Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
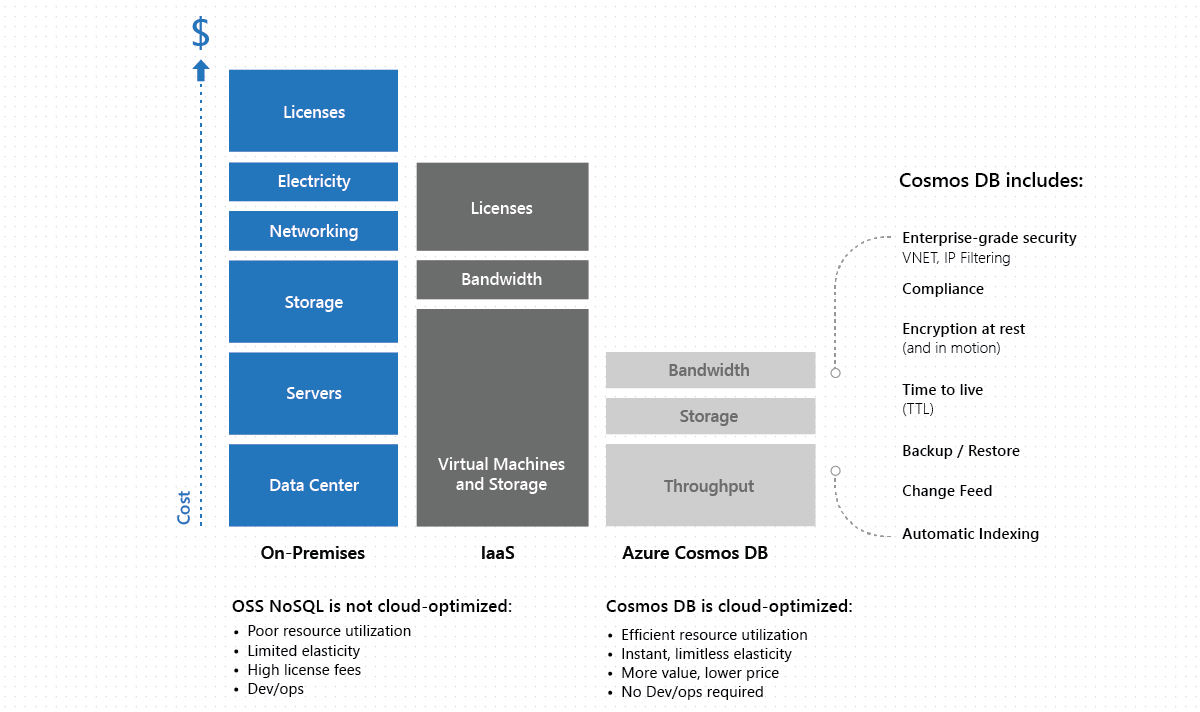
Azure Cosmos DB is designed with the fine grained multi-tenancy and resource governance. This design allows Azure Cosmos DB to operate at significantly lower cost and help users save. Currently Azure Cosmos DB supports more than 280 customer workloads on a single machine with the density continuously increasing, and thousands of customer workloads within a cluster. It load balances replicas of customers' workloads across different machines in a cluster and across multiple clusters within a data center. To learn more, see Azure Cosmos DB: Pushing the frontier of multiple-regionally distributed databases. Because of resource-governance, multi-tenancy, and native integration with the rest of Azure infrastructure, Azure Cosmos DB is on average 4 to 6 times cheaper than MongoDB, Cassandra, or other OSS NoSQL running on IaaS and up to 10 times cheaper than the database engines running on premises. See the paper on The total cost of (non) ownership of a NoSQL database cloud service.
The OSS NoSQL database solutions, such as Apache Cassandra, MongoDB, HBase, engines were designed for on-premises. When offered as a managed service they are equivalent to a Resource Manager template with a tenant database for managing the provisioned clusters and monitoring support. OSS NoSQL architectures require significant operational overhead, and the expertise can be difficult and expensive to find. On the other hand, Azure Cosmos DB is a fully managed cloud service, which allows developers to focus on business innovation rather than on managing and maintaining database infrastructure.
Unlike a cloud-native database service Azure Cosmos DB, OSS NoSQL database engines were not designed and built with the resource governance or fine-grained multi-tenancy as the fundamental architectural principles. OSS NoSQL database engines like Cassandra and MongoDB make a fundamental assumption that all the resources of the virtual machine on which they are running are available for their use. Many of these database engines cannot function if the amount of resources drops below a certain threshold. For example, for small VM instances, and they are available with vendor-recommended configurations suggesting typically large-scale VMs with higher cost. So, it is not possible to host an OSS NoSQL or any other on-premises database engine and make it available by using a consumption-based charging model like requests per second or consumed storage.
Total cost of ownership of Azure Cosmos DB
The serverless provisioning model of Azure Cosmos DB eliminates the need to over-provision the database infrastructure. Azure Cosmos DB resources are provided without any need for specialized configurations or licensing. As a result, the Azure Cosmos DB-backed applications can run with as much as a 70 percent Total cost of ownership savings when compared to OSS NoSQL databases. For some real-time examples, see customer use-cases. Other benefits of the Azure Cosmos DB pricing model include:
Great value for the price: Market analysts, customers, and partners have confirmed a greater value of all the features that Azure Cosmos DB offers for a much lower price compared to what customers can get when implementing these solutions on their own or through other vendors. The database features such multiple-regional distribution, multi-region writes, well-defined and intuitive consistency models, automatic indexing are greatly simplified with Azure Cosmos DB without any complexity, overhead, or downtime.
No NoSQL DevOps administration is required: With Azure Cosmos DB one does not need to employ DevOps to manage deployments, perform maintenance, scale, or patch. You can execute the all the workloads that you would do with OSS NoSQL cluster hosted on-premises or on cloud infrastructure.
Ability to elastically scale: Azure Cosmos DB throughput can be scaled up and down, allowing you to reduce the cost of ownership during non-peak times. OSS NoSQL clusters deployed on cloud infrastructure offer limited elasticity, and on-premises deployments aren't elastic by definition. In Azure Cosmos DB, if you provision more throughput, your throughput is guaranteed to scale linearly. This guarantee is backed up by financial SLAs and at the 99th percentile at any scale.
Economies of scale: A managed service like Azure Cosmos DB operates with a large number of nodes, integrated natively with networking, storage, and computes. Because of Azure Cosmos DB's large scale, standardization you can save costs.
Optimized for the cloud: Azure Cosmos DB is designed from the ground-up with fine-grained multi-tenancy and performance isolation. This allows for optimally placing, executing, and balancing thousands of tenants and their workloads across clusters and data centers. In contrast, the current generation of OSS NoSQL databases operate on-premises with the entire virtual machine assumed to run a single tenant’s workload. These databases are also not designed to leverage a cloud provider’s infrastructure and hardware to the full extent. For example, an OSS NoSQL database engine isn't aware of the differences between a virtual machine being down Vs a routine image upgrade, or the fact that premium disk is already three-way replicated. It can't take advantage of these benefits and pass on the benefits and savings to customers.
You pay by the hour: For large-scale workloads, that need to scale at any point in time, you are only charged by the hour. The workloads on an application typically vary across times of the year, and by the data that is queried. With Azure Cosmos DB, you can scale up or down as you need and pay only for what you need. With on-premises or IaaS-hosted systems, you can't match this model, because there isn't a way to decommission the hardware every hour. In such cases, you can potentially save between 10 to 14 times on an average with Azure Cosmos DB.
You get numerous features for free: In Azure Cosmos DB, write workloads are substantially cheaper compared to alternative database services. In addition, Azure Cosmos DB offers features such as such as automatic indexing, Time to Live (TTL), Change Feed and others without any additional charges, something that other database services typically charge.
Uses unified currency for diverse workloads: Unlike alternative offerings, in Azure Cosmos DB, you do not need to segment workloads, for example, into reads and writes. Or provision throughput on a per workload type that is read throughput vs. write throughput. In Azure Cosmos DB, provisioned throughput is reserved using a unified and normalized currency in terms of Request Units or RU/sec. Azure Cosmos DB doesn't force you to assign priority to your workloads, perform capacity planning or pay for each type of capacity separately. Such approach enables you to easily interchange the same RU/s between various operations and workload types.
Doesn't require provisioning VMs to scale: Most operational databases require you to go with large virtual machines to avoid noisy neighbors and for loose resource governance, if you want scale. This puts the burden and the upfront commitment of cost on the customers. With Azure Cosmos DB, you can start small and grow into the large scale workload sizes seamlessly, and without any downtime or impact on data availability.
You can utilize provisioned throughput to a maximum limit: By the virtue of sub-core multiplexing in Azure Cosmos DB, you can saturate the provisioned throughput to a greater extent than IaaS hosted options or third party offers. This method saves a lot more than the alternative solutions.
Deep integration of Azure Cosmos DB with other Azure services. Azure Cosmos DB has a native integration with Networking, Compute, Azure Functions (serverless), Azure IoT, and others Azure services. With this integration, you get the best performance, speed of data replication around China with robust guarantees. The third party solutions won't be able to match or would typically charge a premium to offer such features.
You automatically get high availability, with at least 10-20 fault domains by default: Azure Cosmos DB supports the distribution of workloads across fault domains, a feature that is critical for high availability. It offers 99.999 high availability for reads and writes at the 99th percentile across anywhere in China. The cost of implementing something like this on your own or through a third-party solution, would be high.
You automatically get all enterprise capabilities, at no additional cost. Azure Cosmos DB offers the most comprehensive set of compliance certifications, security, and encryption at rest and in motion at no additional cost (compared to our competition). You automatically get regional availability anywhere in China. You can span your database across any number of Azure regions and add or remove regions at any point in China.
Capacity planning
As an aid for estimating TCO, it can be helpful to start with capacity planning. If you are planning a migration to Azure Cosmos DB from an existing database cluster, you can use information about your existing database cluster for capacity planning.
- If all you know is the number of vcores and servers in your existing database cluster, read about estimating request units using vCores or vCPUs
- If you know typical request rates for your current database workload, read about estimating request units using Azure Cosmos DB capacity planner
Next steps
- Trying to do capacity planning for a migration to Azure Cosmos DB? You can use information about your existing database cluster for capacity planning.
- If all you know is the number of vcores and servers in your existing database cluster, read about estimating request units using vCores or vCPUs
- If you know typical request rates for your current database workload, read about estimating request units using Azure Cosmos DB capacity planner
- Learn more about How Azure Cosmos DB pricing model is cost-effective for customers
- Learn more about Optimizing for development and testing
- Learn more about Optimizing throughput cost
- Learn more about Optimizing storage cost
- Learn more about Optimizing the cost of reads and writes
- Learn more about Optimizing the cost of queries
- Learn more about Optimizing the cost of multi-region Azure Cosmos DB accounts
- Learn more about The Total Cost of (Non) Ownership of a NoSQL Database Cloud Service