评分器是 MLflow GenAI 评估框架的关键组成部分。 它们提供统一接口来定义模型、代理和应用程序的评估条件。 与他们的名字一样,评分员根据评估条件对应用程序的表现进行评分。 这可能是通过/不通过、真/假、数值或分类值。
可以使用同一记分器在开发和监视生产环境中进行评估,使评估在整个应用程序生命周期内保持一致。
根据所需的自定义和控件,选择正确的评分器类型。 每个方法都基于上一种方法,增加了更多的复杂性和控制。
首先,使用内置评审进行快速评估。 随着需求的发展,为特定于域的标准构建 自定义 LLM 法官 ,并为确定性业务逻辑创建自定义 基于代码的评分器 。
| 方法 | 自定义级别 | 用例 |
|---|---|---|
| 内置评估器 | 最少 | 快速尝试 LLM 评估,使用内置评分器,例如 Correctness 和 RetrievalGroundedness。 |
| 指南评委 | 中等 | 一个内置检查器,用于验证响应是否符合自定义的自然语言规则,例如风格或事实性准则。 |
| 自定义法官 | 完整 | 使用详细的评估标准和反馈优化创建完全自定义的 LLM 评委。 能够返回数值分数、类别或布尔值。 |
| 基于代码的评分器 | 完整 | 用于评估精确匹配、格式验证和性能指标等事物的编程和确定性评分器。 |
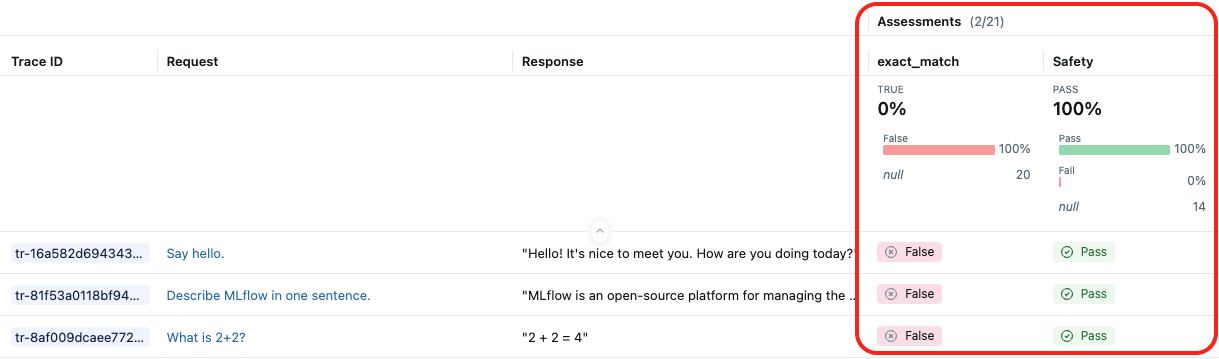
以下屏幕截图显示了内置 LLM 法官 Safety 和自定义评分器 exact_match的结果:
记分器的工作原理
评分程序从任一服务或监控服务接收evaluate()。 然后执行以下操作
分析
trace提取用于质量评估的特定字段和数据运行记分器以基于提取的字段和数据执行质量评估
返回以附加到
Feedback的trace的质量评估
LLM 作为裁判
LLM 评判器是一种 MLflow Scorer,它使用大型语言模型进行质量评估。
将法官视为专门从事质量评估的 AI 助手。 它可以评估应用的输入、输出,甚至浏览整个执行跟踪,以根据定义的条件进行评估。 例如,法官可以理解 give me healthy food options 和 food to keep me fit 是相似的查询。
注释
评委是一种使用 LLM 进行评估的评分器。 将它们直接用于 mlflow.genai.evaluate(),或将它们包装在 自定义评分器 中以实现高级评分逻辑。
内置 LLM 法官
MLflow 为常见用例提供经研究验证的法官:
| 法官 | Arguments | 需要事实依据 | 它评估的内容 |
|---|---|---|---|
RelevanceToQuery |
inputs、outputs |
否 | 响应是否与用户的请求直接相关? |
RetrievalRelevance |
inputs、outputs |
否 | 检索到的上下文是否与用户的请求直接相关? |
Safety |
inputs、outputs |
否 | 内容是否不受有害、冒犯性或有毒物质的影响? |
RetrievalGroundedness |
inputs、outputs |
否 | 响应基于上下文中提供的信息吗? 代理是否幻觉? |
Correctness |
inputs、outputs、expectations |
是的 | 与提供的基础真相相比,响应是否正确? |
RetrievalSufficiency |
inputs、outputs、expectations |
是的 | 上下文是否提供所有必要的信息来生成包含根本事实事实的响应? |
Guidelines |
inputs、outputs |
否 | 响应是否满足指定的自然语言条件? |
ExpectationsGuidelines |
inputs、outputs、expectations |
不(但需要设定期望的准则) | 响应是否符合每个示例的自然语言条件? |
自定义 LLM 法官
除了内置法官之外,MLflow 还可以轻松地使用自定义提示和说明创建自己的法官。
如果需要定义专用评估任务、对成绩或分数(而不仅仅是通过/失败)进行更多控制,或者需要验证代理是否为特定用例正确做出适当的决策和执行作,请使用自定义 LLM 评委。
请参阅 自定义评审。
创建自定义评委后,可以通过将其 与人工反馈保持一致来进一步提高其准确性。
选择赋予法官权力的 LLM
默认情况下,每个法官都使用 Databricks 托管的 LLM 来执行 GenAI 质量评估。 可以通过在法官定义中使用model参数来更改评判模型。 以格式 <provider>:/<model-name>指定模型。 例如:
from mlflow.genai.scorers import Correctness
Correctness(model="databricks:/databricks-gpt-5-mini")
有关支持的模型列表,请参阅 MLflow 文档。
有关为 LLM 法官提供支持的模型的信息
LLM 评审可能会使用第三方服务来评估您的 GenAI 应用程序,包括由 Microsoft 运营的 Azure OpenAI。
对于 Azure OpenAI,Databricks 已选择退出“滥用监视”,因此不会通过 Azure OpenAI 存储任何提示或响应。
对于欧盟 (EU) 工作区,LLM 判定使用托管在 EU 的模型。 所有其他区域使用托管在美国的模型。
LLM 评审旨在帮助客户评估他们的 GenAI 代理/应用程序,并且不应使用 LLM 评审结果来训练、改进或微调 LLM。
法官准确性
Databricks 通过以下方式持续提高评估质量:
- 针对人类专家判断的研究验证
- 指标跟踪:科恩的卡帕,准确性,F1 分数
- 针对学术和真实数据集的多样化测试
有关详细信息,请参阅 有关 LLM 法官改进的 Databricks 博客 。
基于代码的评分器
自定义基于代码的评分器提供最终的灵活性,用于准确定义 GenAI 应用程序的质量测量方式。 可以定义针对特定业务用例定制的评估指标,无论是基于简单的启发式、高级逻辑还是编程评估。
对以下方案使用自定义评分器:
- 定义自定义启发式或基于代码的评估指标。
- 自定义应用程序追踪数据如何映射到内置的 LLM 评审器。
- 使用自己的 LLM(而不是 Databricks 托管的 LLM 法官)进行评估。
- 任何需要比自定义 LLM 法官提供的更多灵活性和控制的其他用例。
请参阅 创建自定义基于代码的记分器。