Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
You can use the MXChip IoT DevKit to develop and prototype Internet of Things (IoT) solutions that take advantage of Azure services. The kit includes an Arduino-compatible board with rich peripherals and sensors, an open-source board package, and a rich sample gallery.
What you learn
- How to create an IoT hub and register a device for the MXChip IoT DevKit.
- How to connect the IoT DevKit to Wi-Fi and configure the IoT Hub connection string.
- How to send the DevKit sensor telemetry data to your IoT hub.
- How to prepare the development environment and develop application for the IoT DevKit.
Don't have a DevKit yet? Try the DevKit simulator or purchase a DevKit.
You can find the source code for all DevKit tutorials from code samples gallery.
What you need
- A MXChip IoT DevKit board with a Micro-USB cable. Get it now.
- A computer running Windows 10, macOS 10.10+ or Ubuntu 18.04+.
- An active Azure subscription. Activate a free 30-day trial Azure account.
You can use the local Azure CLI.
If you prefer, install the Azure CLI to run CLI reference commands.
Local Azure CLI, see how to install the Azure CLI. If you're running on Windows or macOS, consider running Azure CLI in a Docker container. For more information, see How to run the Azure CLI in a Docker container.
Sign in to the Azure CLI by using the az login command. To finish the authentication process, follow the steps displayed in your terminal. For other sign-in options, see Sign in with the Azure CLI.
When you're prompted, install the Azure CLI extension on first use. For more information about extensions, see Use extensions with the Azure CLI.
Run az version to find the version and dependent libraries that are installed. To upgrade to the latest version, run az upgrade.
Prepare the development environment
Follow these steps to prepare the development environment for the DevKit:
Install Visual Studio Code with Azure IoT Tools extension package
Install Arduino IDE. It provides the necessary toolchain for compiling and uploading Arduino code.
- Windows: Use Windows Installer version. Do not install from the app store.
- macOS: Drag and drop the extracted Arduino.app into
/Applicationsfolder. - Ubuntu: Unzip it into folder such as
$HOME/Downloads/arduino-1.8.8
Install Visual Studio Code, a cross platform source code editor with powerful intellisense, code completion and debugging support as well as rich extensions can be installed from marketplace.
Launch VS Code, look for Arduino in the extension marketplace and install it. This extension provides enhanced experiences for developing on Arduino platform.
Look for Azure IoT Tools in the extension marketplace and install it.
Or copy and paste this URL into a browser window:
vscode:extension/vsciot-vscode.azure-iot-toolsNote
The Azure IoT Tools extension pack contains the Azure IoT Device Workbench which is used to develop and debug on various IoT devkit devices. The Azure IoT Hub extension, also included with the Azure IoT Tools extension pack, is used to manage and interact with Azure IoT Hubs.
Configure VS Code with Arduino settings.
In Visual Studio Code, click File > Preferences > Settings (on macOS, Code > Preferences > Settings). Then click the Open Settings (JSON) icon in the upper-right corner of the Settings page.
The correct path to your Arduino installation must be configured in VS Code. Add following lines to configure Arduino depending on your platform and the directory path where you installed the Arduino IDE:
Windows:
"arduino.path": "C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Arduino", "arduino.additionalUrls": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/VSChina/azureiotdevkit_tools/master/package_azureboard_index.json"macOS:
"arduino.path": "/Applications", "arduino.additionalUrls": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/VSChina/azureiotdevkit_tools/master/package_azureboard_index.json"Ubuntu:
Replace the {username} placeholder below with your username.
"arduino.path": "/home/{username}/Downloads/arduino-1.8.13", "arduino.additionalUrls": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/VSChina/azureiotdevkit_tools/master/package_azureboard_index.json"
Click
F1to open the command palette, type and select Arduino: Board Manager. Search for AZ3166 and install the latest version.
Install ST-Link drivers
ST-Link/V2 is the USB interface that IoT DevKit uses to communicate with your development machine. You need to install it on Windows to flash the compiled device code to the DevKit. Follow the OS-specific steps to allow the machine access to your device.
Windows: Download and install USB driver from STMicroelectronics website.
macOS: No driver is required for macOS.
Ubuntu: Run the commands in terminal and sign out and sign in for the group change to take effect:
# Copy the default rules. This grants permission to the group 'plugdev' sudo cp ~/.arduino15/packages/AZ3166/tools/openocd/0.10.0/linux/contrib/60-openocd.rules /etc/udev/rules.d/ sudo udevadm control --reload-rules # Add yourself to the group 'plugdev' # Logout and log back in for the group to take effect sudo usermod -a -G plugdev $(whoami)
Now you are all set with preparing and configuring your development environment.
Prepare Azure resources
For this article, you will need to have an IoT Hub created and a device registered to use the hub. The following subsections show how to create the resources with the Azure CLI.
You can also create an IoT Hub and register a device within Visual Studio code using the Azure IoT Tools extensions. For more information on creating the hub and device within VS Code, see Use Azure IoT Tools for VS Code.
Create an IoT hub
If you haven't already created a IoT Hub, follow the steps in Create an IoT Hub using Azure CLI.
Register a device
A device must be registered for the IoT DevKit in your IoT hub before it can connect. Use the steps below for the Azure Cloud Shell to register a new device.
