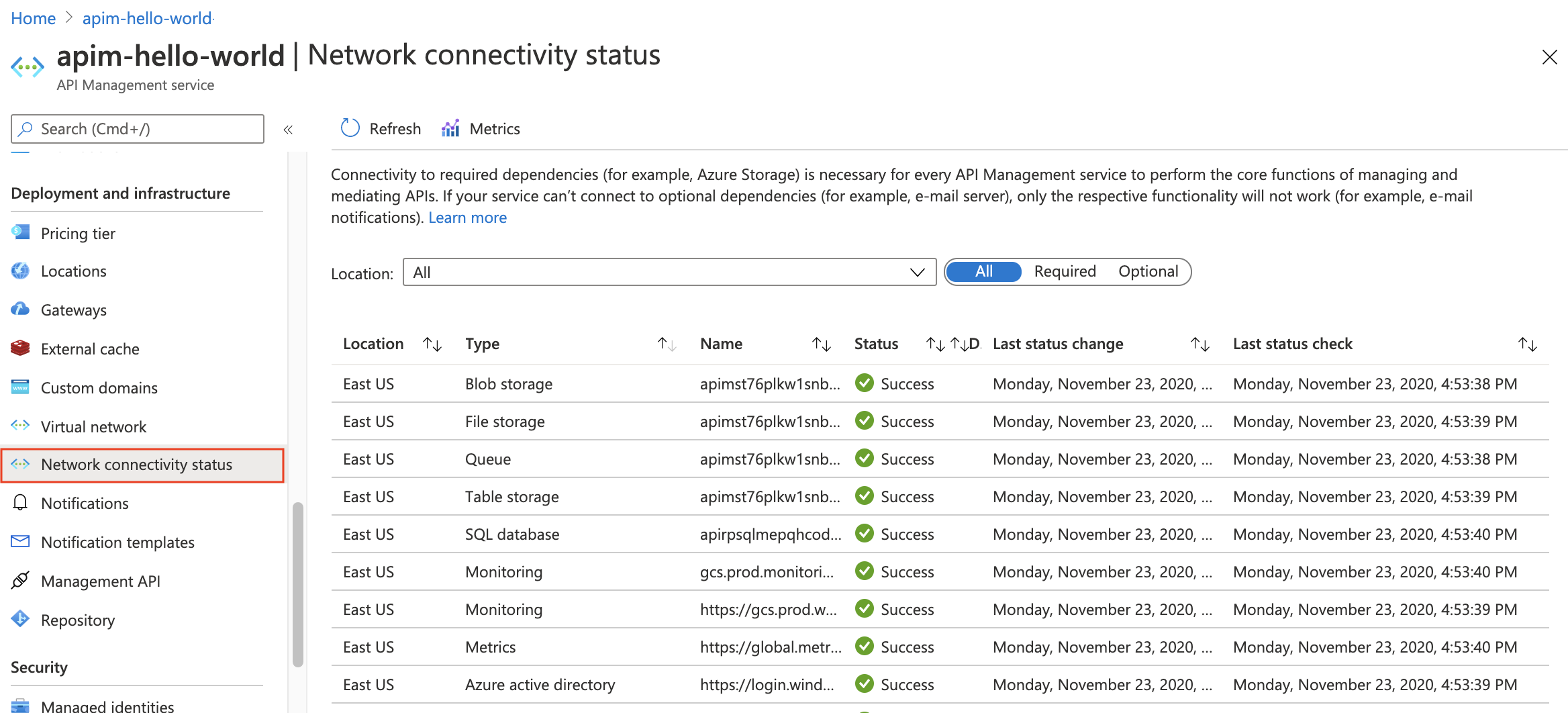
Verify network status
After deploying API Management into the subnet, use the portal to check the connectivity of your instance to dependencies, such as Azure Storage.
In the portal, in the sidebar menu, under Deployment + infrastructure, select Network > Network status.
| Filter | Description |
|---|---|
| Required | Select to review the required Azure services connectivity for API Management. Failure indicates that the instance is unable to perform core operations to manage APIs. |
| Optional | Select to review the optional services connectivity. Failure indicates only that the specific functionality won't work (for example, SMTP). Failure may lead to degradation in using and monitoring the API Management instance and providing the committed SLA. |
To help troubleshoot connectivity issues, select:
Metrics - to review network connectivity status metrics
Diagnose - to run a virtual network verifier over a specified time period
To address connectivity issues, review network configuration settings and fix required network settings.
Incremental updates
When making changes to your network, refer to NetworkStatus API to verify that the API Management service hasn't lost access to critical resources. The connectivity status should be updated every 15 minutes.
To apply a network configuration change to the API Management instance using the portal:
- In the left-hand menu for your instance, under Deployment and infrastructure, select Network > Virtual network.
- Select Apply network configuration.
Challenges encountered in reassigning API Management instance to previous subnet
- VNet lock - When moving an API Management instance back to its original subnet, immediate reassignment may not be possible due to the VNet lock, which takes up to one hour to be removed.
- Resource group lock - Another scenario to consider is the presence of a scope lock at the resource group level or higher, hindering the Resource Navigation Link Deletion process. To resolve this, remove the scope lock and allow a delay of approximately 4-6 hours for the API Management service to unlink from the original subnet before the lock removal, enabling deployment to the desired subnet.
Troubleshoot connection to Microsoft Graph from inside a VNet
Network connectivity to Microsoft Graph is needed for features including user sign-in to the developer portal using the Microsoft Entra identity provider.
To troubleshoot connectivity to Microsoft Graph from inside a VNet:
Ensure that NSG and other network rules are configured for outbound connectivity from your API Management instance to Microsoft Graph (using the AzureActiveDirectory service tag).
Ensure DNS resolution and network access to
microsoftgraph.chinacloudapi.cnfrom within the VNet. For example, provision a new VM inside the VNet, connect to it, and try toGET https://microsoftgraph.chinacloudapi.cn/v1.0/$metadatafrom a browser or using cURL, PowerShell, or other tools.
Related content
Learn more about: