Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this quickstart, you create a simulated X.509 device on a Windows computer. You use device sample Java code to connect this simulated device with your IoT hub using an individual enrollment with the Device Provisioning Service (DPS).
Prerequisites
- Familiar with provisioning concepts.
- Completion of Set up IoT Hub Device Provisioning Service with the Azure portal.
- An Azure account with an active subscription. Create a trial subscription.
- Java SE Development Kit 8.
- Maven.
- Git.
Prepare the environment
Make sure you have Java SE Development Kit 8 installed on your machine.
Download and install Maven.
Make sure Git is installed on your machine and is added to the environment variables accessible to the command window. See Software Freedom Conservancy's Git client tools for the latest version of
gittools to install, which includes the Git Bash, the command-line app that you can use to interact with your local Git repository.Open a command prompt. Clone the GitHub repo for device simulation code sample:
git clone https://github.com/Azure/azure-iot-sdk-java.git --recursiveNavigate to the root
azure-iot-sdk-java` directory and build the project to download all needed packages.cd azure-iot-sdk-java mvn install -DskipTests=trueNavigate to the certificate generator project and build the project.
cd azure-iot-sdk-java/provisioning/provisioning-tools/provisioning-x509-cert-generator mvn clean install
Create a self-signed X.509 device certificate and individual enrollment entry
In this section you, will use a self-signed X.509 certificate, it is important to keep in mind the following:
- Self-signed certificates are for testing only, and should not be used in production.
- The default expiration date for a self-signed certificate is one year.
You will use sample code from the Azure IoT SDK for Java to create the certificate to be used with the individual enrollment entry for the simulated device.
The Azure IoT Device Provisioning Service supports two types of enrollments:
- Enrollment groups: Used to enroll multiple related devices.
- Individual enrollments: Used to enroll a single device.
This article demonstrates individual enrollments.
Using the command prompt from previous steps, navigate to the
targetfolder, then execute the .jar file created in the previous step.cd target java -jar ./provisioning-x509-cert-generator-{version}-with-deps.jarEnter N for Do you want to input common name. Copy to the clipboard the output of
Client Cert, starting from -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- through -----END CERTIFICATE-----.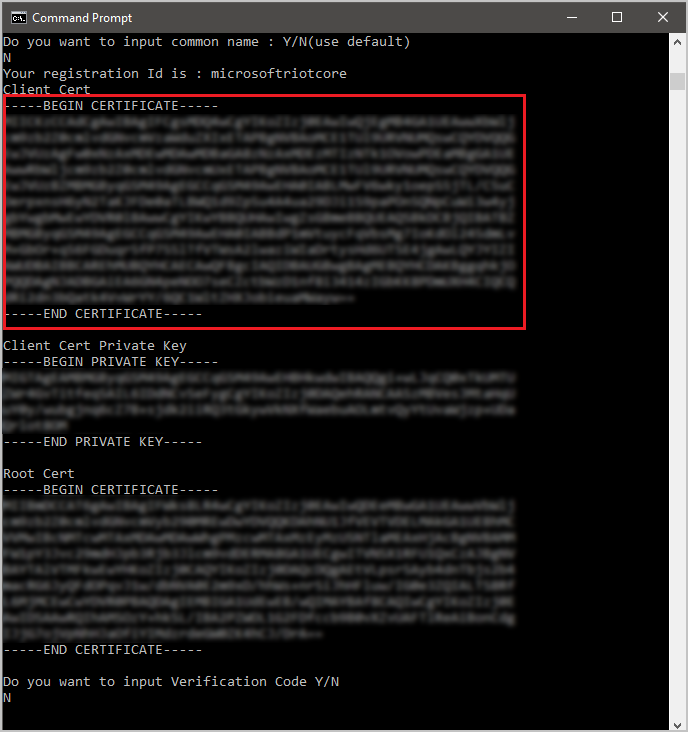
Create a file named X509individual.pem on your Windows machine, open it in an editor of your choice, and copy the clipboard contents to this file. Save the file and close your editor.
In the command prompt, enter N for Do you want to input Verification Code and keep the program output open for reference later in the quickstart. Later you copy the
Client CertandClient Cert Private Keyvalues, for use in the next section.Sign in to the Azure portal, select the All resources button on the left-hand menu and open your Device Provisioning Service instance.
From the Device Provisioning Service menu, select Manage enrollments. Select Individual Enrollments tab and select the Add individual enrollment button at the top.
In the Add Enrollment panel, enter the following information:
Select X.509 as the identity attestation Mechanism.
Under the Primary certificate .pem or .cer file, choose Select a file to select the certificate file X509individual.pem created in the previous steps.
Optionally, you may provide the following information:
- Select an IoT hub linked with your provisioning service.
- Enter a unique device ID. Make sure to avoid sensitive data while naming your device.