Run the following command in Azure Cloud Shell to create the device identity.
YourIoTHubName: Replace this placeholder below with the name you choose for your IoT hub.
AZ3166Device: The name of the device you're registering. Use AZ3166Device as shown for the example in this article. If you choose a different name for your device, you need to use that name throughout this article, and update the device name in the sample applications before you run them.
az iot hub device-identity create --hub-name YourIoTHubName --device-id AZ3166DeviceNote
If you get an error running
device-identity, install the Azure IoT Extension for Azure CLI. Run the following command to add the Azure IoT Extension for Azure CLI to your Cloud Shell instance. The IoT Extension adds commands that are specific to IoT Hub, IoT Edge, and IoT Device Provisioning Service (DPS) to Azure CLI.az extension add --name azure-iotRun the following commands in Azure Cloud Shell to get the device connection string for the device you just registered:
YourIoTHubName: Replace this placeholder below with the name you choose for your IoT hub.
az iot hub device-identity connection-string show --hub-name YourIoTHubName --device-id AZ3166Device --output tableMake a note of the device connection string, which looks like:
HostName={YourIoTHubName}.azure-devices.net;DeviceId=AZ3166Device;SharedAccessKey={YourSharedAccessKey}You use this value later.
Prepare your hardware
Hook up the following hardware to your computer:
- DevKit board
- Micro-USB cable

To connect the DevKit to your computer, follow these steps:
Connect the USB end to your computer.
Connect the Micro-USB end to the DevKit.
The green LED for power confirms the connection.

Update firmware
The DevKit Get Started firmware (devkit-getstarted-*.*.*.bin) connects to a device-specific endpoint on your IoT hub and sends temperature and humidity telemetry.
Download the latest version of GetStarted firmware (devkit-getstarted-..*.bin) for IoT DevKit. At the time of this update, the latest filename is devkit-getstarted-2.0.0.bin.
Make sure IoT DevKit connect to your computer via USB. Open File Explorer there is a USB mass storage device called AZ3166.
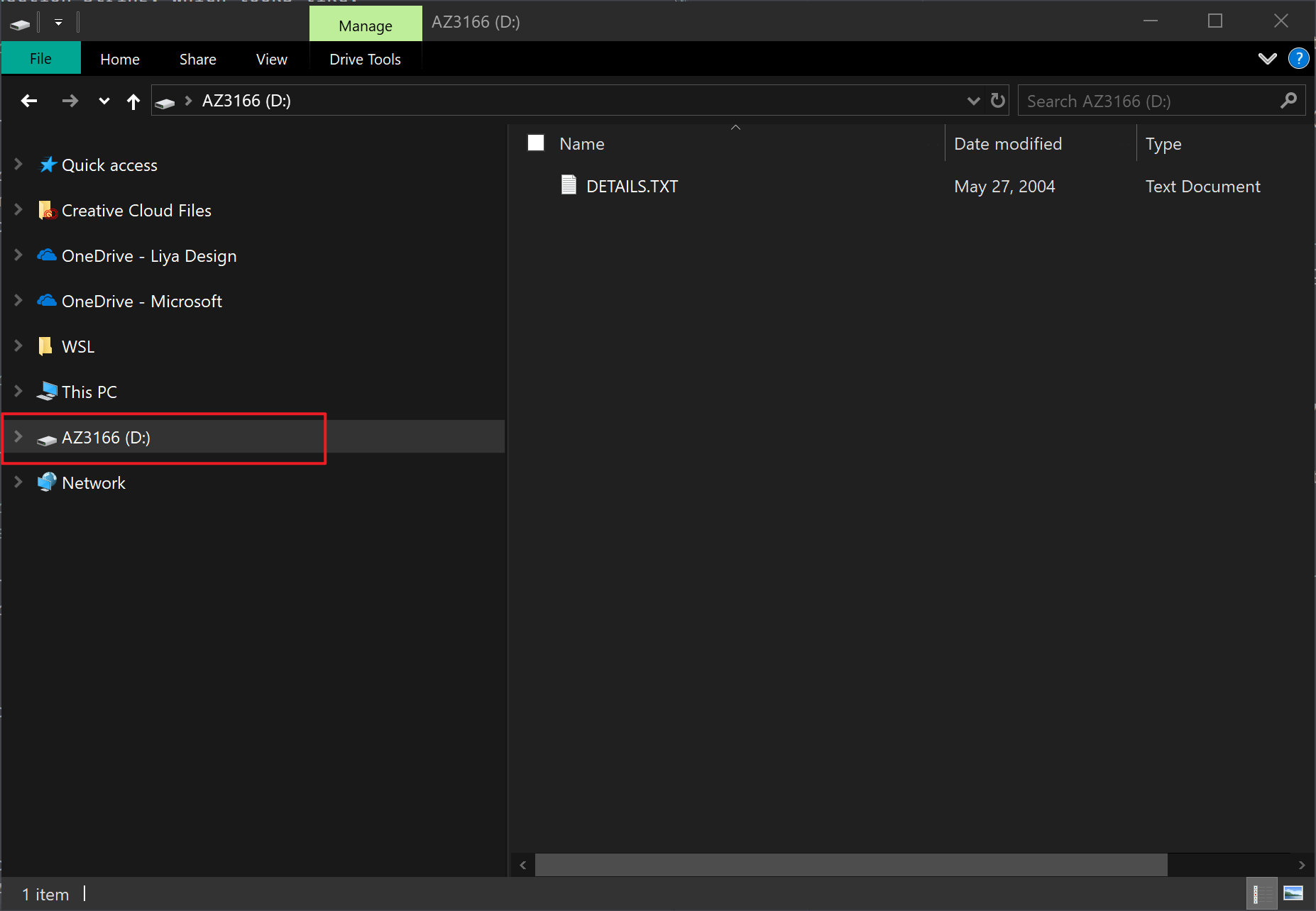
Drag and drop the firmware just downloaded into the mass storage device and it will flash automatically.
