Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
This article describes what linked services are, how they're defined in JSON format, and how they're used in Azure Data Factory and Azure Synapse Analytics.
To learn more, read the introductory article for Azure Data Factory or Azure Synapse.
Overview
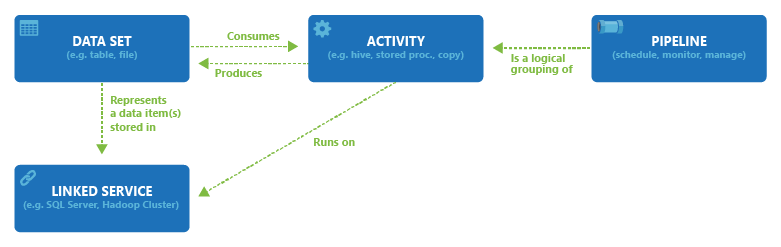
Azure Data Factory and Azure Synapse Analytics can have one or more pipelines. A pipeline is a logical grouping of activities that together perform a task. The activities in a pipeline define actions to perform on your data. For example, you might use a copy activity to copy data from SQL Server to Azure Blob storage. Then, you might use a Hive activity that runs a Hive script on an Azure HDInsight cluster to process data from Blob storage to produce output data. Finally, you might use a second copy activity to copy the output data to Azure Synapse Analytics, on top of which business intelligence (BI) reporting solutions are built. For more information about pipelines and activities, see Pipelines and activities.
Now, a dataset is a named view of data that simply points to or references the data you want to use in your activities as inputs and outputs.
Before you create a dataset, you must create a linked service to link your data store to the Data Factory or Synapse Workspace. Linked services are much like connection strings, which define the connection information needed for the service to connect to external resources. Think of it this way: the dataset represents the structure of the data within the linked data stores, and the linked service defines the connection to the data source. For example, an Azure Storage linked service links a storage account to the service. An Azure Blob dataset represents the blob container and the folder within that Azure Storage account that contains the input blobs to be processed.
Here's a sample scenario. To copy data from Blob storage to a SQL Database, you create two linked services: Azure Storage and Azure SQL Database. Then, create two datasets: Azure Blob dataset (which refers to the Azure Storage linked service) and Azure SQL Table dataset (which refers to the Azure SQL Database linked service). The Azure Storage and Azure SQL Database linked services contain connection strings that the service uses at runtime to connect to your Azure Storage and Azure SQL Database, respectively. The Azure Blob dataset specifies the blob container and blob folder that contains the input blobs in your Blob storage. The Azure SQL Table dataset specifies the SQL table in your SQL Database to which the data is to be copied.
The following diagram shows the relationships among pipeline, activity, dataset, and linked service in the service:
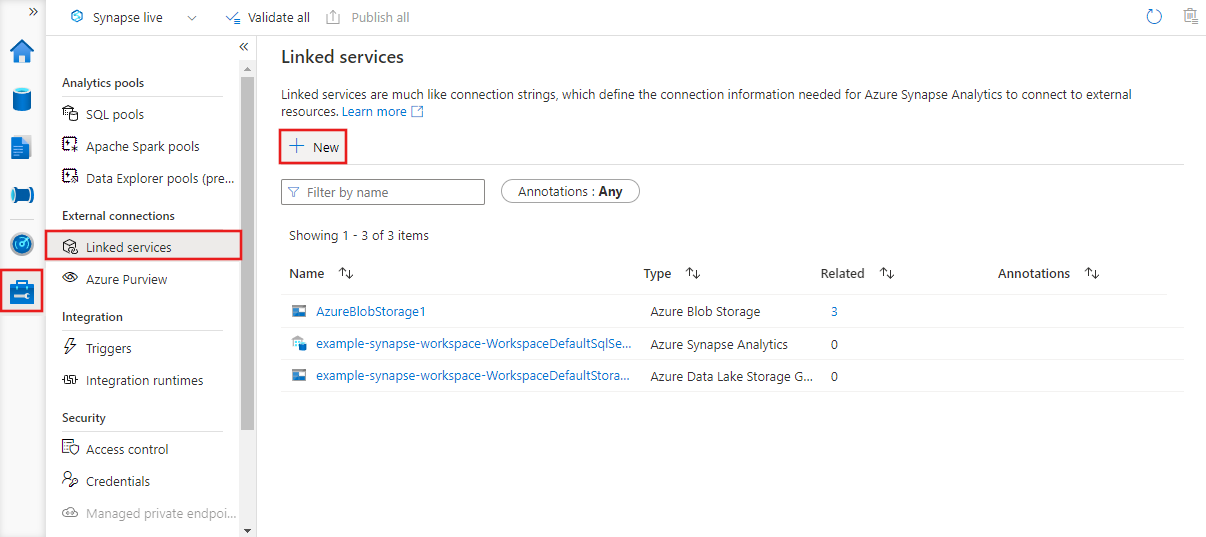
Linked service with UI
To create a new linked service in Azure Data Factory Studio, select the Manage tab and then linked services, where you can see any existing linked services you defined. Select + New to create a new linked service.
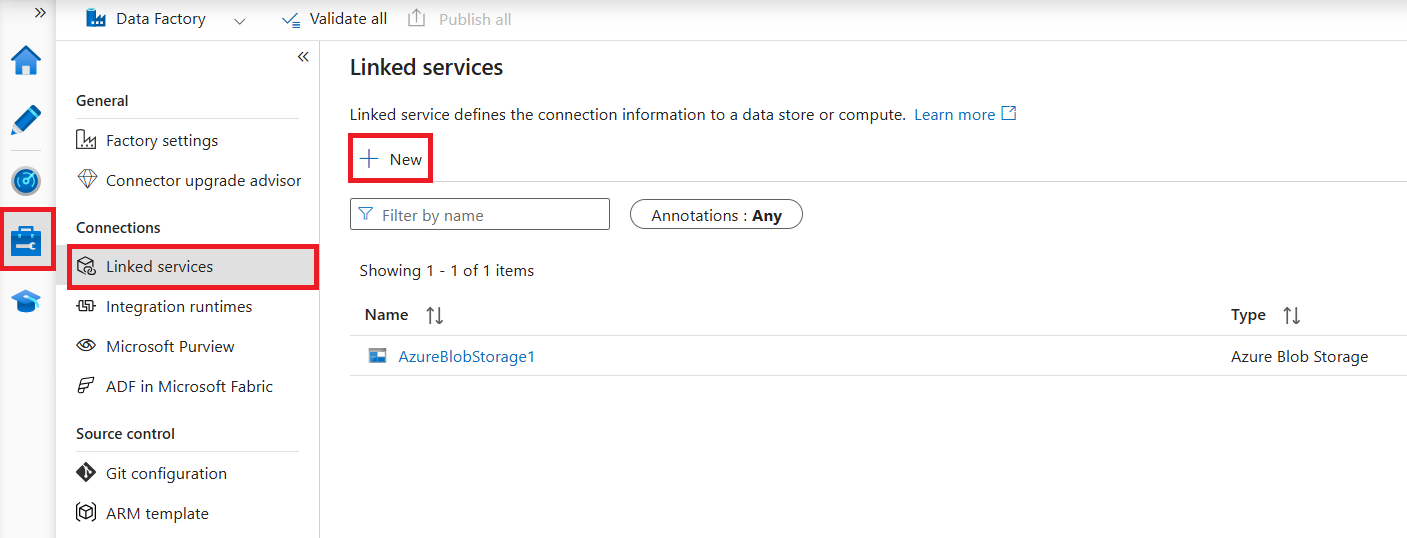
After selecting + New to create a new linked service, you can choose any of the supported connectors and configure its details accordingly. Thereafter you can use the linked service in any pipelines you create.
Linked service JSON
A linked service is defined in JSON format as follows:
{
"name": "<Name of the linked service>",
"properties": {
"type": "<Type of the linked service>",
"typeProperties": {
"<data store or compute-specific type properties>"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
The following table describes properties in the above JSON:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| name | Name of the linked service. See Naming rules. | Yes |
| type | Type of the linked service. For example: AzureBlobStorage (data store) or AzureBatch (compute). See the description for typeProperties. | Yes |
| typeProperties | The type properties are different for each data store or compute. For the supported data store types and their type properties, see the connector overview article. Navigate to the data store connector article to learn about type properties specific to a data store. For the supported compute types and their type properties, see Compute linked services. |
Yes |
| connectVia | The Integration Runtime to be used to connect to the data store. You can use Azure Integration Runtime or Self-hosted Integration Runtime (if your data store is located in a private network). If not specified, it uses the default Azure Integration Runtime. | No |
Linked service example
The following linked service is an Azure Blob storage linked service. Notice that the type is set to Azure Blob storage. The type properties for the Azure Blob storage linked service include a connection string. The service uses this connection string to connect to the data store at runtime.
{
"name": "AzureBlobStorageLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "AzureBlobStorage",
"typeProperties": {
"connectionString": "DefaultEndpointsProtocol=https;AccountName=<accountname>;AccountKey=<accountkey>;EndpointSuffix=core.chinacloudapi.cn"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Create linked services
Linked services can be created in the Azure Data Factory UX via the management hub and any activities, datasets, or data flows that reference them.
You can create linked services by using one of these tools or SDKs: .NET API, PowerShell, REST API, Azure Resource Manager Template, and Azure portal.
When creating a linked service, the user needs appropriate authorization to the designated service. If sufficient access isn't granted, the user can't see the available resources and needs to use manual entry option.
Data store linked services
You can find the list of supported data stores in the connector overview article. Select a data store to learn the supported connection properties.
Compute linked services
Reference compute environments supported for details about different compute environments you can connect to from your service and the different configurations.
Related content
See the following tutorials for step-by-step instructions for creating pipelines and datasets by using one of these tools or SDKs.