- Update the Initial device twin state with the desired initial configuration for the device.
- Once complete, press the Save button.
Upon successful enrollment, your X.509 device appears as microsoftriotcore under the Registration ID column in the Individual Enrollments tab.
Simulate the device
From the Device Provisioning Service menu, select Overview and note your ID Scope and Provisioning Service Global Endpoint.
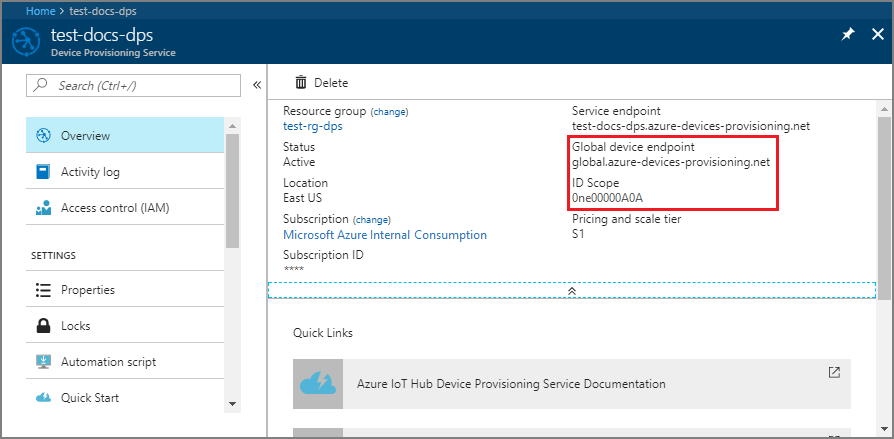
Open a command prompt. Navigate to the sample project folder of the Java SDK repository.
cd azure-iot-sdk-java/provisioning/provisioning-samples/provisioning-X509-sampleEnter the provisioning service and X.509 identity information in your code. This is used during autoprovisioning, for attestation of the simulated device, prior to device registration:
Edit the file
/src/main/java/samples/com/microsoft/azure/sdk/iot/ProvisioningX509Sample.java, to include your ID Scope and Provisioning Service Global Endpoint as noted previously. Also include Client Cert and Client Cert Private Key as noted in the previous section.private static final String idScope = "[Your ID scope here]"; private static final String globalEndpoint = "[Your Provisioning Service Global Endpoint here]"; private static final ProvisioningDeviceClientTransportProtocol PROVISIONING_DEVICE_CLIENT_TRANSPORT_PROTOCOL = ProvisioningDeviceClientTransportProtocol.HTTPS; private static final String leafPublicPem = "<Your Public PEM Certificate here>"; private static final String leafPrivateKey = "<Your Private PEM Key here>";Use the following format when copying/pasting your certificate and private key:
private static final String leafPublicPem = "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----\n" + "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX\n" + "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX\n" + "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX\n" + "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX\n" + "+XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX\n" + "-----END CERTIFICATE-----\n"; private static final String leafPrivateKey = "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\n" + "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX\n" + "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX\n" + "XXXXXXXXXX\n" + "-----END PRIVATE KEY-----\n";
Build the sample. Navigate to the
targetfolder and execute the created .jar file.mvn clean install cd target java -jar ./provisioning-x509-sample-{version}-with-deps.jarIn the Azure portal, navigate to the IoT hub linked to your provisioning service and open the Device Explorer blade. Upon successful provisioning of the simulated X.509 device to the hub, its device ID appears on the Device Explorer blade, with STATUS as enabled. You might need to press the Refresh button at the top if you already opened the blade prior to running the sample device application.

Note
If you changed the initial device twin state from the default value in the enrollment entry for your device, it can pull the desired twin state from the hub and act accordingly. For more information, see Understand and use device twins in IoT Hub.
Clean up resources
If you plan to continue working on and exploring the device client sample, do not clean up the resources created in this quickstart. If you do not plan to continue, use the following steps to delete all resources created by this quickstart.
- Close the device client sample output window on your machine.
- From the left-hand menu in the Azure portal, select All resources and then select your Device Provisioning service. Open the Manage Enrollments blade for your service, and then select the Individual Enrollments tab. Select the check box next to the REGISTRATION ID of the device you enrolled in this quickstart, and press the Delete button at the top of the pane.
- From the left-hand menu in the Azure portal, select All resources and then select your IoT hub. Open the IoT devices blade for your hub, select the check box next to the DEVICE ID of the device you registered in this quickstart, and then press the Delete button at the top of the pane.
Next steps
In this quickstart, you created a simulated X.509 device on your Windows machine. You configured its enrollment in your Azure IoT Hub Device Provisioning Service, then autoprovisioned the device to your IoT hub. To learn how to enroll your X.509 device programmatically, continue to the quickstart for programmatic enrollment of X.509 devices.