Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure Blob Storage is ideal for storing large amounts of unstructured data such as text, images, and videos. Because blob storage also provides static website hosting support, it's a great option in cases where you don't require a web server to render content. Although you're limited to hosting static content such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and image files, you can use serverless architectures including Azure Functions and other Platform as a service (PaaS) services.
If you need a web server to render content, you can use Azure App Service.
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for trial.
- An Azure storage account resource. To learn how to create a storage account, see Create an Azure storage account.
Setting up a static website
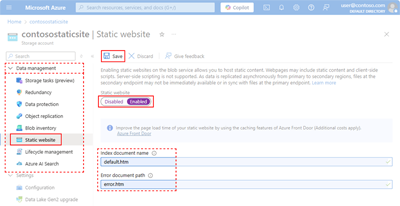
Static website hosting functionality is configured within a storage account and isn't enabled by default. To enable static website hosting, select a storage account. In the left navigation pane, select Static website from the Data management group, and then select Enabled. Provide a name for your Index document name. You can optionally provide a path to a custom 404 page. Finally, select Save to save your configuration changes.
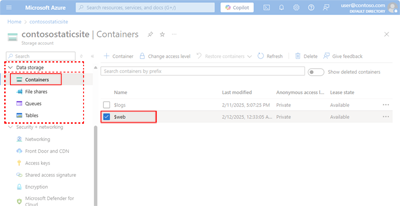
A blob storage container named $web is created for you within the storage account if it doesn't already exist. Add your website's files to the $web container to make them accessible through the static website's primary endpoint.
Files in the $web container are case-sensitive, served through anonymous access requests and are available only through read operations.
For step-by-step guidance, see Host a static website in Azure Storage.
Uploading content
You can use any of these tools to upload content to the $web container:
Viewing content
Users can view site content from a browser by using the public URL of the website. You can find the URL by using the Azure portal, Azure CLI, or PowerShell. See Find the website URL.
The index document that you specify when you enable static website hosting appears when users open the site and don't specify a specific file (For example: https://contosostaticsite.z22.web.core.chinacloudapi.cn).
If the server returns a 404 error, and you haven't specified an error document when you enabled the website, then a default 404 page is returned to the user.
Note
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) support for Azure Storage is not supported with static website.
Secondary endpoints
If you set up redundancy in a secondary region, you can also access website content by using a secondary endpoint. Data is replicated to secondary regions asynchronously. Therefore, the files that are available at the secondary endpoint aren't always in sync with the files that are available on the primary endpoint.
Impact of setting the access level on the web container
You can modify the anonymous access level of the $web container, but making this modification has no impact on the primary static website endpoint because these files are served through anonymous access requests. That means public (read-only) access to all files.
While the primary static website endpoint isn't affected, a change to the anonymous access level does impact the primary blob service endpoint.
For example, if you change the anonymous access level of the $web container from Private (no anonymous access) to Blob (anonymous read access for blobs only), then the level of anonymous access to the primary static website endpoint https://contosostaticsite.z4.web.core.chinacloudapi.cn/index.html doesn't change.
However, anonymous access to the primary blob service endpoint https://contosostaticsite.blob.core.chinacloudapi.cn/$web/index.html does change, enabling users to open that file by using either of these two endpoints.
Disabling anonymous access on a storage account by using the anonymous access setting of the storage account doesn't affect static websites that are hosted in that storage account. For more information, see Remediate anonymous read access to blob data (Azure Resource Manager deployments).
Mapping a custom domain to a static website URL
You can make your static website available via a custom domain.
It's easier to enable HTTP access for your custom domain, because Azure Storage natively supports it.
If the storage account is configured to require secure transfer over HTTPS, then users must use the HTTPS endpoint.
Tip
Consider hosting your domain on Azure. For more information, see Host your domain in Azure DNS.
Pricing
You can enable static website hosting free of charge. You're billed only for the blob storage that your site utilizes and operations costs. For more details on prices for Azure Blob Storage, check out the Azure Blob Storage Pricing Page.
Metrics
You can enable metrics on static website pages. Once you've enabled metrics, traffic statistics on files in the $web container are reported in the metrics dashboard.
To enable metrics on your static website pages, see Enable metrics on static website pages.
Feature support
Support for this feature might be impacted by enabling Data Lake Storage Gen2, Network File System (NFS) 3.0 protocol, or the SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP). If you've enabled any of these capabilities, see Blob Storage feature support in Azure Storage accounts to assess support for this feature.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Does the Azure Storage firewall work with a static website?
Yes. Storage account network security rules, including IP-based and VNET firewalls, are supported for the static website endpoint, and may be used to protect your website.
Do static websites support Microsoft Entra ID?
No. A static website only supports anonymous read access for files in the $web container.
Why am I getting an HTTP 404 error from a static website?
A 404 error can happen if you refer to a file name by using an incorrect case. For example: Index.html instead of index.html. File names and extensions in the url of a static website are case-sensitive even though they're served over HTTP. This can also happen if your Azure CDN endpoint isn't yet provisioned. Wait up to 90 minutes after you provision a new Azure CDN for the propagation to complete.
Why isn't the root directory of the website not redirecting to the default index page?
In the Azure portal, open the static website configuration page of your account and locate the name and extension that is set in the Index document name field. Ensure that this name is exactly the same as the name of the file located in the $web container of the storage account. File names and extensions in the url of a static website are case-sensitive even though they're served over HTTP.
Why am I unable to access static websites in a storage account when a private endpoint is enabled for the blob in the storage account?
Enabling a private endpoint for blobs in a storage account restricts access to that storage account to only resources within the same virtual network. Consequently, this restriction prevents external access to the static website hosted in the storage account, making the static website content inaccessible. The private endpoint configuration limits access to all storage account resources, including the static website content, to resources within the same virtual network where the private endpoint is enabled. The resolution would be to create a private endpoint specifically for the web. The static website needs a dedicated private end point for the $web domain.