本文介绍如何创建:
dmpatterns_getstarted_device.py:一个模拟设备应用,它使用直接方法重新启动设备并报告上次重新启动时间。 直接方法是从云中调用的。
dmpatterns_getstarted_service.py:一个 Python 控制台应用,它通过 IoT 中心调用模拟设备应用中的直接方法。 它显示响应和更新的报告属性。
注意
有关可用于生成设备和后端应用的 SDK 工具的详细信息,请参阅 Azure IoT SDK。
先决条件
有效的 Azure 帐户。 (如果没有帐户,可以创建一个试用帐户,只需几分钟即可完成。)
已注册的设备。 在 Azure 门户中注册一个。
建议使用 Python 版本 3.7 或更高版本。 请确保根据安装程序的要求,使用 32 位或 64 位安装。 在安装过程中出现提示时,请确保将 Python 添加到特定于平台的环境变量中。
确保已在防火墙中打开端口 8883。 本文中的设备示例使用 MQTT 协议,该协议通过端口 8883 进行通信。 在某些公司和教育网络环境中,此端口可能被阻止。 有关解决此问题的更多信息和方法,请参阅连接到 IoT 中心(MQTT)。
在 IoT 中心内注册新设备
在本部分中,将使用 Azure CLI 为本文创建设备标识。 设备 ID 区分大小写。
运行以下命令以安装适用于 Azure CLI 的 Azure IoT 扩展:
az extension add --name azure-iot使用以下命令创建一个名为
myDeviceId的新设备标识并检索设备连接字符串:az iot hub device-identity create --device-id myDeviceId --hub-name {Your IoT Hub name} --resource-group {Resource group of the Hub} az iot hub device-identity connection-string show --device-id myDeviceId --hub-name {Your IoT Hub name} --resource-group {Resource group of the Hub} -o table重要
收集的日志中可能会显示设备 ID 用于客户支持和故障排除,因此,在为日志命名时,请务必避免包含任何敏感信息。
记下结果中的设备连接字符串。 设备应用使用此设备连接字符串以设备身份连接到 IoT 中心。
使用直接方法创建设备应用
本部分的操作:
创建一个 Python 控制台应用,用于响应通过云调用的直接方法。
模拟设备重新启动。
使用报告的属性以确保设备孪生查询可以标识设备及设备上次重新启动的时间。
在命令提示符处,运行以下命令以安装 azure-iot-device 包:
pip install azure-iot-device使用文本编辑器,在工作目录中创建名为 dmpatterns_getstarted_device.py 的文件。
在
import文件开头添加以下 语句。import time import datetime from azure.iot.device import IoTHubDeviceClient, MethodResponse添加 CONNECTION_STRING 变量。 将
{deviceConnectionString}占位符值替换为设备连接字符串。 以前在在 IoT 中心内注册新设备中复制了此连接字符串。CONNECTION_STRING = "{deviceConnectionString}"添加以下函数以实例化为设备上的直接方法配置的客户端。
def create_client(): # Instantiate the client client = IoTHubDeviceClient.create_from_connection_string(CONNECTION_STRING) # Define the handler for method requests def method_request_handler(method_request): if method_request.name == "rebootDevice": # Act on the method by rebooting the device print("Rebooting device") time.sleep(20) print("Device rebooted") # ...and patching the reported properties current_time = str(datetime.datetime.now()) reported_props = {"rebootTime": current_time} client.patch_twin_reported_properties(reported_props) print( "Device twins updated with latest rebootTime") # Create a method response indicating the method request was resolved resp_status = 200 resp_payload = {"Response": "This is the response from the device"} method_response = MethodResponse(method_request.request_id, resp_status, resp_payload) else: # Create a method response indicating the method request was for an unknown method resp_status = 404 resp_payload = {"Response": "Unknown method"} method_response = MethodResponse(method_request.request_id, resp_status, resp_payload) # Send the method response client.send_method_response(method_response) try: # Attach the handler to the client client.on_method_request_received = method_request_handler except: # In the event of failure, clean up client.shutdown() return client启动直接方法示例并等待。
def main(): print ("Starting the IoT Hub Python sample...") client = create_client() print ("Waiting for commands, press Ctrl-C to exit") try: # Wait for program exit while True: time.sleep(1000) except KeyboardInterrupt: print("IoTHubDeviceClient sample stopped") finally: # Graceful exit print("Shutting down IoT Hub Client") client.shutdown() if __name__ == '__main__': main()保存并关闭 dmpatterns_getstarted_device.py 文件。
注意
为简单起见,本教程不实现任何重试策略。 在生产代码中,应按暂时性故障处理一文中所述实现重试策略。
获取 IoT 中心连接字符串
在本文中,你将创建一项在设备上调用直接方法的后端服务。 若要通过 IoT 中心在设备上调用直接方法,服务需要“服务连接”权限。 默认情况下,每个 IoT 中心都使用名为“服务”的共享访问策略创建,该策略会授予此权限。
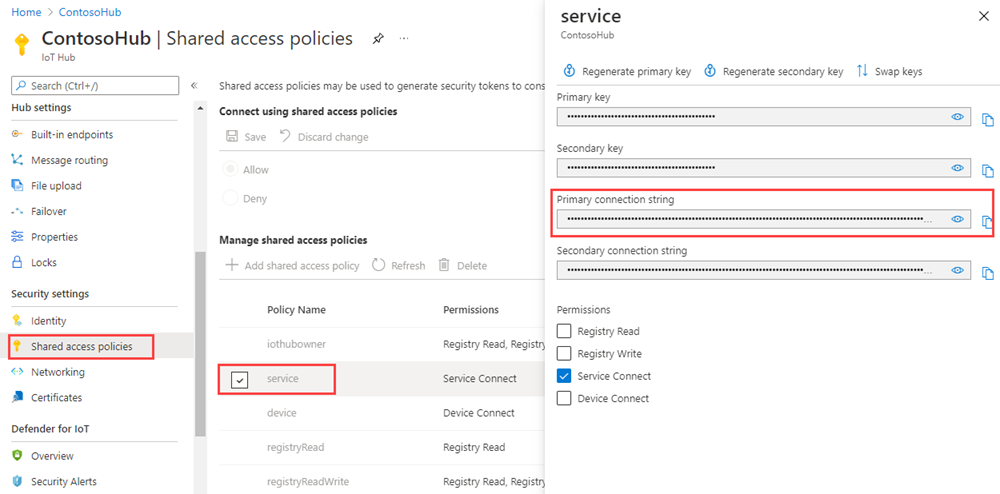
若要获取 service策略的 IoT 中心连接字符串,请执行以下步骤:
在 Azure 门户中,选择“资源组”。 选择中心所在的资源组,然后从资源列表中选择中心。
在 IoT 中心的左侧窗格上,选择“共享访问策略”。
在策略列表中,选择“service”策略。
复制“主连接字符串”并保存该值。
有关 IoT 中心共享访问策略和权限的详细信息,请参阅访问控制和权限。
创建服务应用以触发重新启动
此部分将创建一个 Python 控制台应用,以使用直接方法在设备上启动远程重新启动。 该应用使用设备孪生查询来搜索该设备的上次重新启动时间。
在命令提示符处,运行以下命令以安装 azure-iot-hub 包:
pip install azure-iot-hub使用文本编辑器,在工作目录中创建名为 dmpatterns_getstarted_service.py 的文件。
在
import文件开头添加以下 语句。import sys, time from azure.iot.hub import IoTHubRegistryManager from azure.iot.hub.models import CloudToDeviceMethod, CloudToDeviceMethodResult, Twin添加以下变量声明。 将
{IoTHubConnectionString}占位符值替换为以前在获取 IoT 中心连接字符串中复制的 IoT 中心连接字符串。 将{deviceId}占位符值替换为在在 IoT 中心内注册新设备中注册的设备 ID。CONNECTION_STRING = "{IoTHubConnectionString}" DEVICE_ID = "{deviceId}" METHOD_NAME = "rebootDevice" METHOD_PAYLOAD = "{\"method_number\":\"42\"}" TIMEOUT = 60 WAIT_COUNT = 10添加以下函数以调用设备方法重新启动目标设备,然后查询设备孪生并获取上次重新启动时间。
def iothub_devicemethod_sample_run(): try: # Create IoTHubRegistryManager registry_manager = IoTHubRegistryManager(CONNECTION_STRING) print ( "" ) print ( "Invoking device to reboot..." ) # Call the direct method. deviceMethod = CloudToDeviceMethod(method_name=METHOD_NAME, payload=METHOD_PAYLOAD) response = registry_manager.invoke_device_method(DEVICE_ID, deviceMethod) print ( "" ) print ( "Successfully invoked the device to reboot." ) print ( "" ) print ( response.payload ) while True: print ( "" ) print ( "IoTHubClient waiting for commands, press Ctrl-C to exit" ) status_counter = 0 while status_counter <= WAIT_COUNT: twin_info = registry_manager.get_twin(DEVICE_ID) if twin_info.properties.reported.get("rebootTime") != None : print ("Last reboot time: " + twin_info.properties.reported.get("rebootTime")) else: print ("Waiting for device to report last reboot time...") time.sleep(5) status_counter += 1 except Exception as ex: print ( "" ) print ( "Unexpected error {0}".format(ex) ) return except KeyboardInterrupt: print ( "" ) print ( "IoTHubDeviceMethod sample stopped" ) if __name__ == '__main__': print ( "Starting the IoT Hub Service Client DeviceManagement Python sample..." ) print ( " Connection string = {0}".format(CONNECTION_STRING) ) print ( " Device ID = {0}".format(DEVICE_ID) ) iothub_devicemethod_sample_run()保存并关闭 dmpatterns_getstarted_service.py 文件。
运行应用
你现在已准备好运行设备代码和开始设备重启的服务代码。
在创建了设备的命令提示符下,运行以下命令以开始侦听重启直接方法。
python dmpatterns_getstarted_device.py在创建服务的命令提示符下,运行以下命令以触发远程重启并查询设备孪生以查找上次重启时间。
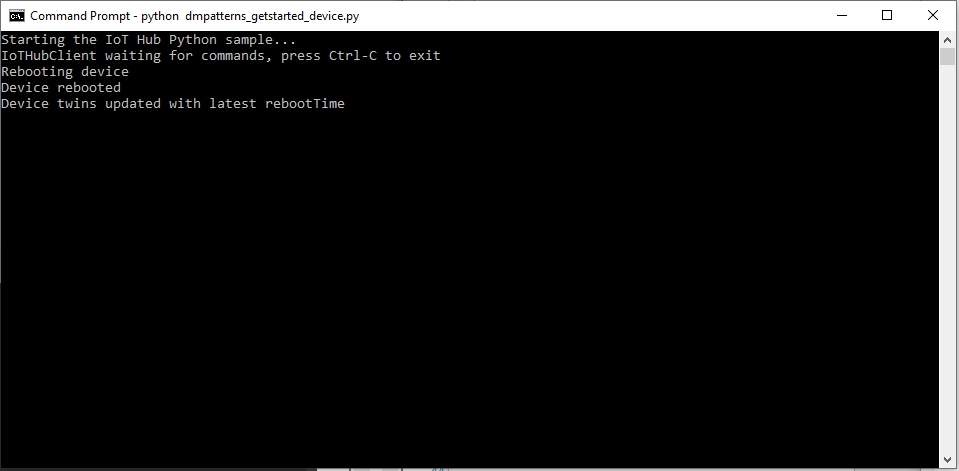
python dmpatterns_getstarted_service.py可在控制台查看对直接方法的设备响应。
下面显示了对重新启动直接方法的设备响应:
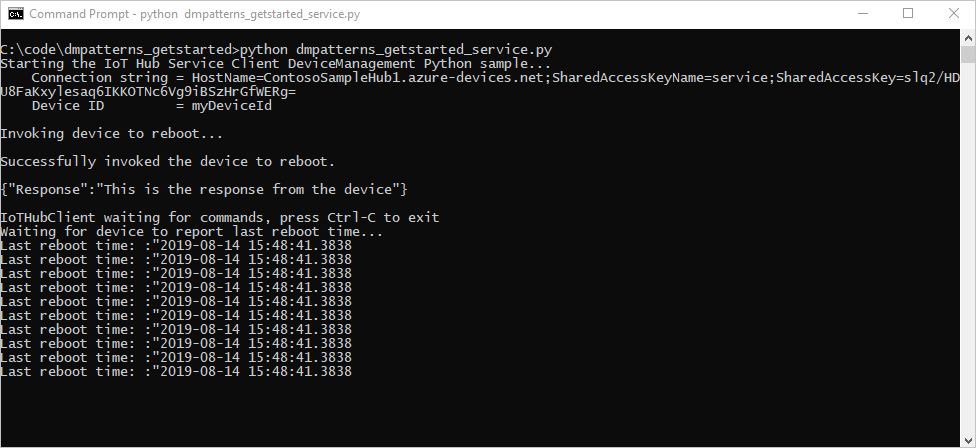
下面显示服务调用重新启动直接方法并轮询设备孪生以获取状态:
自定义和扩展设备管理操作
IoT 解决方案可扩展已定义的设备管理模式集,或通过使用设备孪生和云到设备方法基元启用自定义模式。 设备管理操作的其他示例包括恢复出厂设置、固件更新、软件更新、电源管理、网络和连接管理以及数据加密。
设备维护时段
通常情况下,将设备配置为在某一时间执行操作,以最大程度减少中断和停机时间。 设备维护时段是一种常用模式,用于定义设备应更新其配置的时间。 后端解决方案使用设备克隆所需属性在设备上定义并激活策略,以启用维护时段。 当设备收到维护时段策略时,它可以使用设备克隆报告属性报告策略状态。 然后,后端应用可以使用设备克隆查询来证明设备和每个策略的符合性。
后续步骤
本文使用直接方法触发设备上的远程重新启动。 使用报告属性报告设备上次重新启动时间,并查询设备孪生从云中发现设备上次重新启动时间。
若要了解如何扩展 IoT 解决方案以及在多个设备上计划方法调用,请参阅计划和广播作业。