Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Managed Instance
SQL Server on Azure VM
Azure SQL is a family of managed, secure, and intelligent products that use the SQL Server database engine in the Azure cloud. Azure SQL is built upon the familiar SQL Server engine, so you can migrate applications with ease and continue to use the tools, languages, and resources you're familiar with. Your skills and experience transfer to the cloud, so you can do even more with what you already have.
The three products in the Azure SQL family are:
- Azure SQL Database: Support modern cloud applications on an intelligent, managed database service that includes serverless compute, elastic pools, and elastic job automation.
- Azure SQL Database Hyperscale: A different architecture for the Azure SQL Database engine that emphasizes highly scalable and separate storage and compute tiers, suitable for many workloads, and with similar features including Hyperscale elastic pools.
- Azure SQL Managed Instance: Modernize your existing SQL Server applications at scale with an intelligent fully managed instance as a service, with almost 100% feature parity with the SQL Server database engine. Best for most migrations to the cloud.
- SQL Server on Azure VMs: Lift-and-shift your SQL Server workloads with ease and maintain 100% SQL Server compatibility and operating system-level access.
Learn how each product fits into Microsoft's Azure SQL data platform to match the right option for your business requirements. Whether you prioritize cost savings or minimal administration, this article can help you decide which approach delivers against the business requirements you care about most.
Tip
The Azure portal includes a decision tree in the Azure SQL hub to help you Find the right option for your application architecture in Azure SQL. For an explanation of the decision tree and its choices, see Azure SQL decision tree.
Overview
In today's data-driven world, driving digital transformation increasingly depends on our ability to manage massive amounts of data and harness its potential. But today's data estates are increasingly complex, with data hosted on-premises, in the cloud, or at the edge of the network. Developers who are building intelligent and immersive applications can find themselves constrained by limitations that can ultimately impact their experience. Limitations arising from incompatible platforms, inadequate data security, insufficient resources, and price-performance barriers create complexity that can inhibit app modernization and development.
One of the first things to understand in any discussion of Azure versus on-premises SQL Server databases is that you can use it all. Microsoft's data platform uses SQL Server technology and makes it available across physical on-premises machines, private cloud environments, third-party hosted private cloud environments, and the public cloud.
Fully managed and always up to date
Spend more time innovating and less time patching, updating, and backing up your databases. Azure is the only cloud with evergreen SQL that automatically applies the latest updates and patches so that your databases are always up to date, which eliminates end-of-support hassle. Even complex tasks like performance tuning, high availability, disaster recovery, and backups are automated, freeing you to focus on your applications.
Protect your data with built-in intelligent security
Azure constantly monitors your data for threats. With Azure SQL, you can:
- Remediate potential threats in real time with intelligent advanced threat detection and proactive vulnerability assessment alerts.
- Get industry-leading, multi-layered protection with built-in security controls including T-SQL, authentication, networking, and key management.
- Take advantage of the most comprehensive compliance coverage of any cloud database service.
Business motivations
There are several factors that can influence your decision to choose between the different data offerings:
- Cost: Both platform as a service (PaaS) and infrastructure as a service (IaaS) options include a base price that covers the underlying infrastructure and licensing. However, with the IaaS option you need to invest extra time and resources to manage your database, while in PaaS you get administration features included in the price. Both PaaS and IaaS options give you the ability to pause your resources to help reduce administration costs.
- Administration: PaaS options reduce the amount of time that you need to invest to administer the database. However, it also limits the range of custom administration tasks and scripts that you can perform or run. For example, CLR isn't supported with SQL Database, but is supported in SQL Managed Instance.
- Service-level agreement: Both IaaS and PaaS provide high industry-standard SLAs. PaaS options guarantee 99.99% SLA, while IaaS guarantees 99.95% SLA for the infrastructure, which means you also need to implement additional mechanisms to ensure the availability of your databases. You can attain 99.99% SLA by creating an additional SQL virtual machine, and implementing the SQL Server Always On availability group high availability solution.
- Time to move to Azure: SQL Server on Azure VMs are an exact match of your environment, so migration from on-premises to the Azure VM is no different than moving the databases from one on-premises server to another. SQL Managed Instance also enables easy migration; however, there might be some changes that you need to apply before your migration.
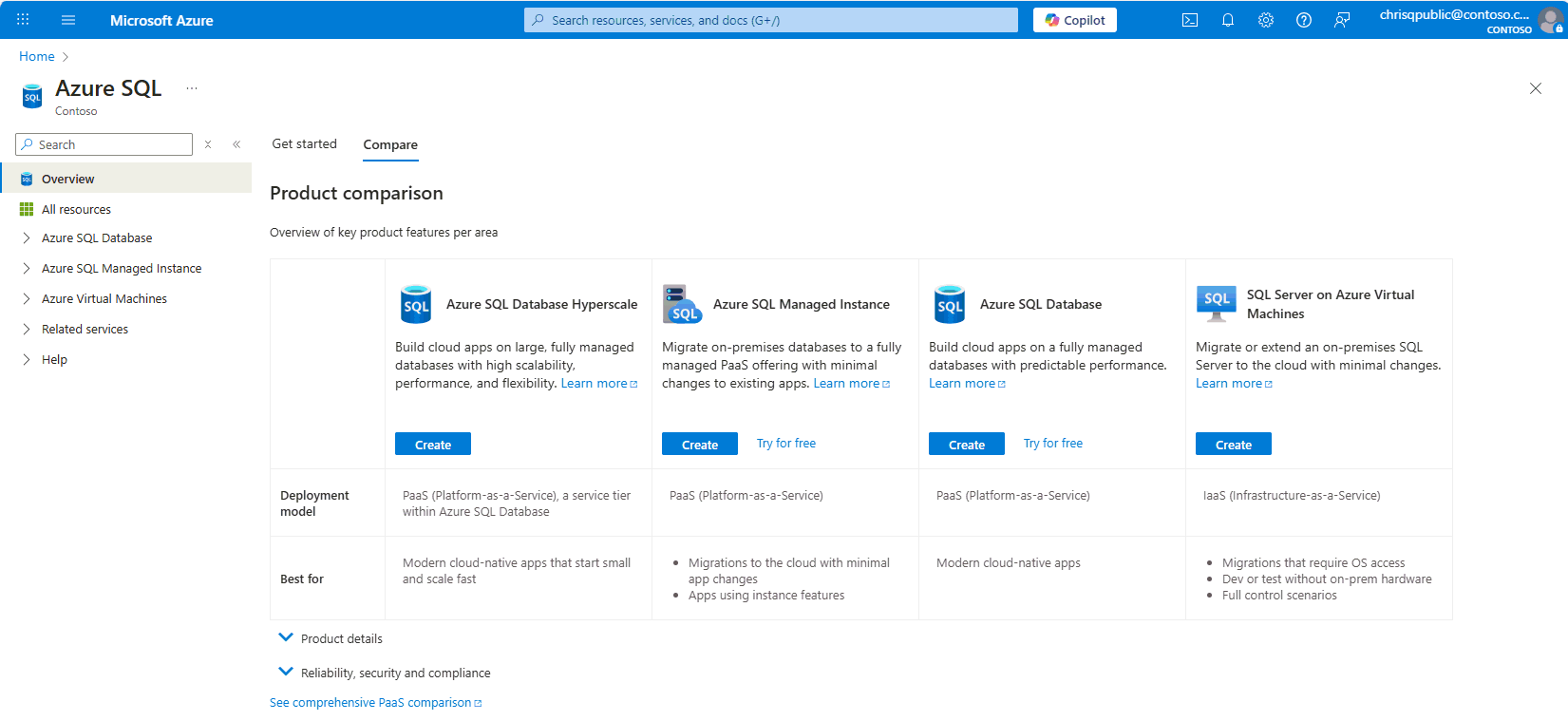
Service comparison
As seen in the diagram, each service offering can be characterized by the level of administration you have over the infrastructure, and by the degree of cost efficiency.
In Azure, you can have your SQL Server workloads running as a hosted service (PaaS), or a hosted infrastructure (IaaS) supporting the software layer, such as Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) or an application. Within PaaS, you have multiple product options, and service tiers within each option. The key question that you need to ask when deciding between PaaS or IaaS is - do you want to manage your database, apply patches, and take backups - or do you want to delegate these operations to Azure?
Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Database is a relational database-as-a-service (DBaaS) hosted in Azure that falls into the industry category of Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS).
- Best for modern cloud applications that want to use the latest stable SQL Server features and have time constraints in development and marketing.
- A fully managed SQL Server database engine, based on the latest stable Enterprise Edition of SQL Server. SQL Database is built on standardized hardware and software that is owned, hosted, and maintained by Azure.
With SQL Server, built-in features and functionality often require extensive configuration (either on-premises or in an Azure virtual machine). When using SQL Database, you pay-as-you-go with options to scale up or out for greater power with no interruption. SQL Database has some additional features that aren't available in SQL Server, such as built-in high availability, intelligence, and management.
Azure SQL Database offers the following deployment options:
- As a single database with its own set of resources managed via a logical server. A single database is similar to a contained database in SQL Server. This option is optimized for modern application development of new cloud-born applications. Hyperscale and serverless options are available.
- An elastic pool, which is a collection of databases with a shared set of resources managed via a logical server. Single databases can be moved into and out of an elastic pool. This option is optimized for modern application development of new cloud-born applications using the multitenant SaaS application pattern. Elastic pools provide a cost-effective solution for managing the performance of multiple databases that have variable usage patterns.
Azure SQL Managed Instance
Azure SQL Managed Instance falls into the industry category of Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and is best for most migrations to the cloud. SQL Managed Instance is a collection of system and user databases with a shared set of resources that is lift-and-shift ready.
- Best for new applications or existing on-premises applications that want to use the latest stable SQL Server features and that are migrated to the cloud with minimal changes. An instance of SQL Managed Instance is similar to an instance of the Microsoft SQL Server database engine offering shared resources for databases and additional instance-scoped features.
- SQL Managed Instance supports database migration from on-premises with minimal to no database changes. This option provides all of the PaaS benefits of Azure SQL Database but adds additional capabilities, such as native virtual network. SQL Managed Instance provides full SQL Server access and feature compatibility to migrate your SQL Server instances to Azure.
SQL Server on Azure VMs
SQL Server on Azure VMs falls into the industry category Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) and allows you to run SQL Server inside a fully managed virtual machine (VM) in Azure.
- SQL Server installed and hosted in the cloud runs on Windows Server or Linux virtual machines in Azure. All supported versions and editions of SQL Server are available to install in an IaaS virtual machine.
- Best for migrations and applications that require OS-level access. SQL virtual machines in Azure are lift-and-shift ready for existing applications that require fast migration to the cloud with minimal changes or no changes. SQL virtual machines offer full administrative control over the SQL Server instance and underlying OS for migration to Azure.
- The most significant difference from SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance is that SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines allows full control over the database engine. You can choose when to start maintenance activities including system updates, change the recovery model to simple or bulk-logged, pause or start the service when needed, and you can fully customize the SQL Server database engine. With this additional control comes the added responsibility to manage the virtual machine.
- Rapid development and test scenarios when you don't want to buy on-premises hardware for SQL Server. SQL virtual machines also run on standardized hardware that is owned, hosted, and maintained by Azure. When using SQL virtual machines, you can either pay-as-you-go for a SQL Server license already included in a SQL Server image or easily use an existing license. You can also stop or resume the VM as needed.
- Optimized for migrating existing applications to Azure or extending existing on-premises applications to the cloud in hybrid deployments. In addition, you can use SQL Server in a virtual machine to develop and test traditional SQL Server applications. With SQL virtual machines, you have the full administrative rights over a dedicated SQL Server instance and a cloud-based VM. It's a perfect choice when an organization already has IT resources available to maintain the virtual machines. These capabilities allow you to build a highly customized system to address your application's specific performance and availability requirements.
Comparison table
Differences between Azure SQL Database, Azure SQL Managed Instance, and SQL Server on Azure VMs are listed in the following table, but both SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance are optimized to reduce overall management costs to a minimum for provisioning and managing many databases. Ongoing administration costs are reduced since you don't have to manage any virtual machines, operating system, or database software. You don't have to manage upgrades, high availability, or backups.
The Azure portal includes a decision tree in the Azure SQL hub to help you Find the right option for your application architecture in Azure SQL. For an explanation of the decision tree and its choices, see Azure SQL decision tree.