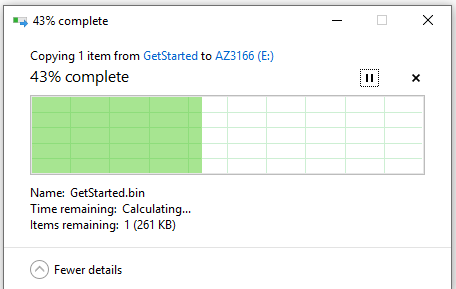
On the DevKit, Hold down the B button, and keep it pressed down. Push and release the Reset button. Afterwards, release button B. Your DevKit enters AP mode. To confirm, the screen displays the service set identifier (SSID) of the DevKit and the configuration portal IP address.
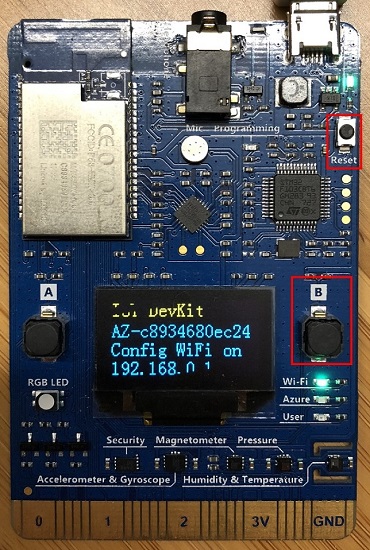
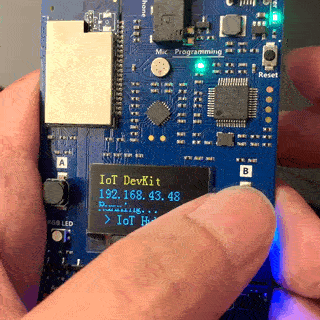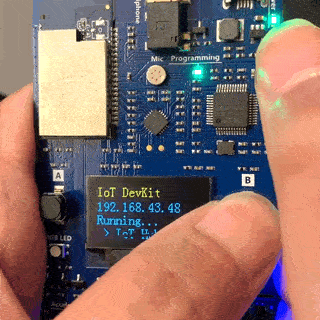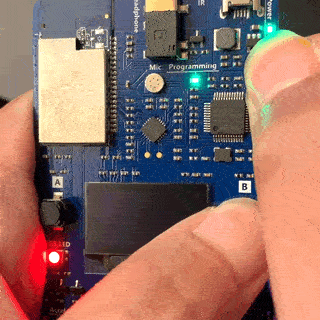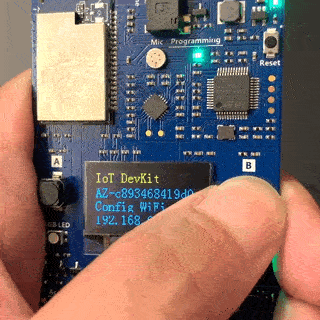
Use a Web browser on a different Wi-Fi enabled device (computer or mobile phone) to connect to the IoT DevKit SSID displayed in the previous step. If it asks for a password, leave it empty.
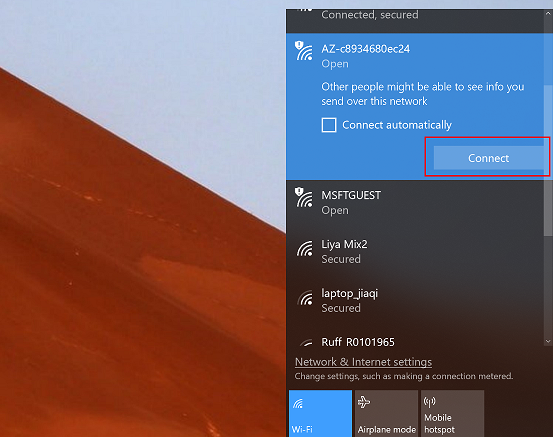
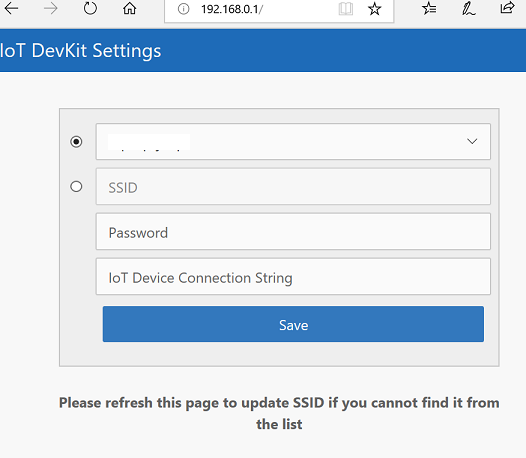
Open 192.168.0.1 in the browser. Select the Wi-Fi that you want the IoT DevKit to connect to, type the Wi-Fi password, then paste the device connection string you made note of previously. Then click Configure Device.
Note
The IoT DevKit only supports 2.4GHz network. Check FAQ for more details.
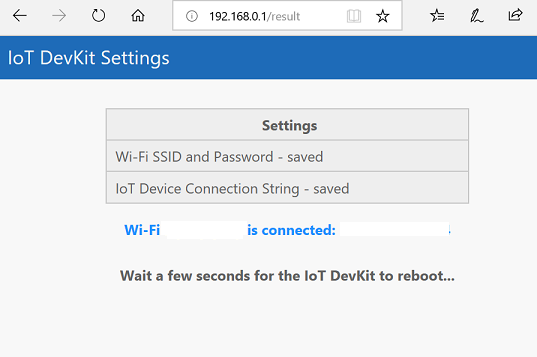
The WiFi information and device connection string will be stored into the IoT DevKit when you see the result page.
Note
After Wi-Fi is configured, your credentials will persist on the device for that connection, even if the device is unplugged.
The IoT DevKit reboots in a few seconds. On the DevKit screen, you see the IP address for the DevKit follows by the telemetry data including temperature and humidity value with message count send to Azure IoT Hub.


To verify the telemetry data sent to Azure, run the following command in Azure Cloud Shell:
az iot hub monitor-events --hub-name YourIoTHubName --output tableThis command monitors device-to-cloud (D2C) messages sent to your IoT Hub
Build your first project
Open sample code from sample gallery
The IoT DevKit contains a rich gallery of samples that you can use to learn connect the DevKit to various Azure services.
Make sure your IoT DevKit is not connected to your computer. Start VS Code first, and then connect the DevKit to your computer.
Click
F1to open the command palette, type and select Azure IoT Device Workbench: Open Examples.... Then select MXChip IoT DevKit as board.In the IoT Workbench Examples page, find Get Started and click Open Sample. Then select the default path to download the sample code.
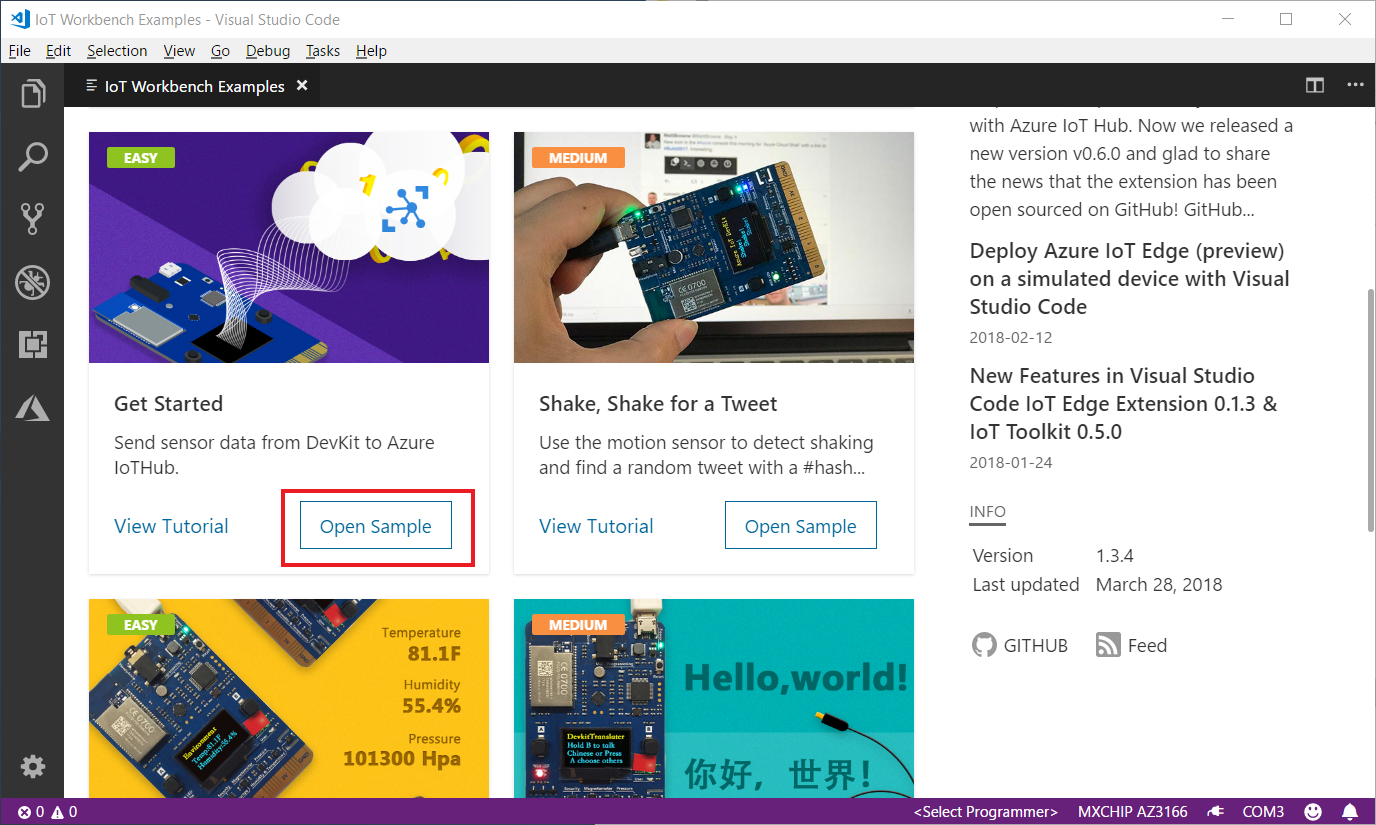
Review the code
The GetStarted.ino is the main Arduino sketch file.

To see how device telemetry is sent to the Azure IoT Hub, open the utility.cpp file in the same folder. View API Reference to learn how to use sensors and peripherals on IoT DevKit.
The DevKitMQTTClient used is a wrapper of the iothub_client from the Azure IoT SDKs and libraries for C to interact with Azure IoT Hub.
Configure and compile device code
In the bottom-right status bar, check the MXCHIP AZ3166 is shown as selected board and serial port with STMicroelectronics is used.
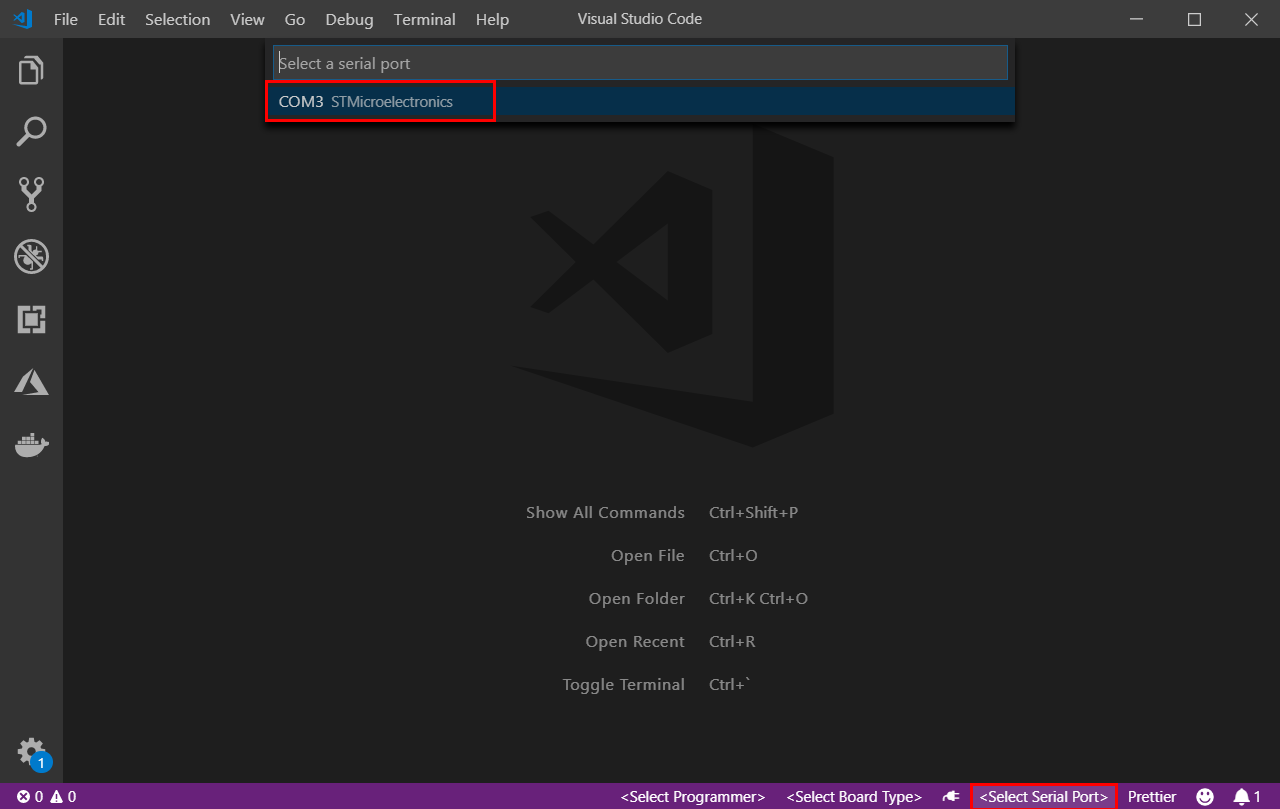
Click
F1to open the command palette, type and select Azure IoT Device Workbench: Configure Device Settings..., select Config Device Connection String. Then paste the connection string for your IoT device.On DevKit, hold down button A, push and release the reset button, and then release button A. Your DevKit enters configuration mode and saves the connection string.

Click
F1again, type and select Azure IoT Device Workbench: Upload Device Code. It starts compile and upload the code to DevKit.
The DevKit reboots and starts running the code. The DevKit will start sending telemetry to the hub.
Note
If there is any errors or interruptions, you can always recover by running the command again.
Use the Serial Monitor
The Serial Monitor in VS Code is useful to view logging information sent from the code. This logging information is generated using the LogInfo() API. This is useful for debugging purposes.
Click the power plug icon on the status bar to open the Serial Monitor:

The sample application is running successfully when you see the following results:
- The Serial Monitor displays the message sent to the IoT Hub.
- The LED on the MXChip IoT DevKit is blinking.
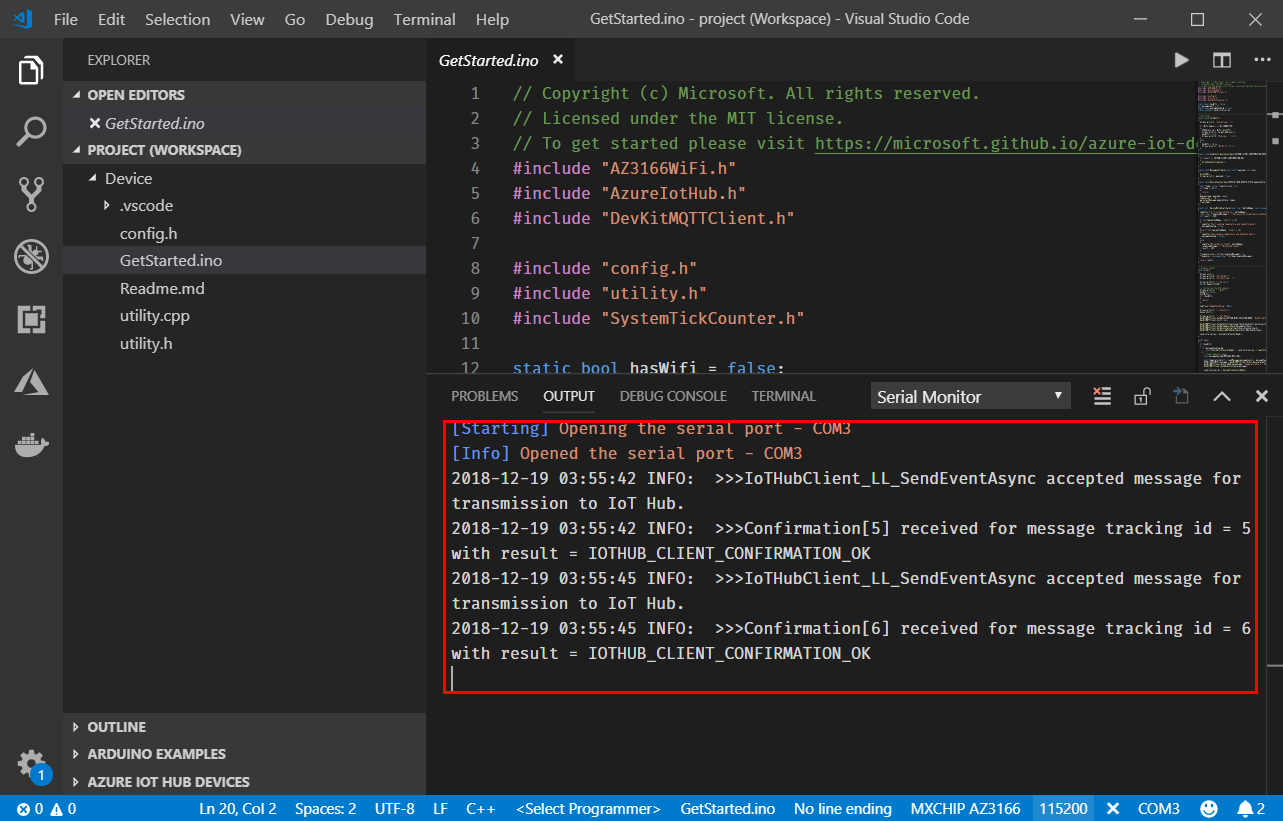
Note
You might encounter an error during testing in which the LED isn't blinking, the Azure portal doesn't show incoming data from the device, but the device OLED screen shows as Running.... To resolve the issue, in the Azure portal, go to the device in the IoT hub and send a message to the device. If you see the following response in the serial monitor in VS Code, it's possible that direct communication from the device is blocked at the router level. Check firewall and router rules that are configured for the connecting devices. Also, ensure that outbound port 1833 is open.
ERROR: mqtt_client.c (ln 454): Error: failure opening connection to endpoint
INFO: >>>Connection status: disconnected
ERROR: tlsio_mbedtls.c (ln 604): Underlying IO open failed
ERROR: mqtt_client.c (ln 1042): Error: io_open failed
ERROR: iothubtransport_mqtt_common.c (ln 2283): failure connecting to address atcsliothub.azure-devices.net.
INFO: >>>Re-connect.
INFO: IoThub Version: 1.3.6On DevKit, hold down button A, push and release the Reset button, and then release button A. Your DevKit stops sending telemetry and enters configuration mode. A full command list for configuration mode is shown in the Serial Monitor output window in VS Code.
************************************************ ** MXChip - Microsoft IoT Developer Kit ** ************************************************ Configuration console: - help: Help document. - version: System version. - exit: Exit and reboot. - scan: Scan Wi-Fi AP. - set_wifissid: Set Wi-Fi SSID. - set_wifipwd: Set Wi-Fi password. - set_az_iothub: Set IoT Hub device connection string. - set_dps_uds: Set DPS Unique Device Secret (UDS) for X.509 certificates.. - set_az_iotdps: Set DPS Symmetric Key. Format: "DPSEndpoint=global.azure-devices-provisioning.net;IdScope=XXX;DeviceId=XXX;SymmetricKey=XXX". - enable_secure: Enable secure channel between AZ3166 and secure chip.This mode supports commands like changing the IoT Hub device connection string you want to use. You can send text commands in the Serial Monitor by pressing
F1and choosing Arduino: Send Text to Serial Port.On DevKit, press and release the Reset button. This reboots the device so it can start sending telemetry again.
Use VS Code to view hub telemetry
At the end of the Prepare your hardware section, you used the Azure CLI to monitor device-to-cloud (D2C) messages in your IoT Hub. You can also monitor device-to-cloud (D2C) messages in VS Code using the Azure IoT Tools.
Sign in Azure portal, find the IoT Hub you created.
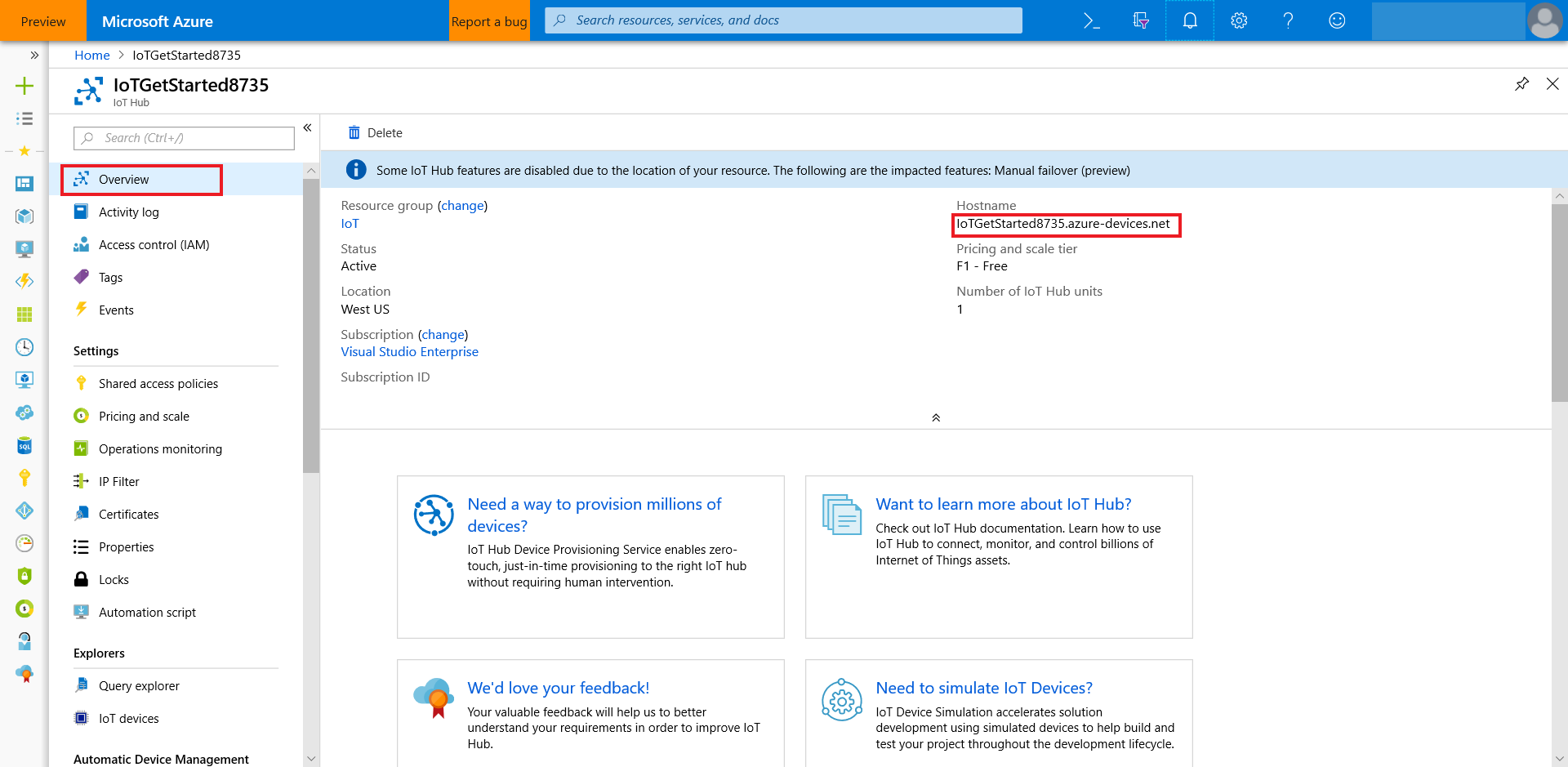
In the Shared access policies pane, click the iothubowner policy, and copy the connection string of your IoT hub.

In VS Code, click
F1, type and select Azure IoT Hub: Set IoT Hub Connection String. Paste your IoT Hub connection string into the field.
Expand the AZURE IOT HUB pane on the left, right click on the device name you created and select Start Monitoring Built-in Event Endpoint.
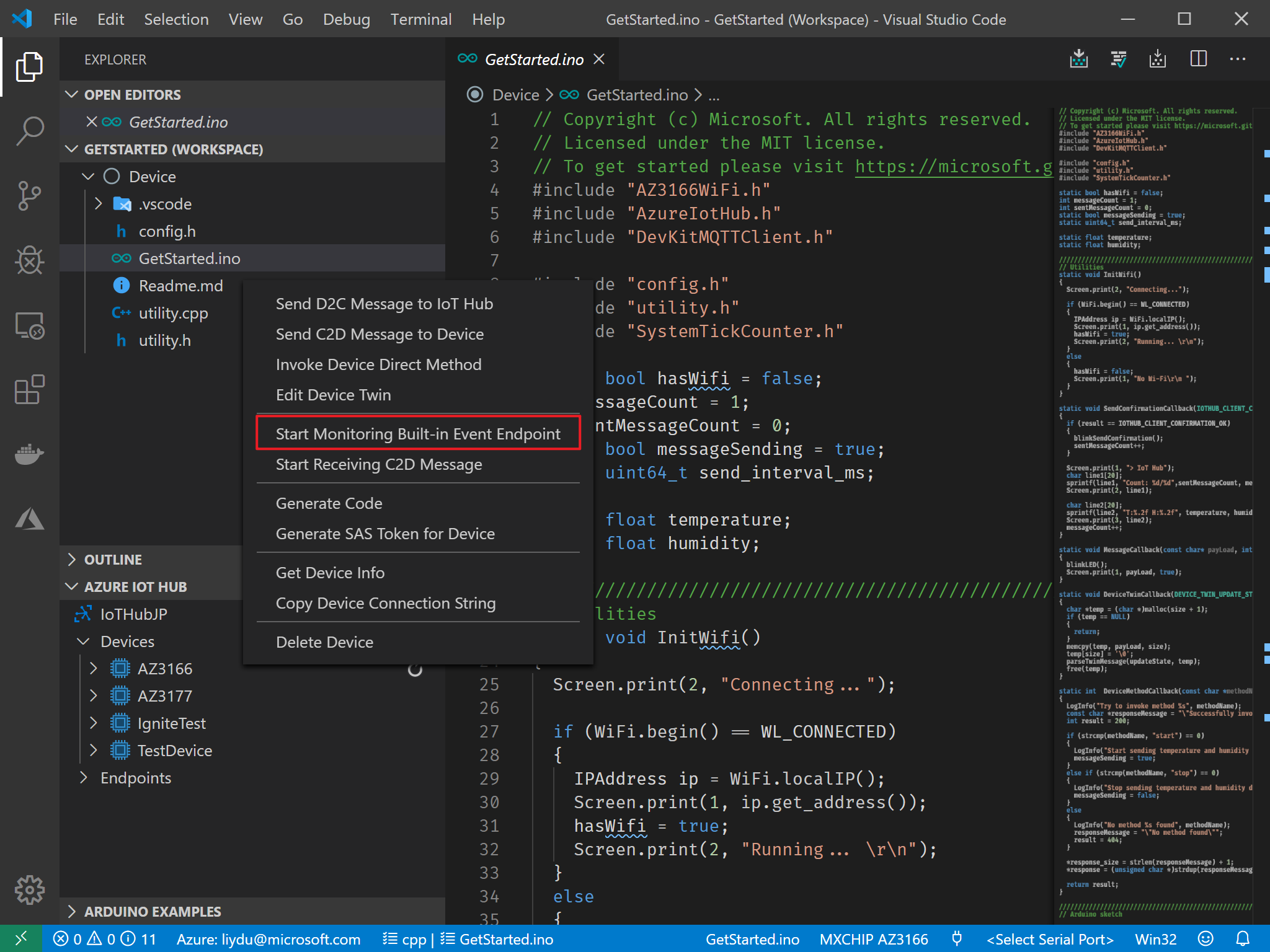
If you are prompted for a built-in endpoint, use the Event Hub-compatible endpoint shown by clicking Built-in endpoints for your IoT Hub in the Azure portal.
In OUTPUT pane, you can see the incoming D2C messages to the IoT Hub.
Make sure the output is filtered correctly by selecting Azure IoT Hub. This filtering can be used to switch between hub monitoring and the Serial Monitor output.

Problems and feedback
If you encounter problems, you can check for a solution in the IoT DevKit FAQ or reach out to us from Gitter. You can also give us feedback by leaving a comment on this page.
Next steps
You have successfully connected an MXChip IoT DevKit to your IoT hub, and you have sent the captured sensor data to your IoT hub.
To continue to get started with Azure IoT Hub and to explore other IoT scenarios using IoT DevKit, see the following: