Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO:
 Azure CLI ml extension v2 (current)
Azure CLI ml extension v2 (current)
 Python SDK azure-ai-ml v2 (current)
Python SDK azure-ai-ml v2 (current)
In this article, you learn how to schedule machine learning pipelines to run on Azure. You can schedule routine tasks like retraining models or regularly updating batch predictions based on elapsed time.
This article shows you how to create, retrieve, update, and deactivate schedules by using the Azure Machine Learning CLI, Azure Machine Learning SDK v2 for Python, or Azure Machine Learning studio UI.
Tip
To schedule jobs by using an external orchestrator, like Azure Data Factory or Microsoft Fabric, consider deploying your pipeline jobs under a batch endpoint.
Prerequisites
- An Azure subscription. If you don't have one, create a Trial before you begin.
- An Azure Machine Learning workspace. To create a workspace, see Create workspace resources.
- An understanding of Azure Machine Learning pipelines. For information, see What are machine learning pipelines.
- The Azure CLI and
mlextension installed by following the instructions in Install, set up, and use the CLI (v2). - Knowledge of how to create Azure Machine Learning YAML pipelines. For information, see Create and run machine learning pipelines using components with the Azure Machine Learning CLI.
Limitations
- Azure Machine Learning v2 schedules don't support event-based triggers.
- CLI and SDK v2 schedules support specifying complex recurrence patterns that contain multiple trigger timestamps. The studio UI displays the complex patterns but doesn't support editing them.
- The studio UI supports only v2 schedules, and can't list or access v1 schedules that are based on published pipelines or pipeline endpoints. You can create a schedule for an unpublished pipeline.
- If recurrence is set as the 31st or 30th day of every month, the schedule doesn't trigger jobs in months that have fewer days.
DAYSandMONTHSvalues aren't supported in cron schedule expressions. Values passed for these parameters are ignored and treated as*.- Even after assigning a managed identity to a schedule, the author must retain their job run permissions for the schedule to function.
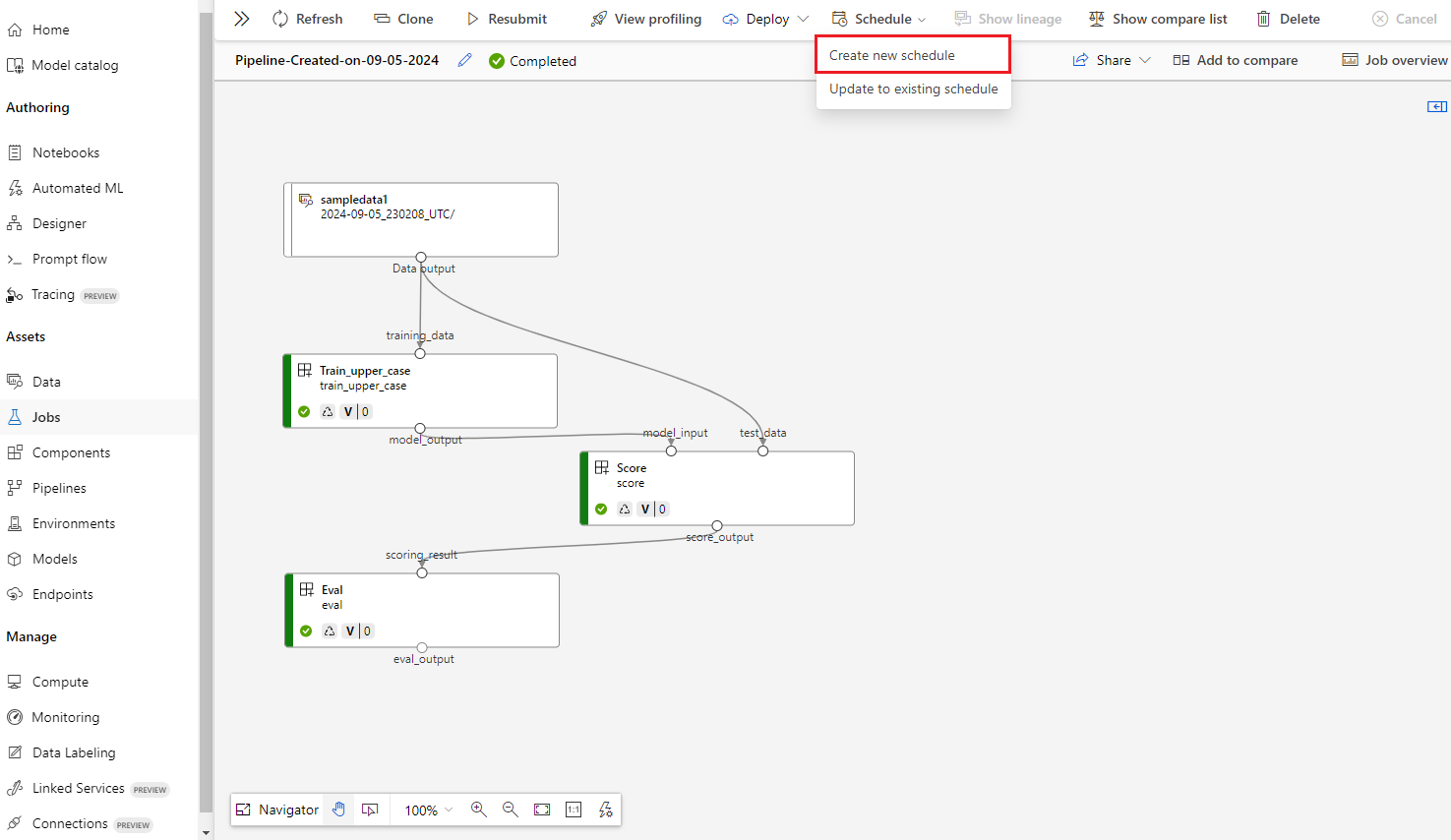
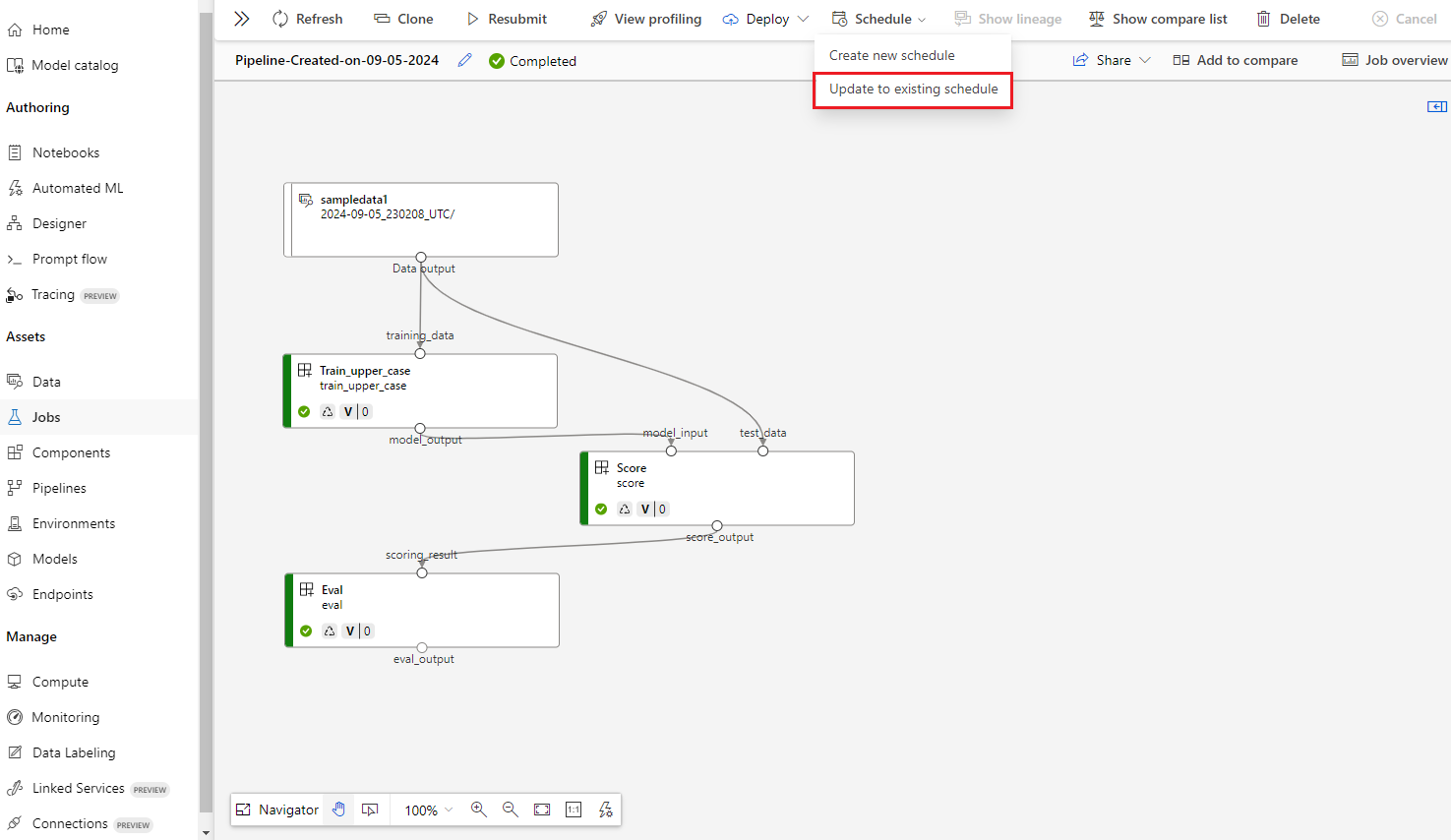
Create a schedule
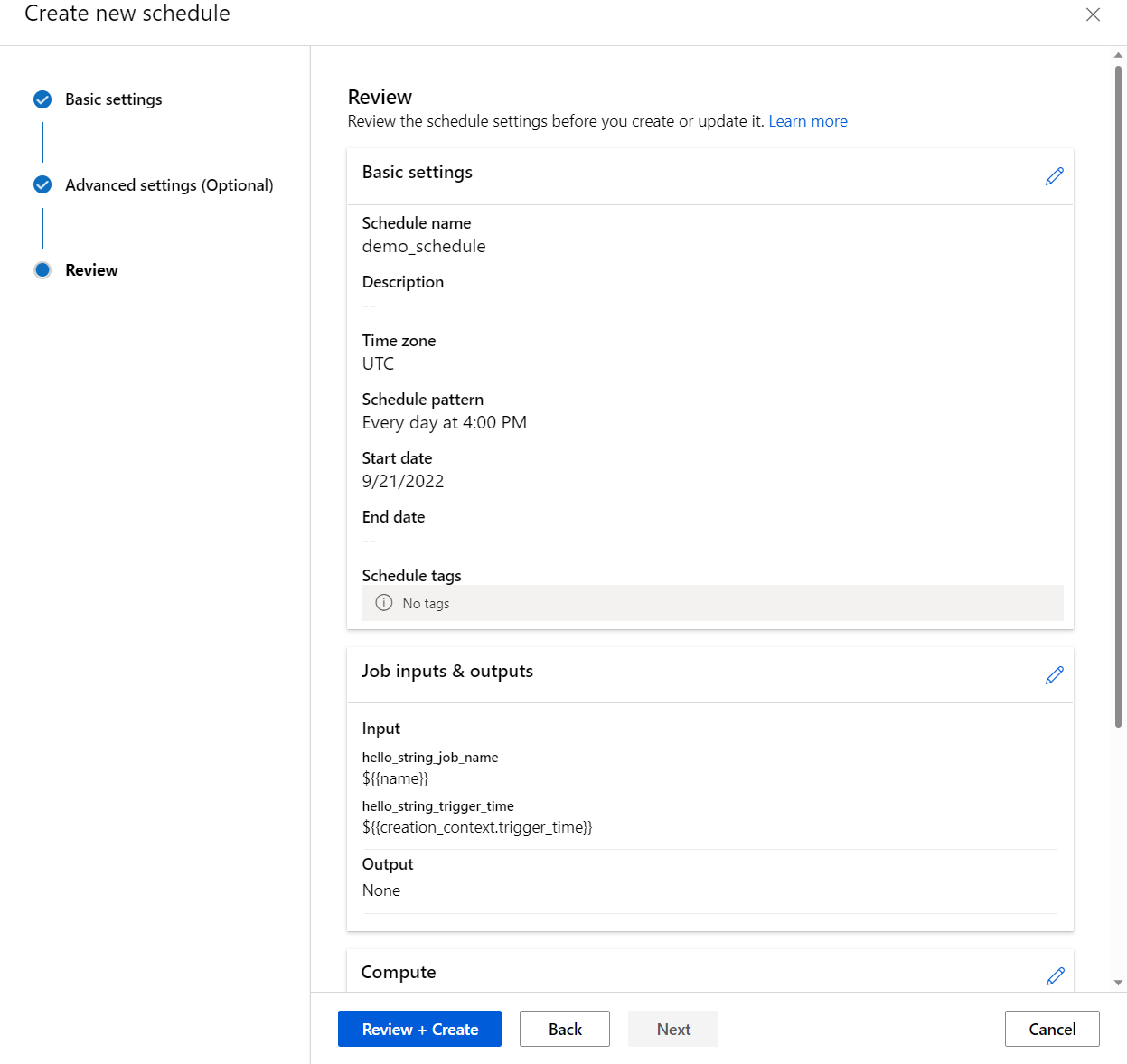
When you have a pipeline job with satisfying performance and outputs, you can set up a schedule to automatically trigger the job regularly. To do so, you must create a schedule that associates the job with a trigger. The trigger can be either a recurrence pattern or a cron expression that specifies the interval and frequency to run the job.
In both cases, you need to define a pipeline job first, either inline or by specifying an existing pipeline job. You can define pipelines in YAML and run them from the CLI, author pipelines inline in Python, or compose pipelines in Azure Machine Learning studio. You can create pipeline jobs locally or from existing jobs in the workspace.
You can create v2 schedules for v2 or v1 pipeline jobs by using the studio UI, SDK v2, or CLI v2. You don't have to publish existing pipelines first to set up schedules for pipeline jobs.
The code examples in this article are from Working with Schedule in Azure Machine Learning CLI 2.0.
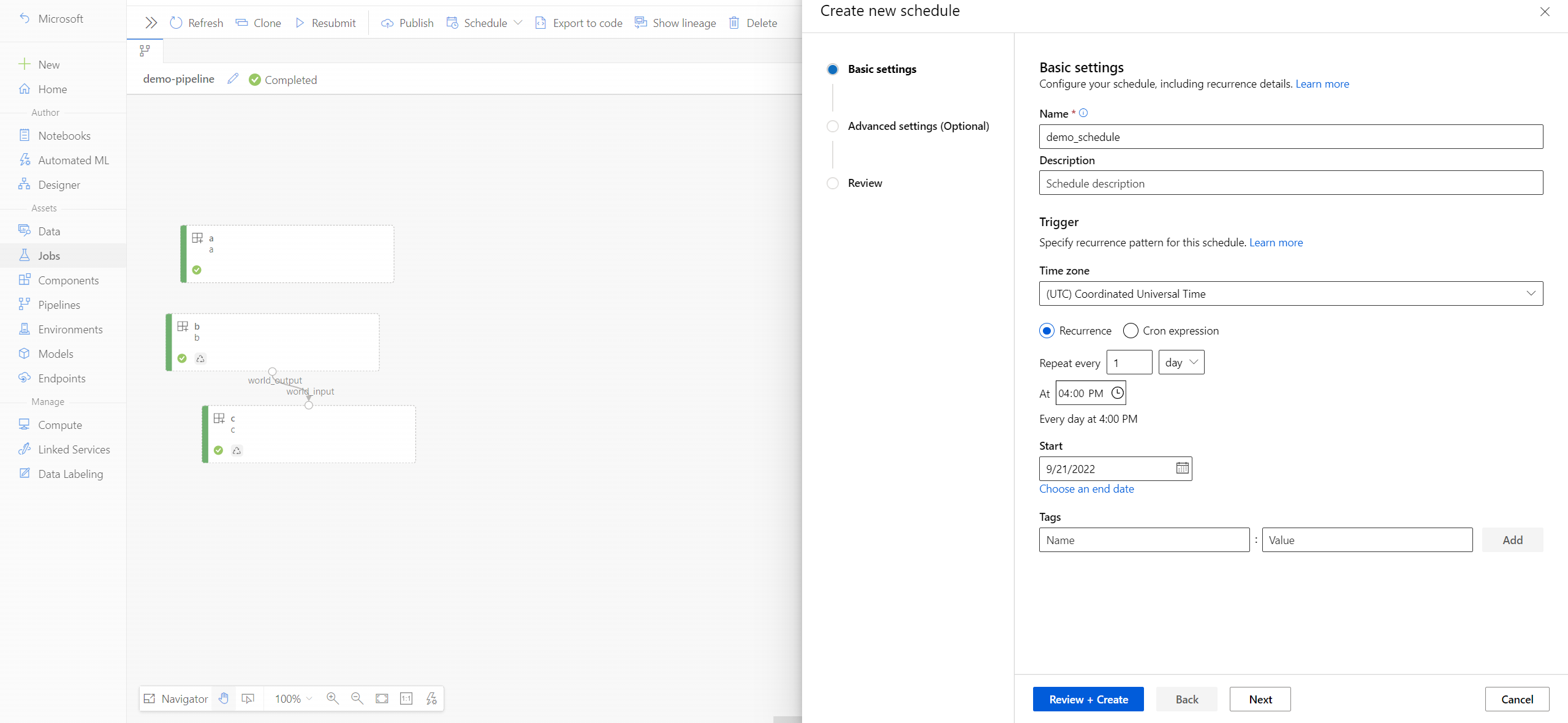
Define a time-based schedule with a recurrence pattern
The following YAML code defines a recurring schedule for a pipeline job. The required type parameter specifies that the trigger type is recurrence.
$schema: https://azuremlschemas.azureedge.net/latest/schedule.schema.json
name: simple_recurrence_job_schedule
display_name: Simple recurrence job schedule
description: a simple hourly recurrence job schedule
trigger:
type: recurrence
frequency: day #can be minute, hour, day, week, month
interval: 1 #every day
schedule:
hours: [4,5,10,11,12]
minutes: [0,30]
start_time: "2022-07-10T10:00:00" # optional - default will be schedule creation time
time_zone: "Pacific Standard Time" # optional - default will be UTC
create_job: ./simple-pipeline-job.yml
# create_job: azureml:simple-pipeline-job
You must or can provide the following schedule parameters:
Parameters
frequency(required) is the time unit on which basis the schedule fires. Can beminutes,hours,days,weeks, ormonths.interval(required) is the number of time units between schedule recurrences.schedule(optional) defines the recurrence pattern, which can containhours,minutes, andweekdays. If omitted, jobs trigger according to the logic ofstart_time,frequency, andinterval.- When
frequencyisday, the pattern can specifyhoursandminutes. - When
frequencyisweekormonth, the pattern can specifyhours,minutes, andweekdays.hoursis an integer or list from 0 to 23.minutesis an integer or list from 0 to 59.weekdaysis a string or list frommondaytosunday.
- When
start_time(optional) is the start date and time with timezone. If omitted, the default is equal to schedule creation time. If the start time is in the past, the first job runs at the next calculated run time.end_time(optional) is the end date and time with timezone. If omitted, the schedule remains active until manually disabled.time_zone(optional) specifies the time zone of the recurrence schedule. If omitted, the default is Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). For more information about timezone values, see the appendix for timezone values.
After you create the schedule YAML, use the following command to create the schedule via CLI:
# This action creates related resources for a schedule. It takes dozens of seconds to complete.
az ml schedule create --file simple-pipeline-job.yml --no-wait
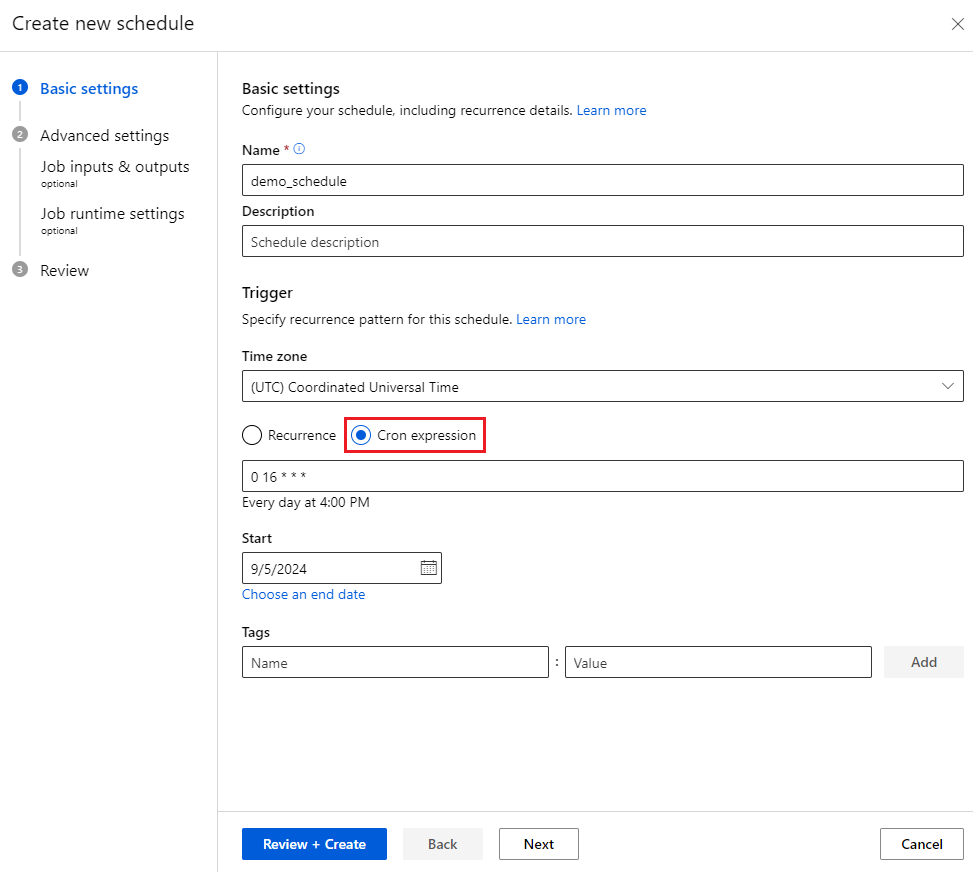
Define a time-based schedule with a cron expression
A cron expression can specify a flexible and customized recurrence pattern for a schedule. A standard crontab expression is composed of the space-delimited fields MINUTES HOURS DAYS MONTHS DAYS-OF-WEEK. A wildcard * means all values for a field.
In an Azure Machine Language schedule cron expression:
MINUTESis an integer or list from 0 to 59.HOURSis an integer or list from 0 to 23.DAYSvalues aren't supported, and are always treated as*. The*value inDAYSmeans all days in a month, which varies with month and year.MONTHSvalues aren't supported, and are always treated as*.DAYS-OF-WEEKis an integer or list from 0 to 6, where 0 = Sunday. Names of days are also accepted.
For example, the expression 15 16 * * 1 means 4:15 PM UTC every Monday. For more information about crontab expressions, see the Crontab Expression wiki on GitHub.
The following YAML code defines a recurring schedule for a pipeline job. The required type parameter specifies that the trigger type is cron.
$schema: https://azuremlschemas.azureedge.net/latest/schedule.schema.json
name: simple_cron_job_schedule
display_name: Simple cron job schedule
description: a simple hourly cron job schedule
trigger:
type: cron
expression: "0 * * * *"
start_time: "2022-07-10T10:00:00" # optional - default will be schedule creation time
time_zone: "Pacific Standard Time" # optional - default will be UTC
# create_job: azureml:simple-pipeline-job
create_job: ./simple-pipeline-job.yml
You must or can provide the following schedule parameters:
Parameters
expression(required) is a standard crontab expression that expresses a recurring schedule.start_time(optional) is the schedule start date and time with timezone. For example,start_time: "2022-05-10T10:15:00-04:00"means the schedule starts from 10:15:00 AM on May 10, 2022 in UTC-4 timezone. If omitted, the default is equal to schedule creation time. If the start time is in the past, the first job runs at the next calculated run time.end_time(optional) is the end date and time with timezone. If omitted, the schedule remains active until manually disabled.time_zone(optional) specifies the time zone of the recurrence schedule. If omitted, the default is UTC.
After you create the schedule YAML, use the following command to create the schedule via CLI:
# This action creates related resources for a schedule. It takes dozens of seconds to complete.
az ml schedule create --file simple-pipeline-job.yml --no-wait
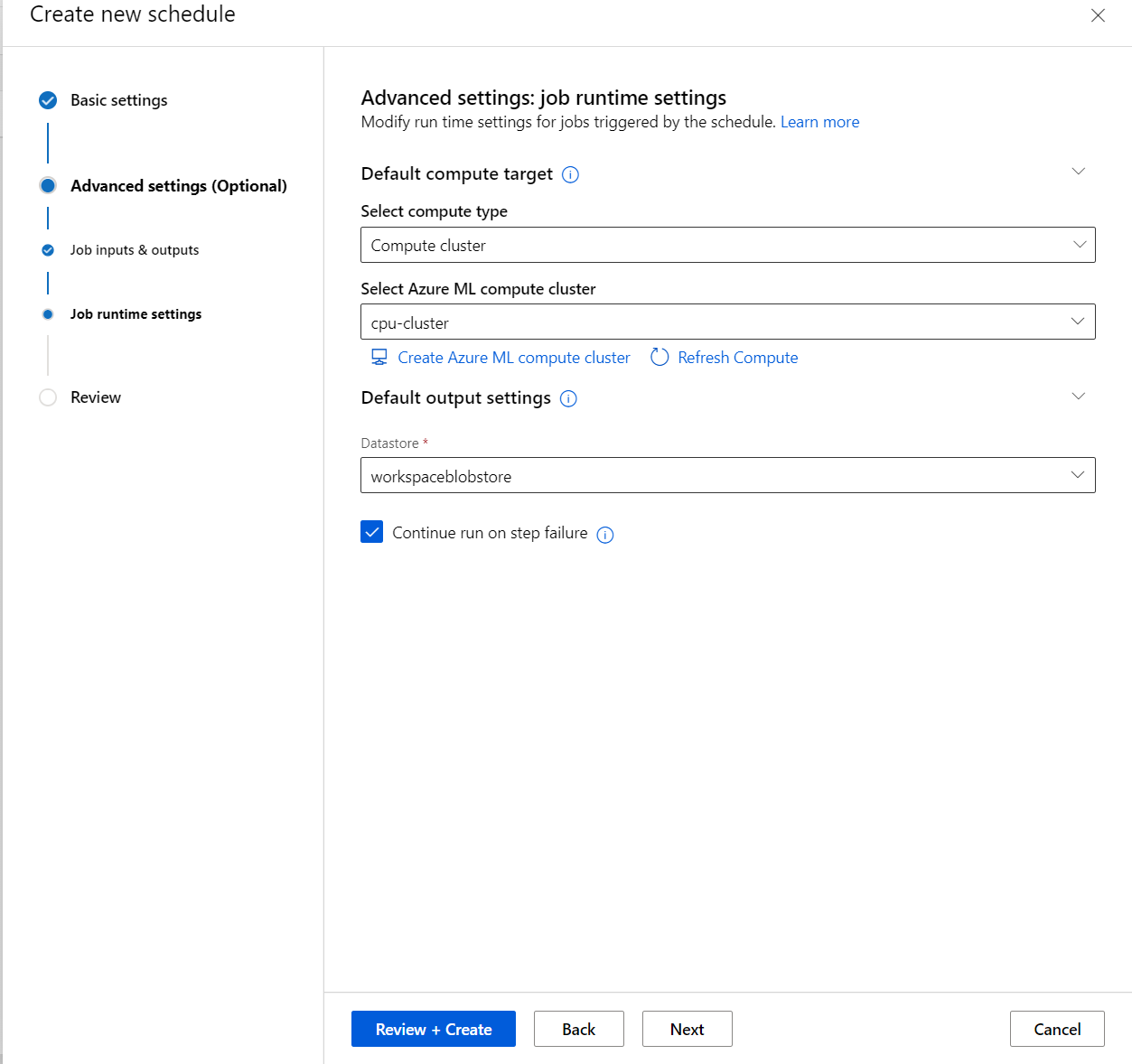
Change job settings when you define schedules
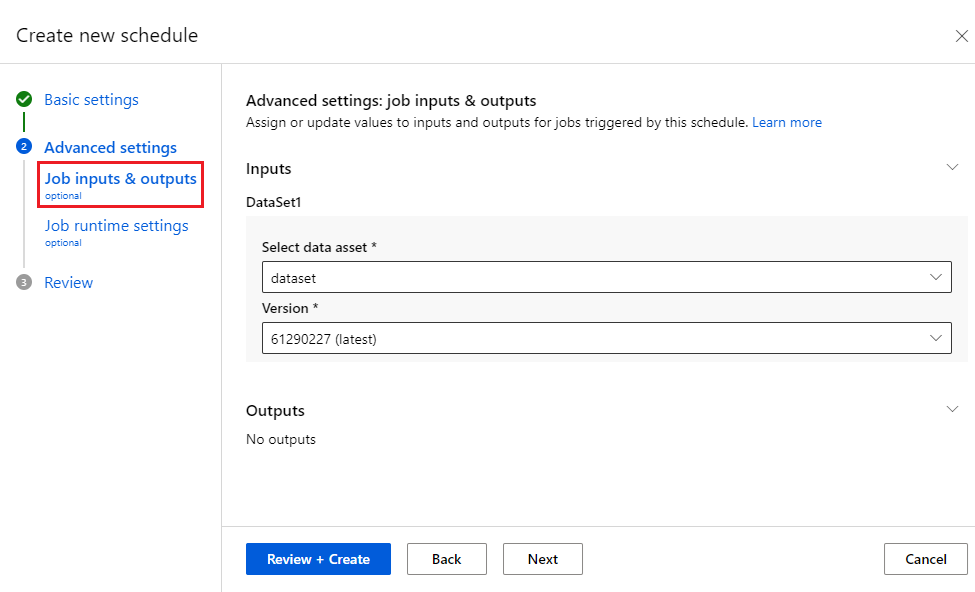
Sometimes you might want the jobs triggered by schedules to have different configurations from the test jobs. When you define a schedule by using an existing job, you can change the job settings. This approach lets you define multiple schedules that use the same job with different inputs.
When you define a schedule, you can change the settings, inputs, or outputs to use when running the pipeline job. You can also change the experiment_name of the triggered job.
The following schedule definition changes the settings of an existing job.
$schema: https://azuremlschemas.azureedge.net/latest/schedule.schema.json
name: cron_with_settings_job_schedule
display_name: Simple cron job schedule
description: a simple hourly cron job schedule
trigger:
type: cron
expression: "0 * * * *"
start_time: "2022-07-10T10:00:00" # optional - default will be schedule creation time
time_zone: "Pacific Standard Time" # optional - default will be UTC
create_job:
type: pipeline
job: ./simple-pipeline-job.yml
# job: azureml:simple-pipeline-job
# runtime settings
settings:
#default_compute: azureml:cpu-cluster
continue_on_step_failure: true
inputs:
hello_string_top_level_input: ${{name}}
tags:
schedule: cron_with_settings_schedule
Use supported expressions in schedules
When you define a schedule, you can use the following macro expressions to define dynamic parameter values that resolve to actual values during job runtime.
| Expression | Description | Supported properties |
|---|---|---|
${{name}} |
Name of the job | outputs path of the pipeline job |
${{creation_context.trigger_time}} |
Trigger time of the job | String type inputs of the pipeline job |
Manage schedule
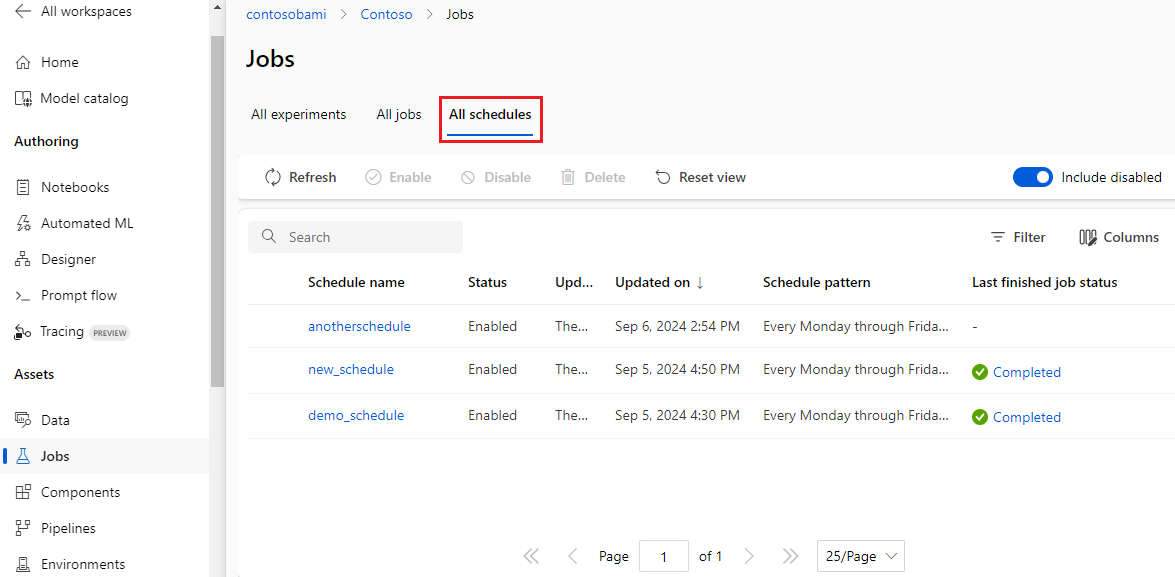
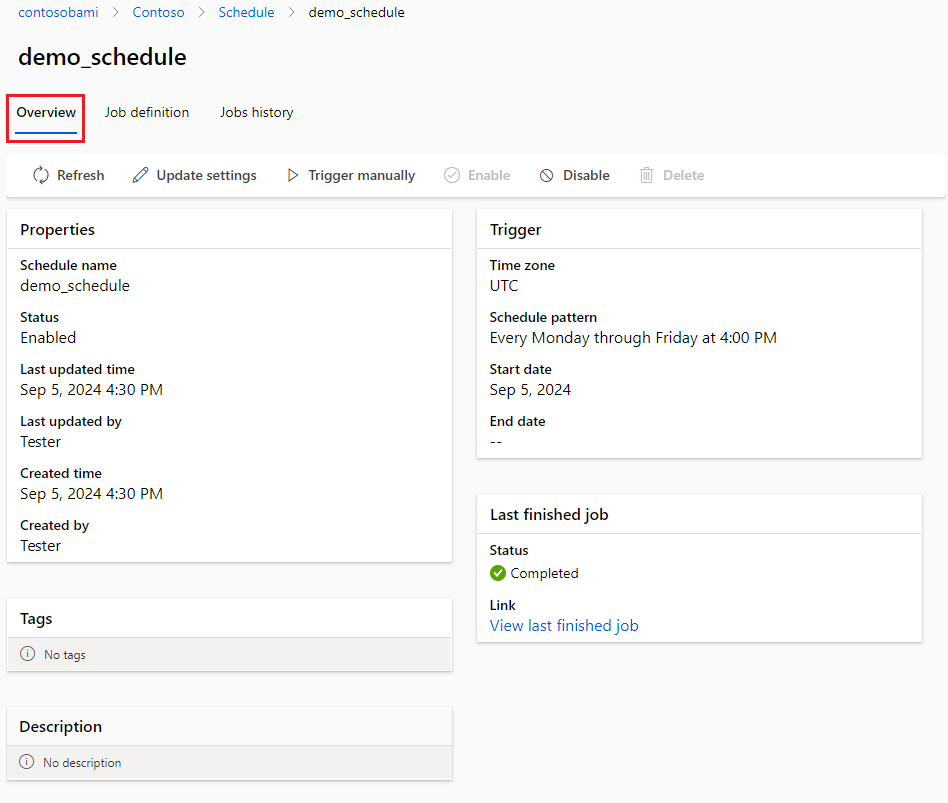
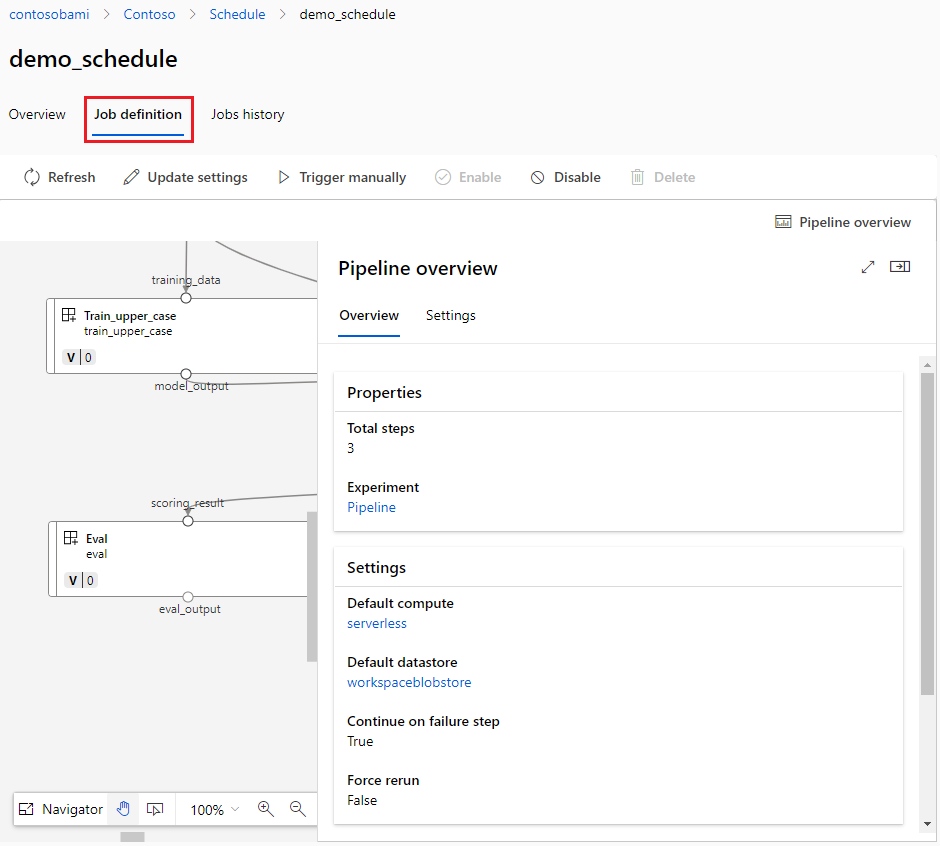
You can list, view details, update, disable, enable, and delete schedules in a workspace.
List schedules
az ml schedule list
View schedule details
az ml schedule show -n simple_cron_job_schedule
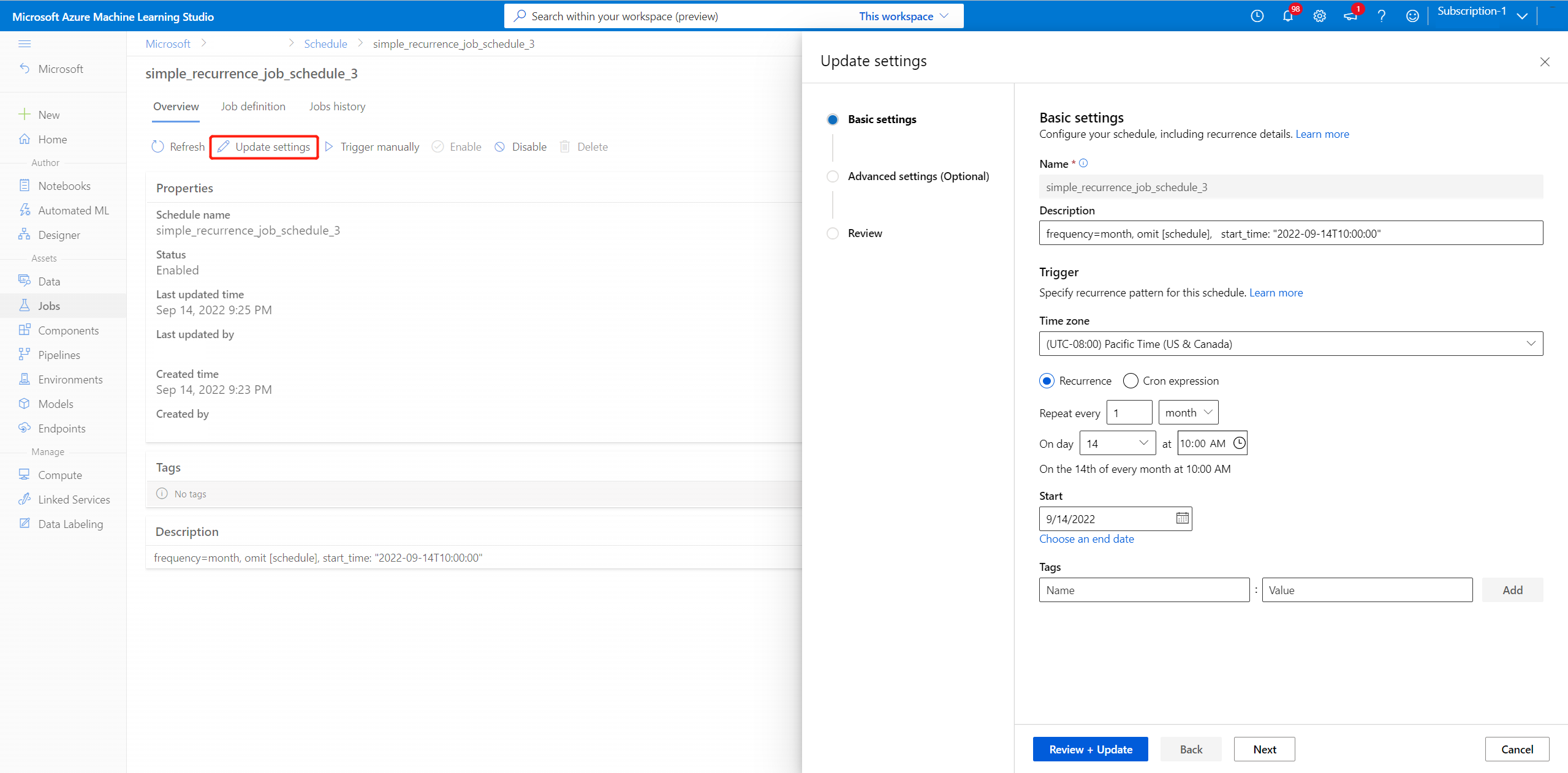
Update a schedule
az ml schedule update -n simple_cron_schedule --set description="new description" --no-wait
Note
To update more than just tags and description, consider using az ml schedule create --file update_schedule.yml.
Disable a schedule
az ml schedule disable -n simple_cron_job_schedule --no-wait
Enable a schedule
az ml schedule enable -n simple_cron_job_schedule --no-wait
Delete a schedule
Important
You must first disable a schedule to delete it. Deletion is permanent and unrecoverable.
az ml schedule enable -n simple_cron_schedule --no-wait
Query triggered jobs from a schedule
Jobs triggered by a specific schedule all have the display name <schedule_name>-YYYYMMDDThhmmssZ. For example, if a schedule named named-schedule runs every 12 hours starting at 6 AM on January 1, 2021, the display names of the jobs created are as follows:
- named-schedule-20210101T060000Z
- named-schedule-20210101T180000Z
- named-schedule-20210102T060000Z
- named-schedule-20210102T180000Z, and so on
You can also apply Azure CLI JMESPath query to query the jobs triggered by a schedule name.
# query triggered jobs from schedule, please replace the simple_cron_schedule to your schedule name
az ml job list --query "[?contains(display_name,'simple_cron_schedule')]"
Tip
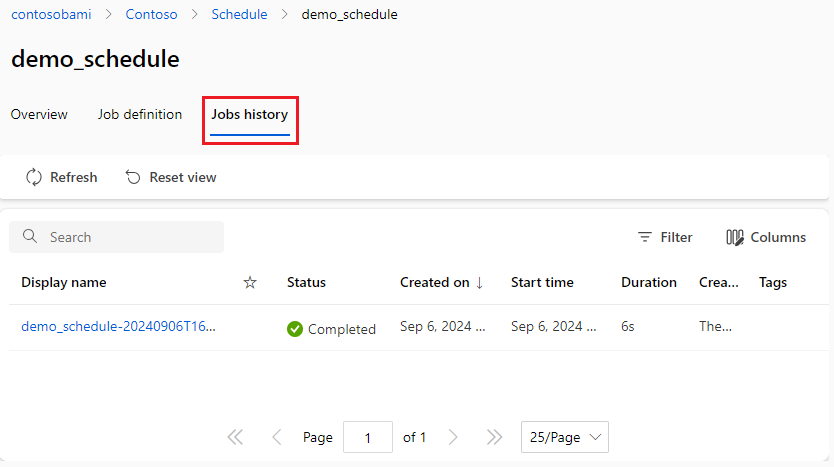
The Jobs history tab on the schedule detail page in the studio provides a simple way to find all jobs triggered by a schedule.
Role-based access controls (RBAC) support
Because schedules are used for production, it's important to reduce the possibility and impact of misoperation. Workspace admins can restrict access to schedule creation and management in a workspace.
Admins can configure the following action rules related to schedules in the Azure portal. For more information, see Manage access to Azure Machine Learning workspaces.
| Action | Description | Rule |
|---|---|---|
| Read | Get and list schedules | Microsoft.MachineLearningServices/workspaces/schedules/read |
| Write | Create, update, disable, and enable schedules | Microsoft.MachineLearningServices/workspaces/schedules/write |
| Delete | Delete schedules | Microsoft.MachineLearningServices/workspaces/schedules/delete |
Cost considerations
Schedules are billed based on the number of schedules. Each schedule creates a logic app that Azure Machine Learning hosts on behalf of (HOBO) the user. Therefore the logic app can't be shown as a resource under the user's subscription in Azure portal.
On the other hand, the logic app charges back to the user's Azure subscription. HOBO resource costs are billed using the same meter emitted by the original resource provider. Charges appear under the host resource, which is the Azure Machine Learning workspace.