In general, SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance can dramatically increase the number of databases managed by a single IT or development resource. Elastic pools for SQL Database also support SaaS multitenant application architectures with features including tenant isolation and the ability to scale to reduce costs by sharing resources across databases. SQL Managed Instance provides support for instance-scoped features enabling easy migration of existing applications, as well as sharing resources among databases. Whereas SQL Server on Azure VMs provide DBAs with an experience most similar to the on-premises environment they're familiar with.
| Azure SQL Database | Azure SQL Managed Instance | SQL Server on Azure VMs |
|---|---|---|
| Supports most on-premises database-level capabilities. The most commonly used SQL Server features are available. 99.995% availability guaranteed. Built-in backups, patching, recovery. Latest stable Database Engine version. Ability to assign necessary resources (CPU/storage) to individual databases. Built-in advanced intelligence and security. Online change of resources (CPU/storage). |
Supports almost all on-premises instance-level and database-level capabilities. High compatibility with SQL Server. 99.99% availability guaranteed. Built-in backups, patching, recovery. Latest stable Database Engine version. Easy migration from SQL Server. Private IP address within Azure Virtual Network. Built-in advanced intelligence and security. Online change of resources (CPU/storage). |
You have full control over the SQL Server engine. Supports all on-premises capabilities. Up to 99.99% availability. Full parity with the matching version of on-premises SQL Server. Easy migration from SQL Server. Private IP address within Azure Virtual Network. You have the ability to deploy application or services on the host where SQL Server is placed. Manage your SQL Server VM from the Azure portal and unlock a number of additional benefits when you register with the Windows SQL Server IaaS Agent extension. |
| Migration from SQL Server might be challenging. Some SQL Server features aren't available. Configurable maintenance windows. Compatibility with the SQL Server version can be achieved only using database compatibility levels. Private IP address support with Azure Private Link. |
There's still some minimal number of SQL Server features that aren't available. Configurable maintenance windows. Compatibility with the SQL Server version can be achieved only using database compatibility levels. |
You might use manual or automated backups. You need to implement your own High-Availability solution. There's a downtime while changing the resources(CPU/storage) |
| Databases of up to 128 TB. | Up to 16 TB. | SQL Server instances with up to 256 TB of storage. The instance can support as many databases as needed. |
| On-premises application can access data in Azure SQL Database. | Configure an existing virtual network for Azure SQL Managed Instance and connectivity to your on-premises environment using Azure Express Route or VPN Gateway. | With SQL virtual machines, you can have applications that run partly in the cloud and partly on-premises. For example, you can extend your on-premises network and Active Directory Domain to the cloud via Azure Virtual Network. For more information on hybrid cloud solutions, see Extending on-premises data solutions to the cloud. |
Cost
Whether you're a startup that is strapped for cash, or a team in an established company that operates under tight budget constraints, limited funding is often the primary driver when deciding how to host your databases.
In this section, learn about the billing and licensing basics in Azure associated with the Azure SQL family of products, and calculating the total application cost.
Billing and licensing basics
Currently, both Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance are sold as a service and are available with several options and in several service tiers with different prices for resources, all of which are billed hourly at a fixed rate based on the service tier and compute size you choose. For the latest information on the current supported service tiers, compute sizes, and storage amounts, see DTU-based purchasing model overview for Azure SQL Database and vCore-based purchasing model for both SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance.
- With SQL Database, you can choose a purchasing model, service tier and compute tier that fits your needs from a wide range of prices starting from 32.24¥/month for the Basic tier and you can create elastic pools to share resources among databases to reduce costs and accommodate usage spikes.
- With SQL Server on Azure VMs, you can choose a VM size and storage configuration that fits your needs. The cost of the VM is based on the size of the VM and the number of cores.
- You can activate the Azure Hybrid Benefit (AHB), which offers a discount on the allocation of SQL Server licenses to the SQL Server Database Engine. Use the Pricing Calculator to see the potential cost savings of the Azure Hybrid Benefit.
In addition, you're billed for outgoing Internet traffic at regular data transfer rates. You can dynamically adjust service tiers and compute sizes to match your application's varied throughput needs.
With SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance, the database software is automatically configured, patched, and upgraded by Azure, which reduces your administration costs. In addition, its built-in backup capabilities help you achieve significant cost savings, especially when you have a large number of databases.
With SQL Server on Azure VMs, you can use any of the platform-provided SQL Server images, or self-install SQL Server to an Azure VM and then register with the Windows SQL Server IaaS Agent extension for additional benefits. All the supported SQL Server versions (2016, 2017, 2019, 2022, 2025) and editions (Developer, Express, Web, Standard, Enterprise) are available. When using the Azure provided images, the operational cost depends on the VM size and the edition of SQL Server you choose. Regardless of VM size or SQL Server edition, you pay per-minute licensing cost of SQL Server and the Windows or Linux Server, along with the Azure Storage cost for the VM disks. The per-minute billing option allows you to use SQL Server for as long as you need without buying addition SQL Server licenses.
Calculate the total application cost
When you start using a cloud platform, the cost of running your application includes the cost for new development and ongoing administration costs, plus the public cloud platform service costs.
For more information on pricing, see the following resources:
- SQL Database & SQL Managed Instance pricing
- Virtual machine pricing for SQL and for Windows
- Azure Pricing Calculator
Administration
For many businesses, the decision to transition to a cloud service is as much about offloading complexity of administration as it's cost. With IaaS and PaaS, Azure administers the underlying infrastructure and automatically replicates all data to provide disaster recovery, configures and upgrades the database software, manages load balancing, and does transparent failover if there's a server failure within a data center.
- With SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance, you can continue to administer your database, but you no longer need to manage the database engine, operating system, or the hardware. Examples of items you can continue to administer include databases and logins, index and query tuning, and auditing and security. Additionally, configuring high availability to another data center requires minimal configuration and administration.
- With SQL Server on Azure VMs, you have full control over the operating system and SQL Server instance configuration. With a VM, it's up to you to decide when to update/upgrade the operating system and database software and when to install any extra software such as anti-virus. Some automated features are provided to dramatically simplify patching, backup, and high availability. In addition, you can control the size of the VM, the number of disks, and their storage configurations. Azure allows you to change the size of a VM as needed. For information, see Virtual Machine and Cloud Service Sizes for Azure.
Service-level agreement (SLA)
For many IT departments, meeting up-time obligations of a service-level agreement (SLA) is a top priority. In this section, we look at what SLA applies to each database hosting option.
For both Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance, Azure provides an availability SLA of 99.99%. For the latest information, see Service-level agreement.
For SQL Server on Azure VMs, Azure provides an availability SLA of 99.95% for two virtual machines in an availability set, or 99.99% for two virtual machines in different availability zones. This means that at least one of the two virtual machines is available for the given SLA, but it doesn't cover the processes (such as SQL Server) running on the VM. For the latest information, see the VM SLA. For database high availability (HA) within VMs, you should configure one of the supported high availability options in SQL Server, such as Always On availability groups. Using a supported high availability option doesn't provide an additional SLA, but allows you to achieve >99.99% database availability.
Time to move to Azure
Azure SQL Database is the right solution for cloud-designed applications when developer productivity and fast time-to-market for new solutions are critical. With programmatic DBA-like functionality, it's perfect for cloud architects and developers as it lowers the need for managing the underlying operating system and database. For more information, see High availability and disaster recovery checklist - Azure SQL Database.
Azure SQL Managed Instance greatly simplifies the migration of existing applications to Azure, enabling you to bring migrated database applications to market in Azure quickly. For more information, see High availability and disaster recovery checklist - Azure SQL Managed Instance.
SQL Server on Azure VMs is perfect if your existing or new applications require large databases or access to all features in SQL Server or Windows/Linux, and you want to avoid the time and expense of acquiring new on-premises hardware. It's also a good fit when you want to migrate existing on-premises applications and databases to Azure as-is. Since you don't need to change the presentation, application, and data layers, you save time and budget on having to rearchitect your existing solution. Instead, you can focus on migrating all your solutions to Azure and in doing some performance optimizations that might be required by the Azure platform. For more information, see Checklist: Best practices for SQL Server on Azure VMs.
