Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article discusses how to update your Apache HBase cluster on Azure HDInsight to a newer version.
This article applies only if you use the same Azure Storage account for your source and destination clusters. To upgrade with a new or different Storage account for your destination cluster, see Migrate Apache HBase to HDInsight 5.1 with a new Storage account.
The downtime for upgrading may take more than 20 minutes. This downtime caused by the steps to flush all in-memory data, and wait for all procedure to complete and the time to configure and restart the services on the new cluster. Your results vary, depending on the number of nodes, amount of data, and other variables.
Review Apache HBase compatibility
Before upgrading Apache HBase, ensure the HBase versions on the source and destination clusters are compatible. Review the HBase version compatibility matrix and release notes in the HBase Reference Guide to make sure your application is compatible with the new version.
Here's an example compatibility matrix. Y indicates compatibility and N indicates a potential incompatibility:
| Compatibility type | Major version | Minor version | Patch |
|---|---|---|---|
| Client-Server wire compatibility | N | Y | Y |
| Server-Server compatibility | N | Y | Y |
| File format compatibility | N | Y | Y |
| Client API compatibility | N | Y | Y |
| Client binary compatibility | N | N | Y |
| Server-side limited API compatibility | |||
| Stable | N | Y | Y |
| Evolving | N | N | Y |
| Unstable | N | N | N |
| Dependency compatibility | N | Y | Y |
| Operational compatibility | N | N | Y |
For more information about HDInsight versions and compatibility, see Azure HDInsight versions.
Apache HBase cluster migration overview
To upgrade your Apache HBase cluster on Azure HDInsight, complete the following basic steps. For detailed instructions, see the detailed steps and commands, or use the scripts from the section Migrate HBase using scripts for automated migration.
Prepare the source cluster:
- Stop data ingestion.
- Check cluster health
- Stop replication if needed
- Flush
memstoredata. - Stop HBase.
- For clusters with accelerated writes, back up the Write Ahead Log (WAL) directory.
Prepare the destination cluster:
- Create the destination cluster.
- Stop HBase from Ambari.
- Update
fs.defaultFSin HDFS service configs to refer to the original source cluster container. - For clusters with accelerated writes, update
hbase.rootdirin HBase service configs to refer to the original source cluster container. - Clean Zookeeper data.
Complete the migration:
- Clean and migrate the WAL.
- Copy apps from the destination cluster's default container to the original source container.
- Start all services from the Ambari destination cluster.
- Verify HBase.
- Delete the source cluster.
Detailed migration steps and commands
Use these detailed steps and commands to migrate your Apache HBase cluster.
Prepare the source cluster
Stop ingestion to the source HBase cluster.
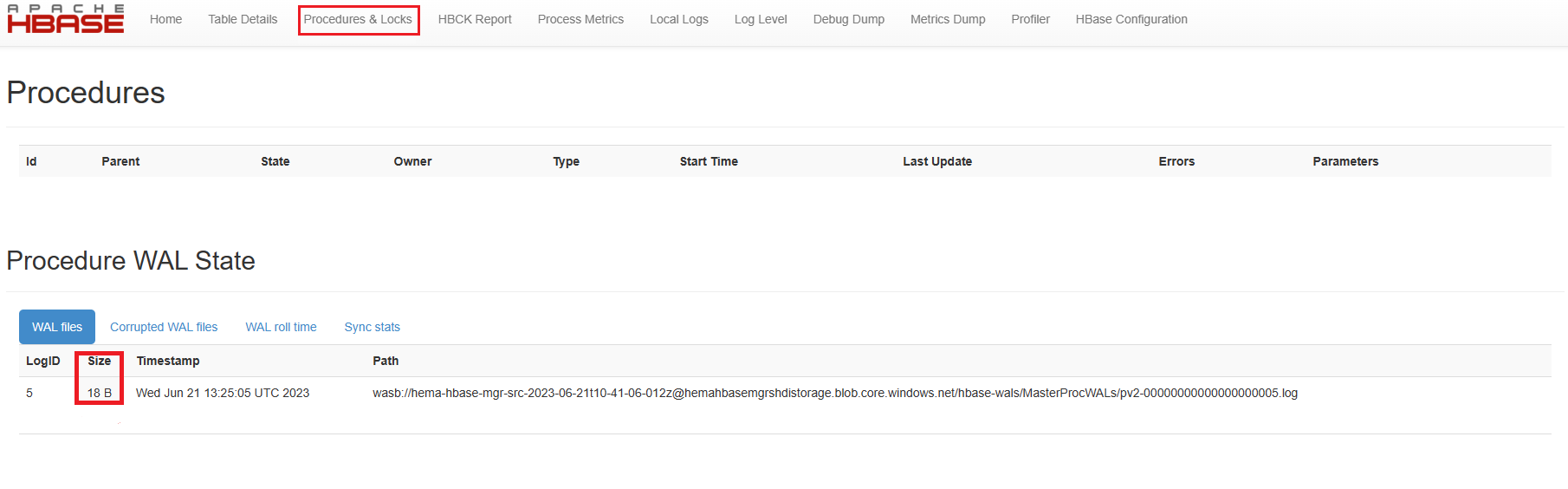
Check Hbase hbck to verify cluster health
- Verify HBCK Report page on HBase UI. Healthy cluster doesn't show any inconsistencies
- If any inconsistencies exist, fix inconsistencies using hbase hbck2
- Verify HBCK Report page on HBase UI. Healthy cluster doesn't show any inconsistencies
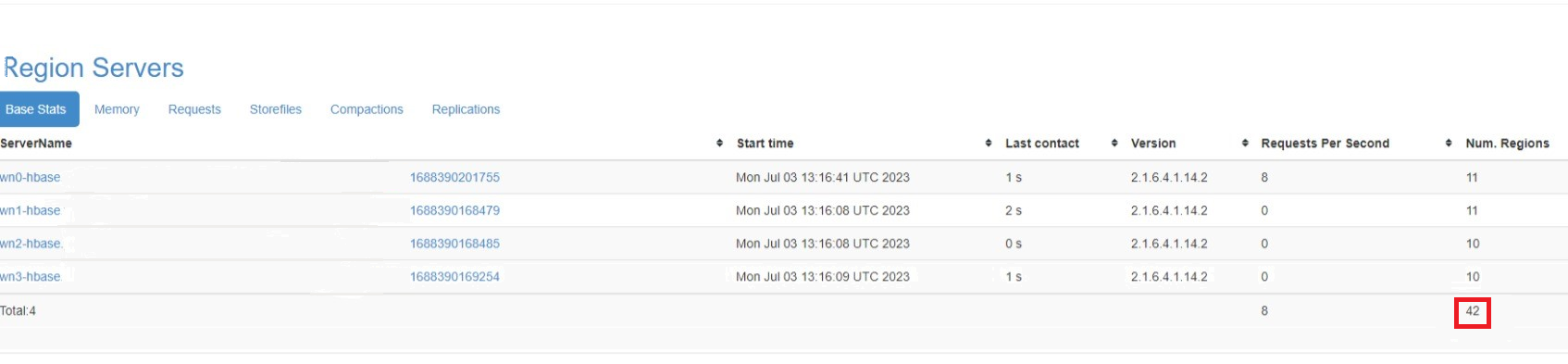
Note down number of regions in online at source cluster, so that the number can be referred at destination cluster after the migration.
If replication enabled on the cluster, stop and reenable the replication on destination cluster after migration. For more information, see Hbase replication guide
Flush the source HBase cluster you're upgrading.
HBase writes incoming data to an in-memory store called a
memstore. After thememstorereaches a certain size, HBase flushes it to disk for long-term storage in the cluster's storage account. Deleting the source cluster after an upgrade also deletes any data in thememstores. To retain the data, manually flush each table'smemstoreto disk before upgrading.You can flush the
memstoredata by running the flush_all_tables.sh script from the Azure hbase-utils GitHub repository.You can also flush
memstoredata by running the following HBase shell command from the HDInsight cluster:hbase shell flush "<table-name>"Wait for 15 mins and verify that all the procedures are completed, and masterProcWal files doesn't have any pending procedures.
STOP HBase
Sign in to Apache Ambari on the source cluster with
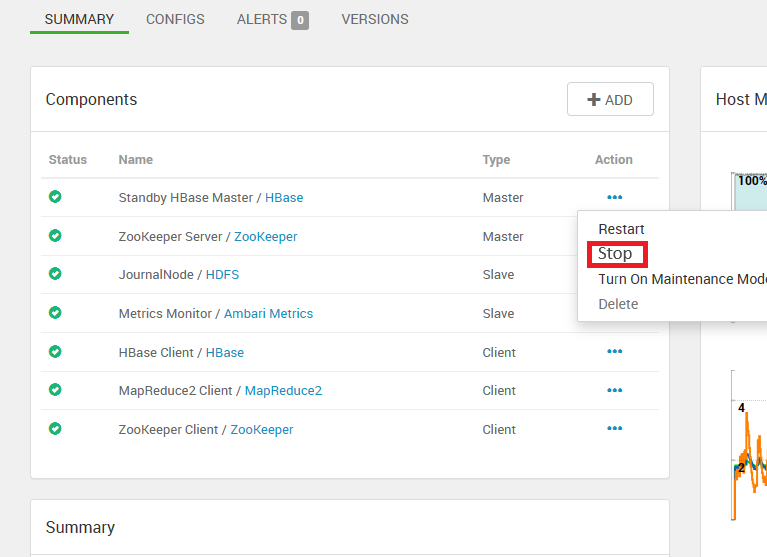
https://<OLDCLUSTERNAME>.azurehdinsight.cnTurn on maintenance mode for HBase.
Stop HBase Masters only first. First stop standby masters, in last stop Active HBase master.
Stop the HBase service, it stops remaining servers.
Note
HBase 2.4.11 doesn't support some of the old Procedures.
For more information on connecting to and using Ambari, see Manage HDInsight clusters by using the Ambari Web UI.
Stopping HBase in the previous steps to avoid creating new master proc WALs.
If your source HBase cluster doesn't have the Accelerated Writes feature, skip this step. For source HBase clusters with Accelerated Writes, back up the WAL directory under HDFS by running the following commands from an SSH session on any of the Zookeeper nodes or worker nodes of the source cluster.
hdfs dfs -mkdir /hbase-wal-backup hdfs dfs -cp hdfs://mycluster/hbasewal /hbase-wal-backup
Prepare the destination cluster
In the Azure portal, set up a new destination HDInsight cluster using the same storage account as the source cluster, but with a different container name:
Sign in to Apache Ambari on the new cluster at
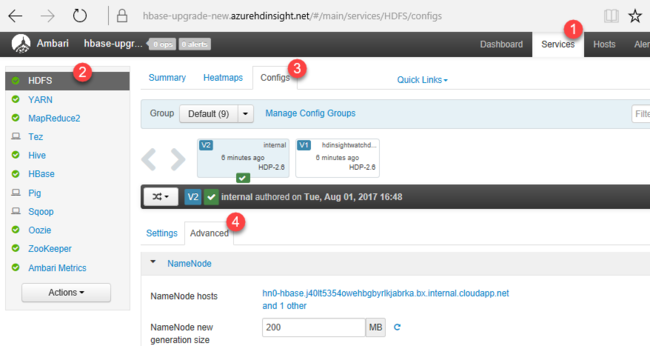
https://<NEWCLUSTERNAME>.azurehdinsight.cn, and stop the HBase services.Under Services > HDFS > Configs > Advanced > Advanced core-site, change the
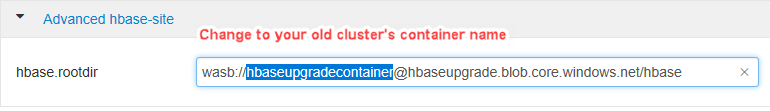
fs.defaultFSHDFS setting to point to the original source cluster container name. For example, the setting in the following screenshot should be changed towasbs://hbase-upgrade-old-2021-03-22.If your destination cluster has the Accelerated Writes feature, change the
hbase.rootdirpath to point to the original source cluster container name. For example, the following path should be changed tohbase-upgrade-old-2021-03-22. If your cluster doesn't have Accelerated Writes, skip this step.Clean the Zookeeper data on the destination cluster by running the following commands in any Zookeeper node or worker node:
hbase zkcli deleteall /hbase-unsecure quitNote
In some versions of Apache ZooKeeper,
rmris used instead ofdeleteall.
Clean and migrate WAL
Run the following commands, depending on your source HDInsight version and whether the source and destination clusters have Accelerated Writes.
- The destination cluster is always HDInsight version 4.0, since HDInsight 3.6 is in Basic support and isn't recommended for new clusters.
- The HDFS copy command is
hdfs dfs <copy properties starting with -D> -cp <source> <destination> # Serial execution.
Note
- The
<source-container-fullpath>for storage type WASB iswasbs://<source-container-name>@<storageaccountname>.blob.core.chinacloudapi.cn. - The
<source-container-fullpath>for storage type Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 isabfs://<source-container-name>@<storageaccountname>.dfs.core.chinacloudapi.cn.
- The source cluster is HDInsight 4.0 with Accelerated Writes, and the destination cluster has Accelerated Writes.
- The source cluster is HDInsight 4.0 without Accelerated Writes, and the destination cluster has Accelerated Writes.
- The source cluster is HDInsight 4.0 without Accelerated Writes, and the destination cluster doesn't have Accelerated Writes.
The source cluster is HDInsight 4.0 with Accelerated Writes, and the destination cluster has Accelerated Writes
Clean the WAL FS data for the destination cluster, and copy the WAL directory from the source cluster into the destination cluster's HDFS. Copy the directory by running the following commands in any Zookeeper node or worker node on the destination cluster:
sudo -u hbase hdfs dfs -rm -r hdfs://mycluster/hbasewal
sudo -u hbase hdfs dfs -cp <source-container-fullpath>/hbase-wal-backup/hbasewal hdfs://mycluster/
The source cluster is HDInsight 4.0 without Accelerated Writes, and the destination cluster has Accelerated Writes
Clean the WAL FS data for the destination cluster, and copy the WAL directory from the source cluster into the destination cluster's HDFS. Copy the directory by running the following commands in any Zookeeper node or worker node on the destination cluster:
sudo -u hbase hdfs dfs -rm -r hdfs://mycluster/hbasewal
sudo -u hbase hdfs dfs -cp <source-container-fullpath>/hbase-wals/* hdfs://mycluster/hbasewal
The source cluster is HDInsight 4.0 without Accelerated Writes, and the destination cluster doesn't have Accelerated Writes
Clean the WAL FS data for the destination cluster, and copy the source cluster WAL directory into the destination cluster's HDFS. To copy the directory, run the following commands in any Zookeeper node or worker node on the destination cluster:
sudo -u hbase hdfs dfs -rm -r /hbase-wals/*
sudo -u hbase hdfs dfs -Dfs.azure.page.blob.dir="/hbase-wals" -cp <source-container-fullpath>/hbase-wals /
Complete the migration
Using the
sudo -u hdfsuser context, copy the folder/hdp/apps/<new-version-name>and its contents from the<destination-container-fullpath>to the/hdp/appsfolder under<source-container-fullpath>. You can copy the folder by running the following commands on the destination cluster:sudo -u hdfs hdfs dfs -cp /hdp/apps/<hdi-version> <source-container-fullpath>/hdp/appsFor example:
sudo -u hdfs hdfs dfs -cp /hdp/apps/4.1.3.6 wasbs://hbase-upgrade-old-2021-03-22@hbaseupgrade.blob.core.chinacloudapi.cn/hdp/appsOn the destination cluster, save your changes, and restart all required services as Ambari indicates.
Point your application to the destination cluster.
Note
The static DNS name for your application changes when you upgrade. Rather than hard-coding this DNS name, you can configure a CNAME in your domain name's DNS settings that points to the cluster's name. Another option is to use a configuration file for your application that you can update without redeploying.
Start the ingestion.
Verify HBase consistency and simple Data Definition Language (DDL) and Data Manipulation Language (DML) operations.
If the destination cluster is satisfactory, delete the source cluster.
Migrate HBase using scripts
Note down number of regions in online at source cluster, so that the number can be referred at destination cluster after the migration.

Flush the source HBase cluster you're upgrading.
HBase writes incoming data to an in-memory store called a
memstore. After thememstorereaches a certain size, HBase flushes it to disk for long-term storage in the cluster's storage account. Deleting the source cluster after an upgrade also deletes any data in thememstores. To retain the data, manually flush each table'smemstoreto disk before upgrading.You can flush the
memstoredata by running the flush_all_tables.sh script from the Azure hbase-utils GitHub repository.You can also flush
memstoredata by running the following HBase shell command from the HDInsight cluster:hbase shell flush "<table-name>"Wait for 15 mins and verify that all the procedures are completed, and masterProcWal files doesn't have any pending procedures.
Execute the script migrate-to-HDI5.1-hbase-source.sh on the source cluster and migrate-hbase-dest.sh on the destination cluster. Use the following instructions to execute these scripts.
Note
These scripts don't copy the HBase old WALs as part of the migration; therefore, the scripts are not to be used on clusters that have either HBase Backup or Replication feature enabled.
On source cluster
sudo bash migrate-to-HDI5.1-hbase-source.shOn destination cluster
sudo bash migrate-hbase-dest.sh -f <src_default_Fs>
Mandatory argument for the above command:
-f, --src-fs
The fs.defaultFS of the source cluster
For example:
-f wasb://anynamehbase0316encoder-2021-03-17t01-07-55-935z@anynamehbase0hdistorage.blob.core.chinacloudapi.cn
Troubleshooting
Use case 1:
If Hbase masters and region servers up and regions stuck in transition or only one region, for example, hbase:meta region is assigned. Waiting for other regions to assign
Solution:
ssh into any ZooKeeper node of original cluster and run
kinit -k -t /etc/security/keytabs/hbase.service.keytab hbase/<zk FQDN>if this is ESP clusterRun
echo "scan 'hbase:meta'" | hbase shell > meta.outto read thehbase:metainto a fileRun
grep "info:sn" meta.out | awk '{print $4}' | sort | uniqto get all RS instance names where the regions were present in old cluster. Output should be likevalue=<wn FQDN>,16020,........Create a dummy WAL dir with that
wnvalueIf the cluster is accelerated write cluster
hdfs dfs -mkdir hdfs://mycluster/hbasewal/WALs/<wn FQDN>,16020,.........If the cluster is nonaccelarated Write cluster
hdfs dfs -mkdir /hbase-wals/WALs/<wn FQDN>,16020,.........Restart active
Hmaster
Next steps
To learn more about Apache HBase and upgrading HDInsight clusters, see the following articles: