自定义基于代码的 评分器 提供最终的灵活性,用于准确定义 GenAI 应用程序的质量测量方式。 可以定义针对特定业务用例定制的评估指标,无论是基于简单的启发式、高级逻辑还是编程评估。
对以下方案使用自定义评分器:
- 定义自定义启发式或基于代码的评估指标。
- 自定义如何将您应用程序追踪中的数据映射到 Databricks 研究支持的 LLM 判断模型。
- 使用自己的 LLM(而不是 Databricks 托管的 LLM 法官)进行评估。
- 任何其他应用场景中,你需要比自定义 LLM 评审提供的更多灵活性和控制。
有关包含许多示例的教程,请参阅 基于代码的记分器示例。
自定义评分器的工作原理
自定义评分器是使用 Python 编写的,可让你完全控制评估应用跟踪中的任何数据。 定义自定义评分器后,可以像 内置 LLM 法官一样使用它。 与其他评分者一样,相同的自定义记分器可用于 开发中的评估 ,并重复使用以便在 生产中监视。
例如,假设你想要一个评分器,用于检查 LLM 的响应时间是否在可接受的范围内。 下面的 MLflow UI 图像显示此自定义指标评分的跟踪。
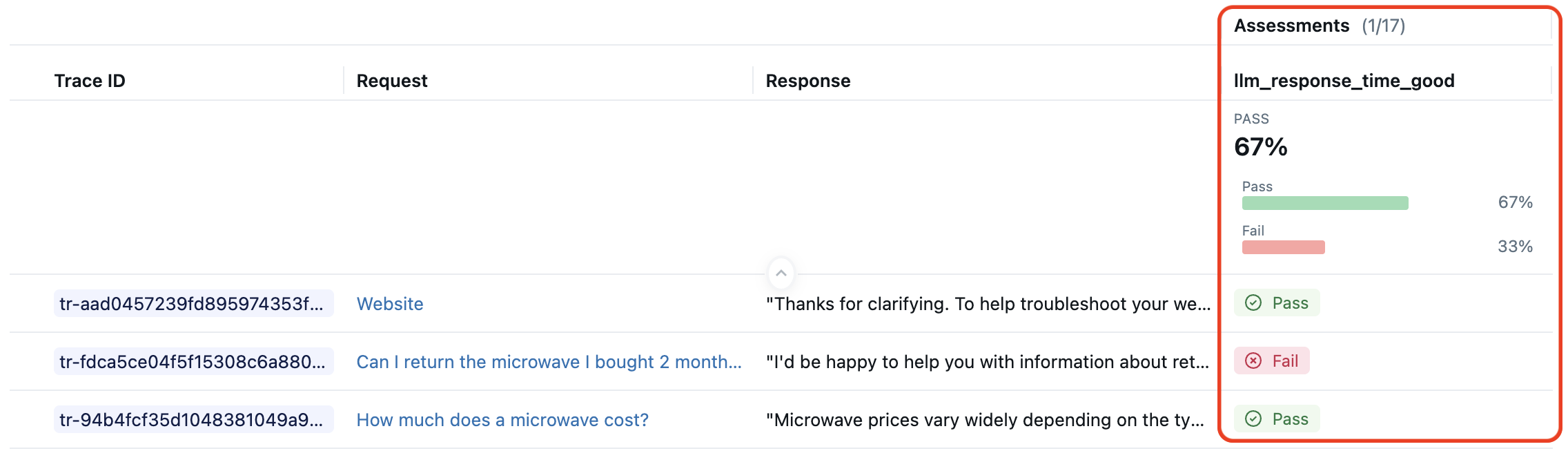
下面的代码片段定义此自定义记分器并将其用于 mlflow.genai.evaluate():
import mlflow
from mlflow.genai.scorers import scorer
from mlflow.entities import Trace, Feedback, SpanType
@scorer
def llm_response_time_good(trace: Trace) -> Feedback:
# Search particular span type from the trace
llm_span = trace.search_spans(span_type=SpanType.CHAT_MODEL)[0]
response_time = (llm_span.end_time_ns - llm_span.start_time_ns) / 1e9 # second
max_duration = 5.0
if response_time <= max_duration:
return Feedback(
value="yes",
rationale=f"LLM response time {response_time:.2f}s is within the {max_duration}s limit."
)
else:
return Feedback(
value="no",
rationale=f"LLM response time {response_time:.2f}s exceeds the {max_duration}s limit."
)
# Evaluate the scorer using pre-generated traces
span_check_eval_results = mlflow.genai.evaluate(
data=generated_traces,
scorers=[llm_response_time_good]
)
上面的示例演示了基于代码的评分器的常见模式:
-
@scorer修饰器用于定义评分器。 - 此评分器的输入是完整的
trace,允许它访问 AI 应用的输入、中间跨度和输出。 - 评分器逻辑可以完全自定义。 可以调用 LLM 或其他评分系统。
- 此评分器的输出是一个包含值和说明的丰富
Feedback对象。 -
指标名称 与
llm_response_time_good记分器函数名称匹配。
基于代码的评分器的这种模式只是其中的一种可能性。 本文的其余部分介绍了用于定义自定义评分器的选项。
使用 @scorer 修饰器定义记分器
大多数基于代码的评分器应使用@scorer修饰器进行定义。 下面是此类评分器的签名,说明了可能的输入和输出。
from mlflow.genai.scorers import scorer
from typing import Optional, Any
from mlflow.entities import Feedback
@scorer
def my_custom_scorer(
*, # All arguments are keyword-only
inputs: Optional[dict[str, Any]], # App's raw input, a dictionary of input argument names and values
outputs: Optional[Any], # App's raw output
expectations: Optional[dict[str, Any]], # Ground truth, a dictionary of label names and values
trace: Optional[mlflow.entities.Trace] # Complete trace with all spans and metadata
) -> Union[int, float, bool, str, Feedback, List[Feedback]]:
# Your evaluation logic here
使用@scorer定义记分器,可以获得比Scorer修饰器更大的灵活性。
输入
评分器接收到包含所有跨度、属性和输出的完整MLflow 跟踪。 为方便起见,MLflow 还会提取常用的数据,并将其作为命名参数传递。 所有输入参数都是可选的,因此请仅声明记分器需要的内容:
-
inputs:发送到应用的请求(例如用户查询、上下文)。 -
outputs:来自应用的响应(例如生成的文本、工具调用) -
expectations:基本真相或标签(例如预期响应、准则等) -
trace:包含所有跨度的完整 MLflow 跟踪 ,允许分析中间步骤、延迟、工具使用情况等。 跟踪作为实例化mlflow.entities.trace类传递到自定义评分器。
在运行mlflow.genai.evaluate()时,可以在inputs参数中指定outputs、expectations和data参数,或者从跟踪中解析这些参数。
用于生产监视的已注册记分器 始终解析跟踪中的 inputs 和 outputs 参数。
expectations 不可用。
输出
评分器可以根据评估需求返回不同类型的 简单值 或 丰富的反馈对象 。
| 返回类型 | MLflow UI 显示 | 用例 |
|---|---|---|
"yes"/"no" |
通过/失败 | 二进制求值 |
True/False |
真/假 | 布尔值检查 |
int/float |
数值 | 分数、计数 |
Feedback |
值 + 理由 | 详细评估 |
List[Feedback] |
多个指标 | 多方面评估 |
简单值
用于输出用于简单通过/不通过或数值评估的原始值。 下面是将字符串作为响应返回的 AI 应用的简单评分器。
@scorer
def response_length(outputs: str) -> int:
# Return a numeric metric
return len(outputs.split())
@scorer
def contains_citation(outputs: str) -> str:
# Return pass/fail string
return "yes" if "[source]" in outputs else "no"
丰富的反馈
返回对象 Feedback 或对象列表 Feedback ,以获取具有分数、理由和元数据的详细评估。
from mlflow.entities import Feedback, AssessmentSource
@scorer
def content_quality(outputs):
return Feedback(
value=0.85, # Can be numeric, boolean, string, or other types
rationale="Clear and accurate, minor grammar issues",
# Optional: source of the assessment. Several source types are supported,
# such as "HUMAN", "CODE", "LLM_JUDGE".
source=AssessmentSource(
source_type="HUMAN",
source_id="grammar_checker_v1"
),
# Optional: additional metadata about the assessment.
metadata={
"annotator": "me@example.com",
}
)
可以将多个反馈对象作为列表返回。 每个反馈都应指定 name 字段,这些名称将在评估结果中显示为单独的指标。
@scorer
def comprehensive_check(inputs, outputs):
return [
Feedback(name="relevance", value=True, rationale="Directly addresses query"),
Feedback(name="tone", value="professional", rationale="Appropriate for audience"),
Feedback(name="length", value=150, rationale="Word count within limits")
]
指标命名行为
定义记分器时,请使用明确的一致名称来指示记分器的目的。 这些名称将在评估和监视结果和仪表板中显示为指标名称。 遵循 MLflow 命名约定,例如 safety_check 或 relevance_monitor。
定义评分器时,无论是使用@scorer 修饰器还是Scorer 类,在评估运行中生成的指标名称都遵循简单的规则:
- 如果记分器返回一个或多个
Feedback对象,则Feedback.name字段优先(如果指定)。 - 对于原始返回值或未命名的
Feedback,将使用函数名称(对于修饰器@scorer)或Scorer.name字段(对于Scorer类)。
将这些规则扩展到所有可能性可提供下表来说明指标命名行为:
| 返回值 |
@scorer 修饰器行为 |
Scorer 类行为 |
|---|---|---|
基元值 (int, float, str) |
函数名称 |
name 字段 |
| 无名称的反馈 | 函数名称 |
name 字段 |
| 具有名称的反馈 |
Feedback 名称 |
Feedback 名称 |
List[Feedback] 包含名称 |
Feedback 名字 |
Feedback 名字 |
对于评估和监视,所有指标都具有不同的名称非常重要。 如果评分器返回 List[Feedback],那么 Feedback 中的每个 List 必须具有不同的名称。
请参阅本教程中的 命名行为示例 。
访问记分器中的机密
自定义记分器可以访问 Databricks 机密 ,以安全地使用 API 密钥和凭据。 这在集成外部服务(例如需要身份验证的自定义 LLM 终结点)(如 Azure OpenAI、AWS Bedrock 等)时非常有用。 此方法适用于开发评估和生产监视
默认情况下, dbutils 记分器运行时环境中不可用。 在记分器函数内部调用 from databricks.sdk.runtime import dbutils 以访问记分器运行时环境中的机密。
以下示例演示如何访问自定义评分器中的机密:
import mlflow
from mlflow.genai.scorers import scorer, ScorerSamplingConfig
from mlflow.entities import Trace, Feedback
@scorer
def custom_llm_scorer(trace: Trace) -> Feedback:
# Explicitly import dbutils to access secrets
from databricks.sdk.runtime import dbutils
# Retrieve your API key from Databricks secrets
api_key = dbutils.secrets.get(scope='my-scope', key='api-key')
# Use the API key to call your custom LLM endpoint
# ... your custom evaluation logic here ...
return Feedback(
value="yes",
rationale="Evaluation completed using custom endpoint"
)
# Register and start the scorer
custom_llm_scorer.register()
custom_llm_scorer.start(sampling_config = ScorerSamplingConfig(sample_rate=1))
错误处理
当记分器遇到跟踪错误时,MLflow 可以捕获该跟踪的错误详细信息,然后继续正常执行。 为了捕获错误详细信息,MLflow 提供了两种方法:
- 让异常自动传播(推荐),以便 MLflow 可以为您捕获错误信息。
- 在代码中显式处理异常。
让例外传播(建议)
最简单的方法是让异常自然引发。 MLflow 自动捕获异常,并创建包含 Feedback 错误详细信息的对象。 在下面的示例中,记分器需要具有特定字段的 JSON。
import mlflow
from mlflow.entities import Feedback
from mlflow.genai.scorers import scorer
@scorer
def is_valid_response(outputs: str) -> Feedback:
import json
# Let json.JSONDecodeError propagate if response isn't valid JSON
data = json.loads(outputs)
# Let KeyError propagate if required fields are missing
summary = data["summary"]
confidence = data["confidence"]
return Feedback(
value=True,
rationale=f"Valid JSON with confidence: {confidence}"
)
# Run the scorer on invalid data that triggers exceptions
invalid_data = [
{
# Valid JSON
"outputs": '{"summary": "this is a summary", "confidence": 0.95}'
},
{
# Invalid JSON
"outputs": "invalid json",
},
{
# Missing required fields
"outputs": '{"summary": "this is a summary"}'
},
]
mlflow.genai.evaluate(
data=invalid_data,
scorers=[is_valid_response],
)
发生异常时,MLflow 会创建以下 Feedback 项:
-
value:None -
error:异常详细信息,例如异常对象、错误消息和堆栈跟踪
错误信息将显示在评估结果中。 打开相应的行以查看错误详细信息。
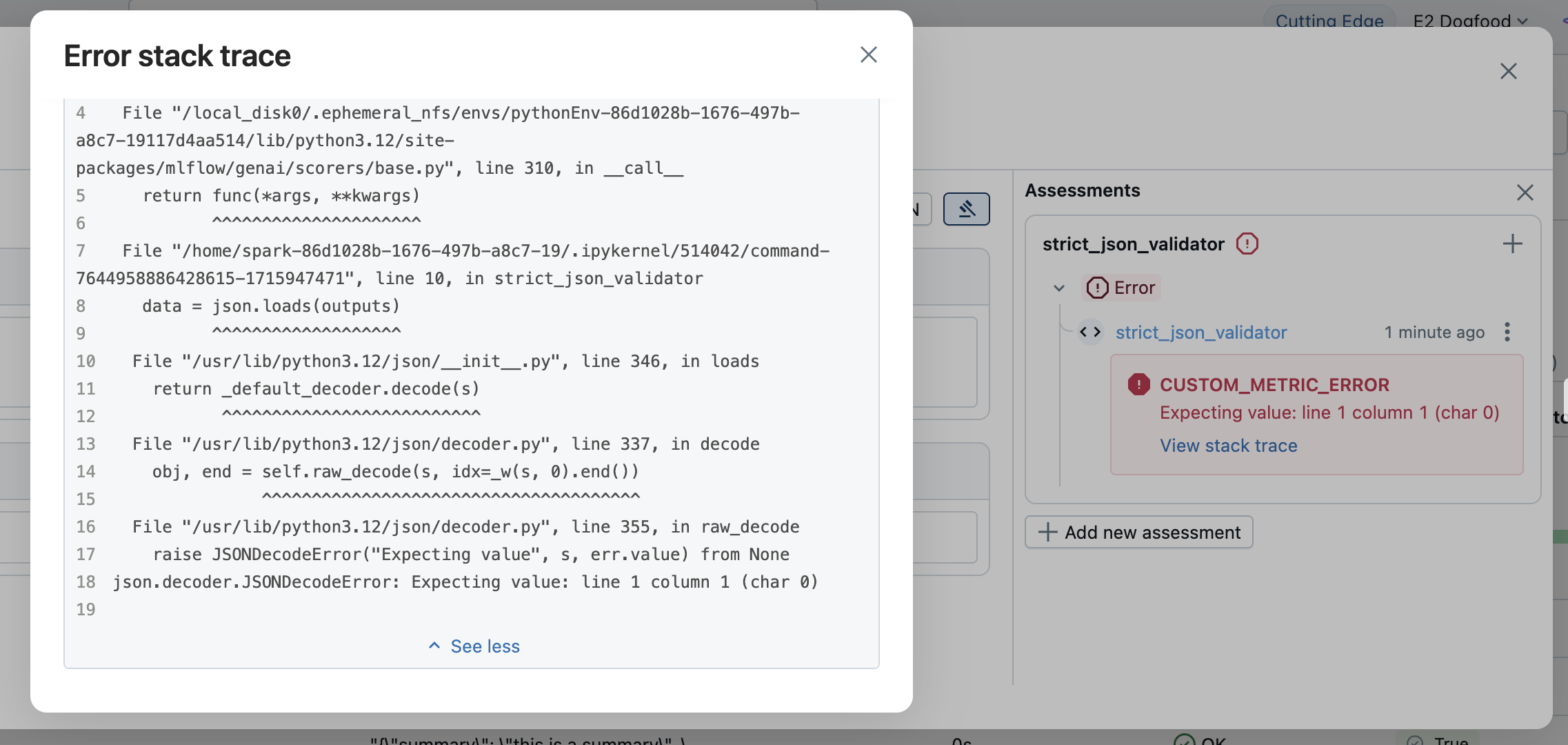
显式处理异常
对于自定义错误处理或提供特定错误消息,请捕获异常并返回 Feedback 值 None 和错误详细信息:
from mlflow.entities import AssessmentError, Feedback
@scorer
def is_valid_response(outputs):
import json
try:
data = json.loads(outputs)
required_fields = ["summary", "confidence", "sources"]
missing = [f for f in required_fields if f not in data]
if missing:
return Feedback(
error=AssessmentError(
error_code="MISSING_REQUIRED_FIELDS",
error_message=f"Missing required fields: {missing}",
),
)
return Feedback(
value=True,
rationale="Valid JSON with all required fields"
)
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
return Feedback(error=e) # Can pass exception object directly to the error parameter
参数 error 接受:
- Python 异常:直接传递异常对象
-
AssessmentError:用于带有错误代码的结构化错误报告
使用 Scorer 类定义记分器
@scorer上述修饰器很简单,通常建议使用,但当它不足时,可以改用Scorer基类。 基于类的定义允许更复杂的评分器,尤其是需要状态的评分器。 该 Scorer 类是 Pydantic 对象,因此可以定义其他字段并在方法中使用 __call__ 它们。
必须定义字段 name 才能设置指标名称。 如果返回对象列表Feedback,则必须在每个name对象中设置Feedback字段以避免命名冲突。
from mlflow.genai.scorers import Scorer
from mlflow.entities import Feedback
from typing import Optional
# Scorer class is a Pydantic object
class CustomScorer(Scorer):
# The `name` field is mandatory
name: str = "response_quality"
# Define additional fields
my_custom_field_1: int = 50
my_custom_field_2: Optional[list[str]] = None
# Override the __call__ method to implement the scorer logic
def __call__(self, outputs: str) -> Feedback:
# Your logic here
return Feedback(
value=True,
rationale="Response meets all quality criteria"
)
状态管理
使用 Scorer 类编写记分器时,请注意使用 Python 类管理状态的规则。 具体而言,请务必使用实例属性,而不是可变类属性。 下面的示例演示了记分器实例之间错误地共享状态。
from mlflow.genai.scorers import Scorer
from mlflow.entities import Feedback
# WRONG: Don't use mutable class attributes
class BadScorer(Scorer):
results = [] # Shared across all instances!
name: str = "bad_scorer"
def __call__(self, outputs, **kwargs):
self.results.append(outputs) # Causes issues
return Feedback(value=True)
# CORRECT: Use instance attributes
class GoodScorer(Scorer):
results: list[str] = None
name: str = "good_scorer"
def __init__(self):
self.results = [] # Per-instance state
def __call__(self, outputs, **kwargs):
self.results.append(outputs) # Safe
return Feedback(value=True)
后续步骤
- 基于代码的记分器示例 - 请参阅许多基于代码的评分器示例
- 开发基于代码的记分器 - 逐步完成自定义评分器的开发工作流
-
在开发期间评估 GenAI - 了解
mlflow.genai.evaluate()如何使用你的评分器 - 在生产环境中监视 GenAI - 部署记分器进行持续监视
API 参考
本指南中使用的 MLflow API 包括: