This article shows you how to configure and manage Azure Route Server using the Azure portal, Azure PowerShell, or Azure CLI. You learn how to add and remove Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) peers, configure route exchange with virtual network gateways, and manage routing preferences.
Prerequisites
Add a BGP peer
In this section, you learn how to add a BGP peering between your route server and a network virtual appliance (NVA). This establishes a BGP session that allows the route server and NVA to exchange routing information.
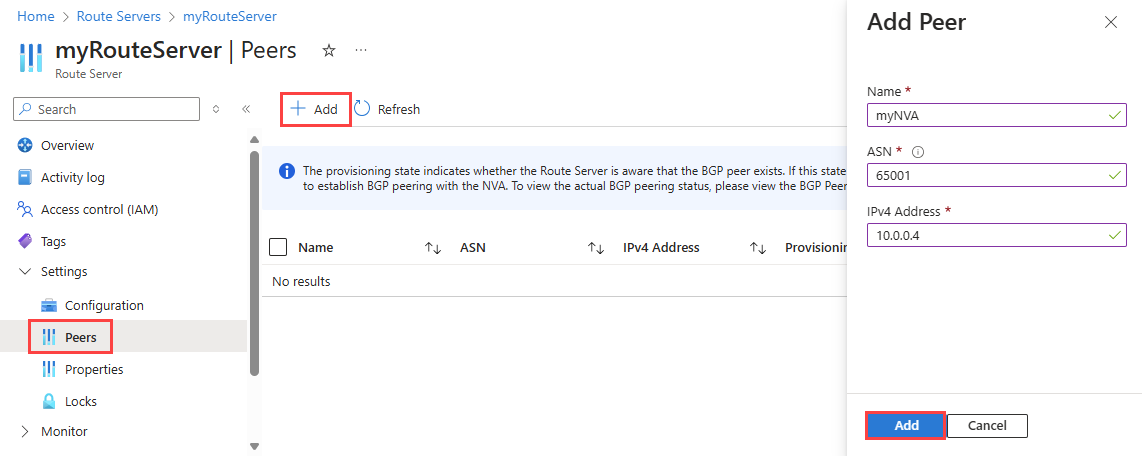
Go to the route server that you want to peer with an NVA.
under Settings, select Peers.
Select + Add to add a new peer.
On the Add Peer page, enter the following information:
| Setting |
Value |
| Name |
A name to identify the peer. It doesn't have to be the same name of the NVA. |
| ASN |
The Autonomous System Number (ASN) of the NVA. For more information, see What Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs) can I use? |
| IPv4 Address |
The private IP address of the NVA. |
Select Add to save the configuration.
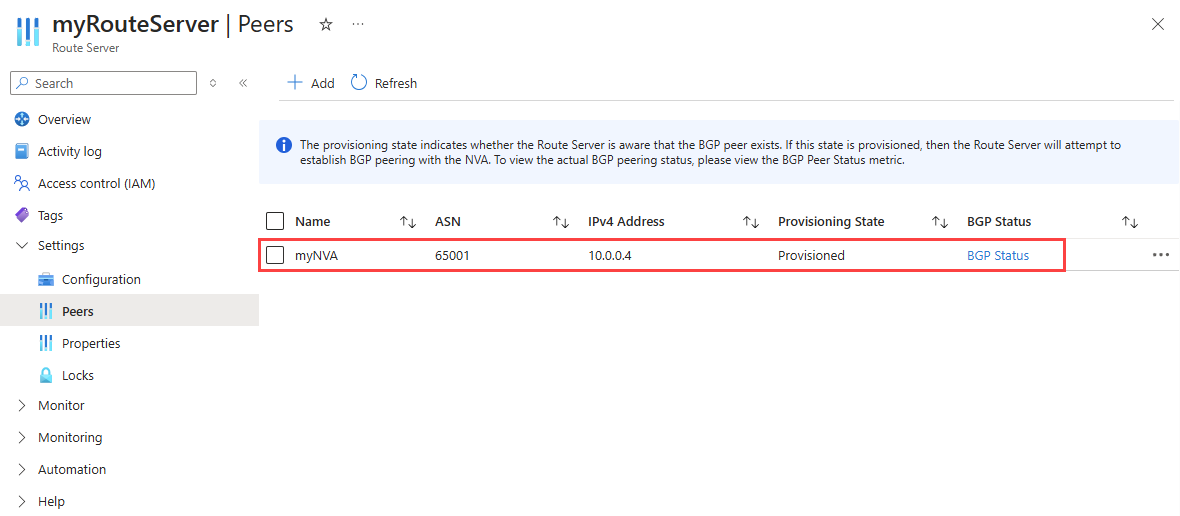
Once the peer NVA is successfully added, you can see it in the list of peers with a Succeeded provisioning state.
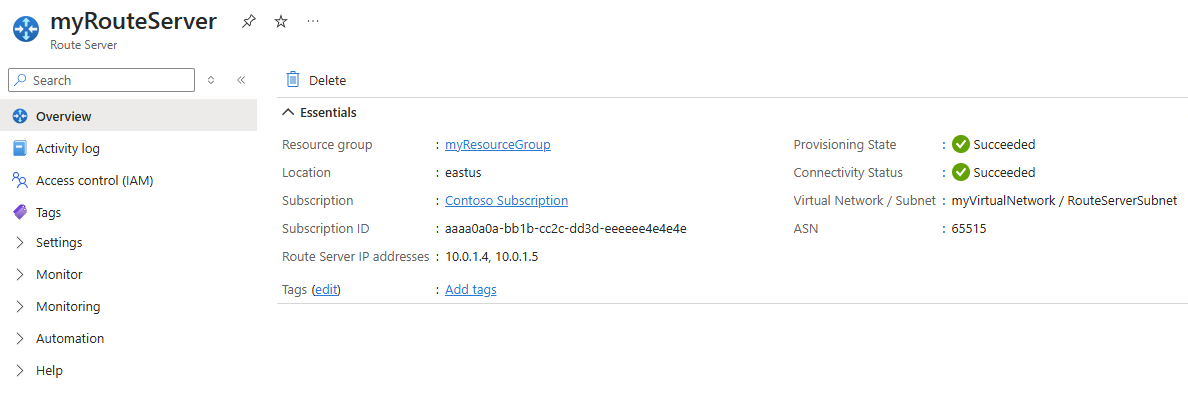
To complete the peering setup, you must configure the NVA to establish a BGP session with the route server using its IP addresses and ASN. You can find the route server's IP addresses and ASN in the Overview page:
Important
We recommend peering each NVA with both route server instances to ensure that virtual network routes are advertised over the NVA connections and achieve high availability.
Use Add-AzRouteServerPeer cmdlet to add a new peer to the route server.
Add-AzRouteServerPeer -PeerName 'myNVA' -PeerAsn '65001' -PeerIp '10.0.0.4' -ResourceGroupName 'myResourceGroup' -RouteServerName 'myRouteServer'
| Parameter |
Value |
-PeerName |
A name to identify the peer. It doesn't have to be the same name of the NVA. |
-PeerAsn |
The Autonomous System Number (ASN) of the NVA. For more information, see What Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs) can I use? |
-PeerIp |
The private IP address of the NVA. |
-ResourceGroupName |
The resource group name of your route server. |
-RouteServerName |
The route server name. This parameter is required when there are more than one route server in the same resource group. |
After you successfully add the peer NVA, you must configure the NVA to establish a BGP session with the route server's peer IPs and ASN. Use Get-AzRouteServer cmdlet to find the route server's peer IPs and ASN:
Get-AzRouteServer -ResourceGroupName 'myResourceGroup' -RouteServerName 'myRouteServer'
| Parameter |
Value |
-ResourceGroupName |
The resource group name of your route server. |
-RouteServerName |
The route server name. You need this parameter when there are more than one route server in the same resource group. |
Important
We recommend peering each NVA with both route server instances to ensure that virtual network routes are advertised over the NVA connections and achieve high availability.
Use az network routeserver peering create command to add a new peer to the route server.
az network routeserver peering create --name 'myNVA' --peer-asn '65001' --peer-ip '10.0.0.4' --resource-group 'myResourceGroup' --routeserver 'myRouteServer'
| Parameter |
Value |
--name |
A name to identify the peer. It doesn't have to be the same name of the NVA. |
--peer-asn |
The Autonomous System Number (ASN) of the NVA. For more information, see What Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs) can I use? |
--peer-ip |
The private IP address of the NVA. |
--resource-group |
The resource group name of your route server. |
--routeserver |
The route server name. |
After you successfully add the peer NVA, you must configure the NVA to establish a BGP session with the route server's peer IPs and ASN. Use az network routeserver show command to find the route server's peer IPs and ASN:
az network routeserver show --name 'myRouteServer' --resource-group 'myResourceGroup'
| Parameter |
Value |
--name |
The route server name. |
--resource-group |
The resource group name of your route server. |
Important
We recommend peering each NVA with both route server instances to ensure that virtual network routes are advertised over the NVA connections and achieve high availability.
In this section, you learn how to enable route exchange between your route server and virtual network gateways (ExpressRoute or VPN) in the same virtual network. This feature is also known as branch-to-branch connectivity.
Important
The Azure VPN gateway must be configured in active-active mode and have the ASN set to 65515. It's not a requirement to have BGP enabled on the VPN gateway to communicate with the route server.
Warning
When you create or delete a route server in a virtual network that contains a virtual network gateway (ExpressRoute or VPN), expect downtime until the operation is complete. If you have an ExpressRoute circuit connected to the virtual network where you're creating or deleting the route server, the downtime doesn't affect the ExpressRoute circuit or its connections to other virtual networks.
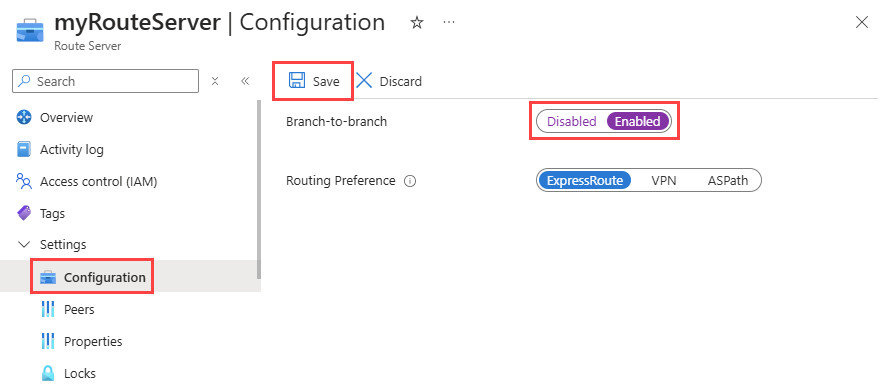
Go to the route server that you want to configure.
Under Settings, select Configuration.
Select Enabled for the Branch-to-branch setting and then select Save.
Use Update-AzRouteServer cmdlet to enable or disable route exchange between the route server and the virtual network gateway.
Update-AzRouteServer -RouteServerName 'myRouteServer' -ResourceGroupName 'myResourceGroup' -AllowBranchToBranchTraffic 1
| Parameter |
Value |
-RouteServerName |
The route server name. |
-ResourceGroupName |
The resource group name of your route server. |
-AllowBranchToBranchTraffic |
The route exchange parameter. Accepted values: 1 and 0. |
To disable route exchange, set the -AllowBranchToBranchTraffic parameter to 0.
Use Get-AzRouteServer cmdlet to verify the configuration.
Use az network routeserver update command to enable or disable route exchange between the route server and the virtual network gateway.
az network routeserver update --name 'myRouteServer' --resource-group 'myResourceGroup' --allow-b2b-traffic true
| Parameter |
Value |
--name |
The route server name. |
--resource-group |
The resource group name of your route server. |
--allow-b2b-traffic |
The route exchange parameter. Accepted values: true and false. |
To disable route exchange, set the --allow-b2b-traffic parameter to false.
Use az network routeserver show command to verify the configuration.
In this section, you learn how to configure routing preference to control how your route server selects routes when multiple paths are available. Routing preference affects route learning and selection behavior.
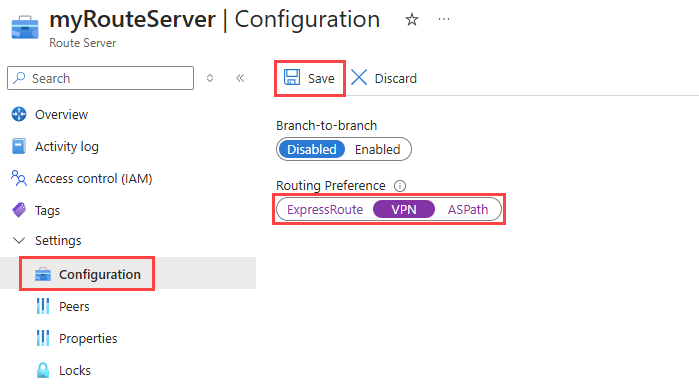
Go to the route server that you want to configure.
Under Settings, select Configuration.
Select the routing preference that you want. Available options: ExpressRoute (default), VPN, and ASPath.
Select Save
Use Update-AzRouteServer cmdlet to configure the routing preference setting of your route server.
Update-AzRouteServer -RouteServerName 'myRouteServer' -ResourceGroupName 'myResourceGroup' -HubRoutingPreference 'ASPath'
| Parameter |
Value |
-RouteServerName |
The route server name. |
-ResourceGroupName |
The resource group name of your route server. |
-HubRoutingPreference |
The routing preference. Accepted values: ExpressRoute (default), VpnGateway, and ASPath. |
Use Get-AzRouteServer cmdlet to verify the configuration.
Use az network routeserver update command to configure the routing preference setting of your route server.
az network routeserver update --name 'myRouteServer' --resource-group 'myResourceGroup' --hub-routing-preference 'ASPath'
| Parameter |
Value |
--name |
The route server name. |
--resource-group |
The resource group name of your route server. |
--hub-routing-preference |
The routing preference. Accepted values: ExpressRoute (default), VpnGateway, and ASPath. |
Use az network routeserver show command to verify the configuration.
View BGP peer details
In this section, you learn how to view the configuration details of a BGP peer, including its name, ASN, IP address, and provisioning state.
Go to the route server that you want to peer with an NVA.
under Settings, select Peers.
In the list of peers, you can see the name, ASN, IP address, and provisioning state of any of the configured peers.

Use Get-AzRouteServerPeer cmdlet to view a route server peering.
Get-AzRouteServerPeer -PeerName 'myNVA' -ResourceGroupName 'myResourceGroup' -RouteServerName 'myRouteServer'
| Parameter |
Value |
-PeerName |
The peer name. |
-ResourceGroupName |
The resource group name of your route server. |
-RouteServerName |
The route server name. |
Use az network routeserver peering show command to view a route server peering.
az network routeserver peering show --name 'myNVA' --resource-group 'myResourceGroup' --routeserver 'myRouteServer'
| Parameter |
Value |
--name |
The peer name. |
--resource-group |
The resource group name of your route server. |
--routeserver |
The route server name. |
View advertised and learned routes
In this section, you learn how to view the routes that your route server advertises to BGP peers and the routes it learns from those peers. This information is useful for troubleshooting routing issues and understanding traffic flow.
Use the Get-AzRouteServerPeerAdvertisedRoute cmdlet to view routes advertised by a route server.
Get-AzRouteServerPeerAdvertisedRoute -PeerName 'myNVA' -ResourceGroupName 'myResourceGroup' -RouteServerName 'myRouteServer'
Use the Get-AzRouteServerPeerLearnedRoute cmdlet to view routes learned by a route server.
Get-AzRouteServerPeerLearnedRoute -PeerName 'myNVA' -ResourceGroupName 'myResourceGroup' -RouteServerName 'myRouteServer'
| Parameter |
Value |
-PeerName |
The peer name. |
-ResourceGroupName |
The resource group name of your route server. |
-RouteServerName |
The route server name. |
Use the az network routeserver peering list-advertised-routes command to view routes advertised by a route server.
az network routeserver peering list-advertised-routes --name 'myNVA' --resource-group 'myResourceGroup' --routeserver 'myRouteServer'
Use the az network routeserver peering list-learned-routes command to view routes learned by a route server.
az network routeserver peering list-learned-routes --name 'myNVA' --resource-group 'myResourceGroup' --routeserver 'myRouteServer'
| Parameter |
Value |
--name |
The peer name. |
--resource-group |
The resource group name of your route server. |
--routeserver |
The route server name. |
Delete a BGP peer
In this section, you learn how to delete an existing BGP peering between your route server and a network virtual appliance (NVA). This removes the BGP session and stops route exchange between the devices.
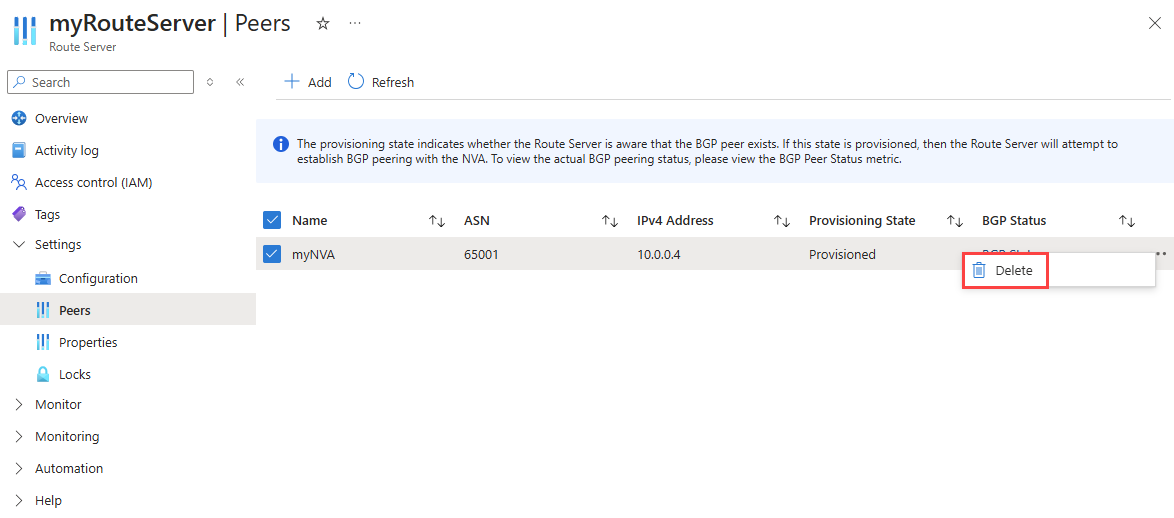
Go to the route server that you want to delete its NVA peering.
under Settings, select Peers.
Select the ellipses ... next to the peer that you want to delete, and then select Delete.
Use Remove-AzRouteServerPeer cmdlet to delete a route server peering.
Remove-AzRouteServerPeer -PeerName 'myNVA' -ResourceGroupName 'myResourceGroup' -RouteServerName 'myRouteServer'
| Parameter |
Value |
-PeerName |
The peer name. |
-ResourceGroupName |
The resource group name of your route server. |
-RouteServerName |
The route server name. |
Use az network routeserver peering delete command to delete a route server peering.
az network routeserver peering delete --name 'myNVA' --resource-group 'myResourceGroup' --routeserver 'myRouteServer'
| Parameter |
Value |
--name |
The peer name. |
--resource-group |
The resource group name of your route server. |
--routeserver |
The route server name. |
Delete Azure Route Server
In this section, you learn how to delete an existing Azure Route Server. Deleting a route server removes all BGP peerings and stops all route advertisements.
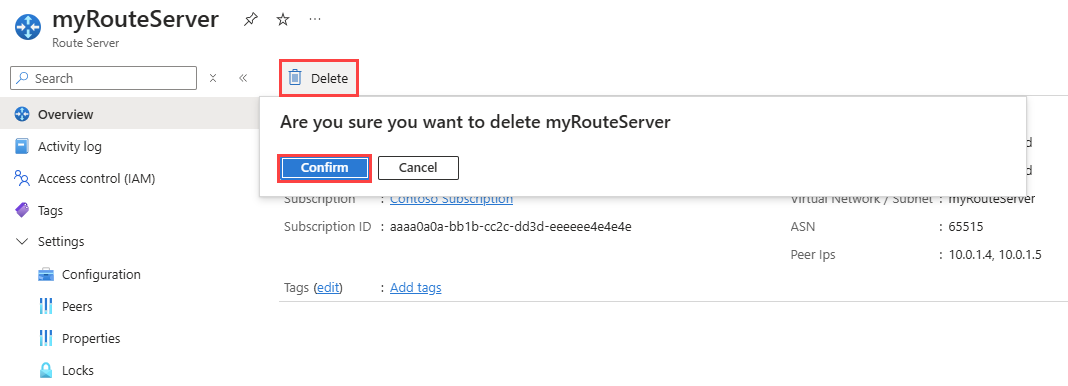
Go to the route server that you want to delete.
Select Delete from the Overview page.
Select Confirm to delete the route server.
Use Remove-AzRouteServer cmdlet to delete a route server.
Remove-AzRouteServer -RouteServerName 'myRouteServer' -ResourceGroupName 'myResourceGroup'
| Parameter |
Value |
-RouteServerName |
The route server name. |
-ResourceGroupName |
The resource group name of your route server. |
Use az network routeserver delete command to delete a route server.
az network routeserver delete --name 'myRouteServer' --resource-group 'myResourceGroup'
| Parameter |
Value |
--name |
The route server name. |
--resource-group |
The resource group name of your route server. |
Next steps






