Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Data collection rules (DCRs) are part of an Extract, transform, and load (ETL)-like data collection process that improves on legacy data collection methods for Azure Monitor. This process uses a common data ingestion strategy for all data sources and a standard method of configuration that's more manageable and scalable than previous collection methods.
For many monitoring scenarios, you don't need to understand how a DCR is created or assigned. You can simply use guidance in the Azure portal to enable and configure data collection, while Azure Monitor creates and configures the DCR for you. This article provides more details about how DCRs work to get you started on creating and configuring them manually so that you can customize the data collection process.
Specific advantages of DCR-based data collection include:
- Consistent method for configuration of different data sources.
- Ability to apply a transformation to filter or modify incoming data before it's sent to a destination.
- Scalable configuration options supporting infrastructure as code and DevOps processes.
- Option of Azure Monitor pipeline in your own environment to provide high-end scalability, layered network configurations, and periodic connectivity.
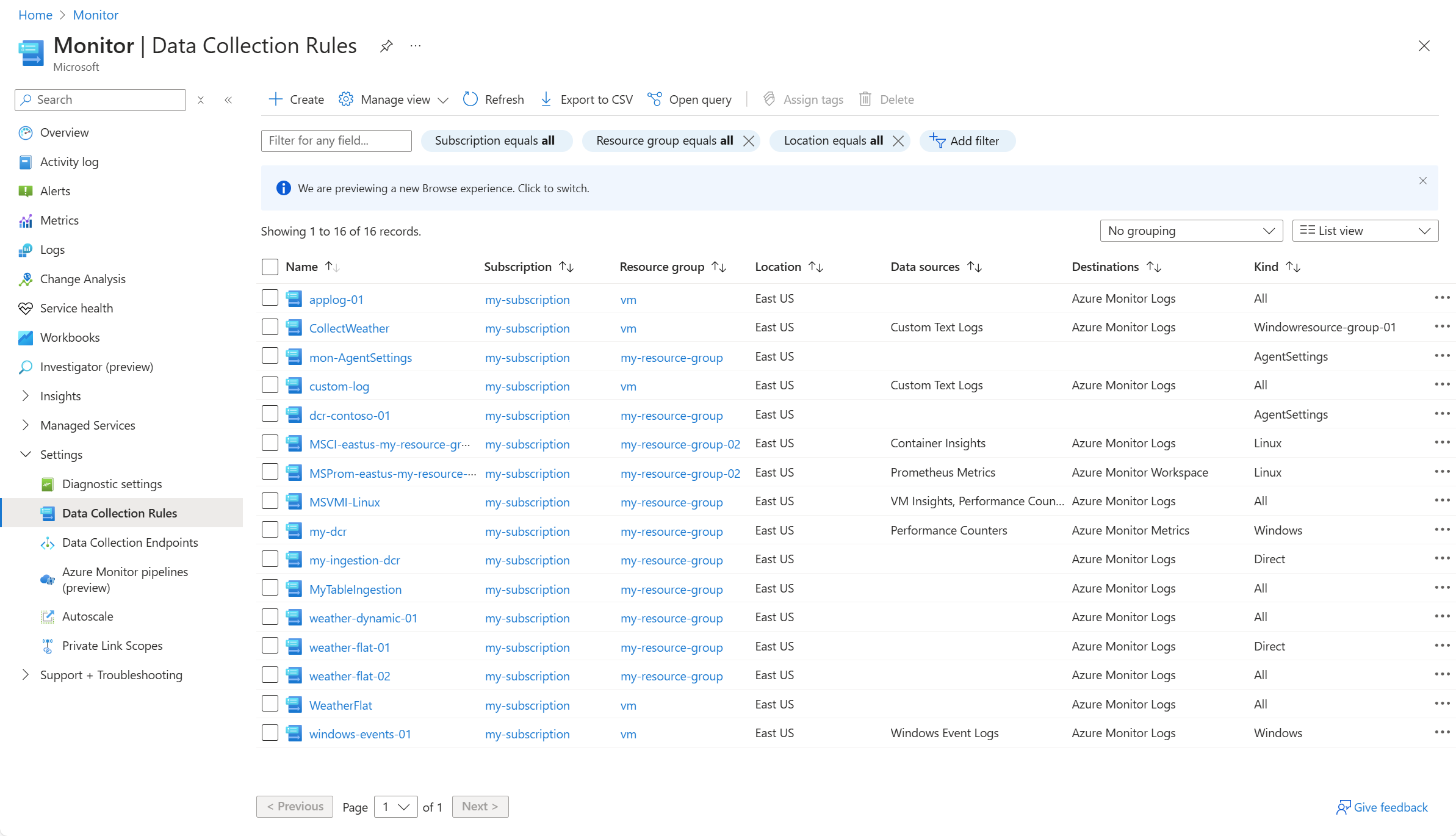
Viewing DCRs
Data collection rules (DCRs) are stored in Azure so they can be centrally deployed and managed like any other Azure resource. They provide a consistent and centralized way to define and customize different data collection scenarios.
View all of the DCRs in your subscription from the Data Collection Rules option of the Monitor menu in the Azure portal. Regardless of the method used to create the DCR and the details of the DCR itself, all DCRs in the subscription are listed in this screen.
Replaced legacy data collection methods
The DCR collection process has either replaced or is in the process of replacing other data collection methods in Azure Monitor. The following table lists the legacy methods with their DCR-based replacements. Other data collection methods in Azure Monitor are expected to also be replaced by DCRs in the future.
| Legacy method | DCR method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Log Analytics agent | Azure Monitor agent | The Azure Monitor agent is now used to monitor virtual machines (VMs) and Kubernetes clusters supporting Container insights. |
| Diagnostic settings (metrics only) |
Metrics export | Diagnostic settings are still currently used to collect resource logs from Azure resources. Platform metrics can now be collected using Metrics export. |
| Data Collector API | Logs ingestion API | The Logs ingestion API is used to send data to a Log Analytics workspace from any REST client. It replaces the Data Collector API which was less secure and less functional. |
Data collection process
The data collection process supported by DCRs provides a common processing path for incoming data. Each data collection scenario is defined in a DCR. The DCR provides instructions for how Azure Monitor should process the data it receives. Depending on the scenario, DCRs specify all or some of the following:
- Data to collect and send to Azure Monitor.
- Schema of the incoming data.
- Transformations to apply to the data before it's stored.
- Destination where the data should be sent.
Data collection rule associations (DCRAs)
Data collection rule associations (DCRAs) are created between the resource and the DCR to enable certain data collection scenarios. This is a many-to-many relationship, where a single DCR can be associated with multiple resources and a single resource can be associated with up to 30 DCRs. This allows you to develop a strategy for maintaining your monitoring across sets of resources with different requirements.
Using a DCR
Once a DCR is created, there are different methods to use it based on the data collection scenario. The following table lists the common scenarios and the method used to collect data in each case. Further details on each are provided below.
| Scenario | Method |
|---|---|
| Azure Monitor agent (AMA) | Data collection rule association (DCRA) |
| Event hubs | Data collection rule association (DCRA) |
| Platform metrics (preview) | Data collection rule association (DCRA) |
| Direct ingestion | DCR specified in the API call that sends the data to Azure Monitor. |
| Workspace transformation DCR | DCR is active for the workspace as soon as it's created. |
Scenarios
The following sections describe the common scenarios for using DCRs to collect data in Azure Monitor. They describe the details included in the DCR and the method used specify which DCR to use for that particular scenario.
Azure Monitor agent (AMA)
Azure Monitor agent (AMA) is used to collect data from virtual machines and Kubernetes clusters. The following diagram illustrates data collection for AMA running on a virtual machine. When the agent is installed, it connects to Azure Monitor to retrieve any DCRs that are associated with it. In this scenario, the DCRs specify events and performance data to collect. For a Kubernetes cluster, this would also include Prometheus metrics. The agent uses that information to determine what data to collect from the machine and send to Azure Monitor. Once the data is delivered, any transformation specified in the DCR are run to filter and modify the data and then sends the data to the specified workspace and table.
See Collect data from virtual machine client with Azure Monitor and Enable monitoring for Kubernetes clusters for details.
Direct ingestion
With direct ingestion, a particular DCR is specified to process the incoming data. For example, the following diagram illustrates data from a custom application using Logs ingestion API. Each API call specifies the DCR that processes its data. The DCR understands the structure of the incoming data, includes a transformation that ensures the data is in the format of the target table, and specifies a workspace and table to send the transformed data.
See Logs ingestion API for details.
Workspace transformation DCR
Workspace transformation DCRs provide transformations for data collection that doesn't use a DCR. They're applied directly to the Log Analytics workspace and are automatically activated when they're created.
See Workspace transformation DCR for details.
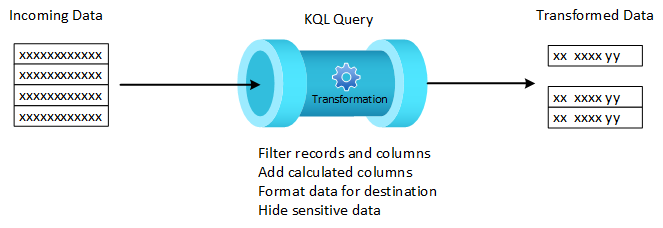
Transformations
Transformations are KQL queries included in a DCR that run against each record received. They allow you to modify incoming data before it's stored in Azure Monitor or sent to another destination. You may filter unneeded data to reduce your ingestion costs, remove sensitive data that shouldn't be persisted in the Log Analytics workspace, or format data to ensure that it matches the schema of its destination. Transformations also enable advanced scenarios such as sending data to multiple destinations or enriching data with additional information.
DCR regions
Data collection rules are available in all public regions where Log Analytics workspaces and the Azure Government and China clouds are supported. Air-gapped clouds aren't yet supported. A DCR gets created and stored in a particular region and is backed up to the paired-region within the same geography. The service is deployed to all three availability zones within the region. For this reason, it's a zone-redundant service, which further increases availability.
Next steps
For more information on how to work with DCRs, see:
- Data collection rule structure for a description of the JSON structure of DCRs and the different elements used for different workflows.
- Sample data collection rules (DCRs) for sample DCRs for different data collection scenarios.
- Create and edit data collection rules (DCRs) in Azure Monitor for different methods to create DCRs for different data collection scenarios.
- Azure Monitor service limits for limits that apply to each DCR.