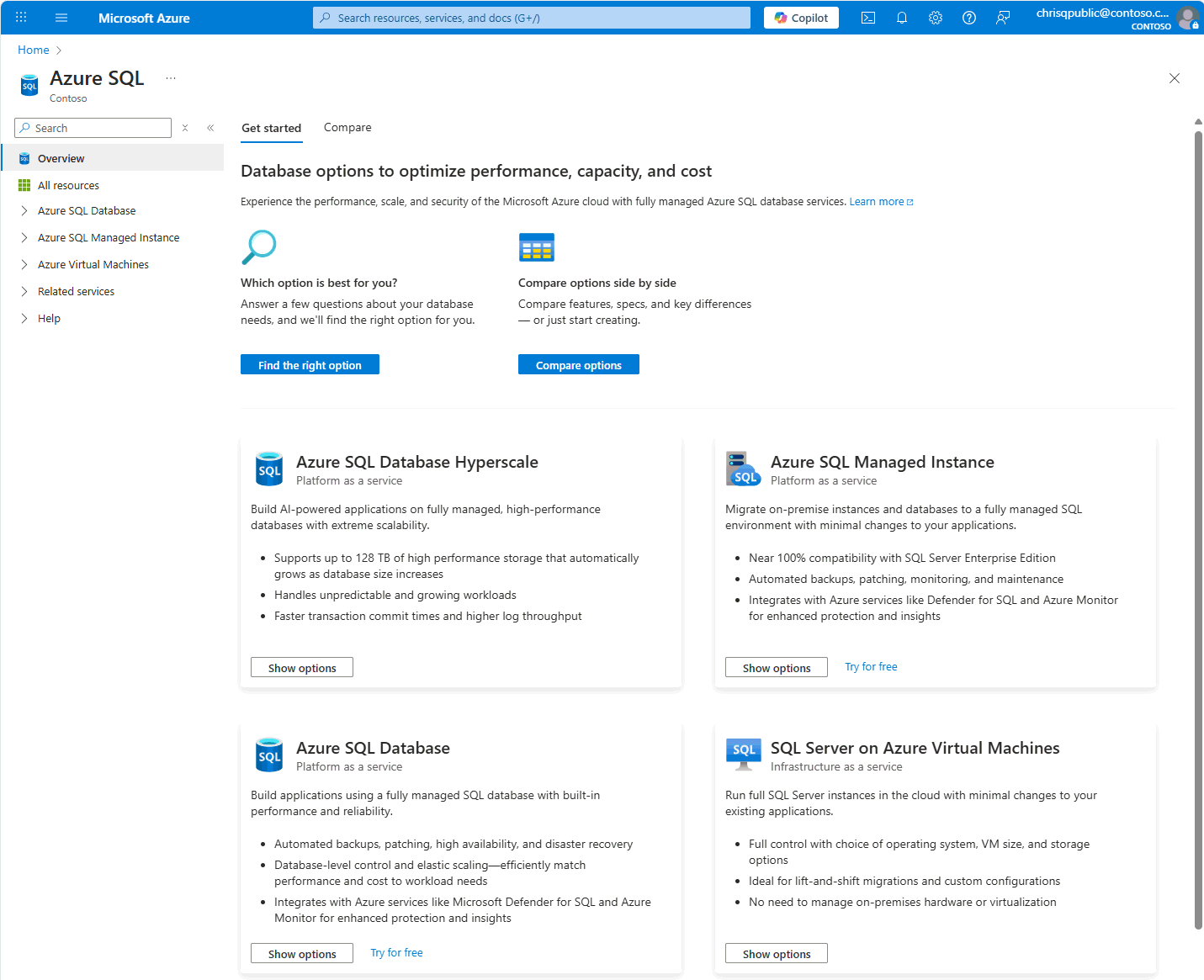
Create Azure SQL resources with the Azure portal
The Azure portal provides a single page to create Azure SQL resources. Get started at azure sql hub:
The Azure SQL hub is the launching point for Azure SQL Database, Azure SQL Database Hyperscale, Azure SQL Managed Instance, and SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines.
The Azure SQL hub includes Find the right option and Compare options informative helpers.
Manage Azure SQL resources with the Azure portal
To access the Azure SQL page, from the Azure portal menu, select Azure SQL or search for and select Azure SQL in any page.
The Azure portal provides a single page where you can manage all of your Azure SQL resources including your SQL Server on Azure virtual machines (VMs). To manage existing resources, select the desired item in the list.
Note
Azure SQL provides a quick and easy way to access all of your SQL resources in the Azure portal, including single and pooled databases in Azure SQL Database as well as the logical server hosting them, Azure SQL Managed Instances, and SQL Server on Azure VMs. What is Azure SQL? isn't a service or resource, but rather a family of SQL-related services.
Related content
For overviews:
To create resources:
For pricing:
To migrate: