Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO: All API Management tiers
This article shows how to manually add an API to Azure API Management. When you want to create mock responses from the API, you can create a blank API. For information about creating mock API responses, see Mock API responses.
If you want to import an existing API, see the Related content section of this article.
In this article, you learn how to create a blank API. You'll specify httpbin.org (a public testing service) as a backend API.
Prerequisites
- Complete the Create an Azure API Management instance quickstart.
Go to your API Management instance
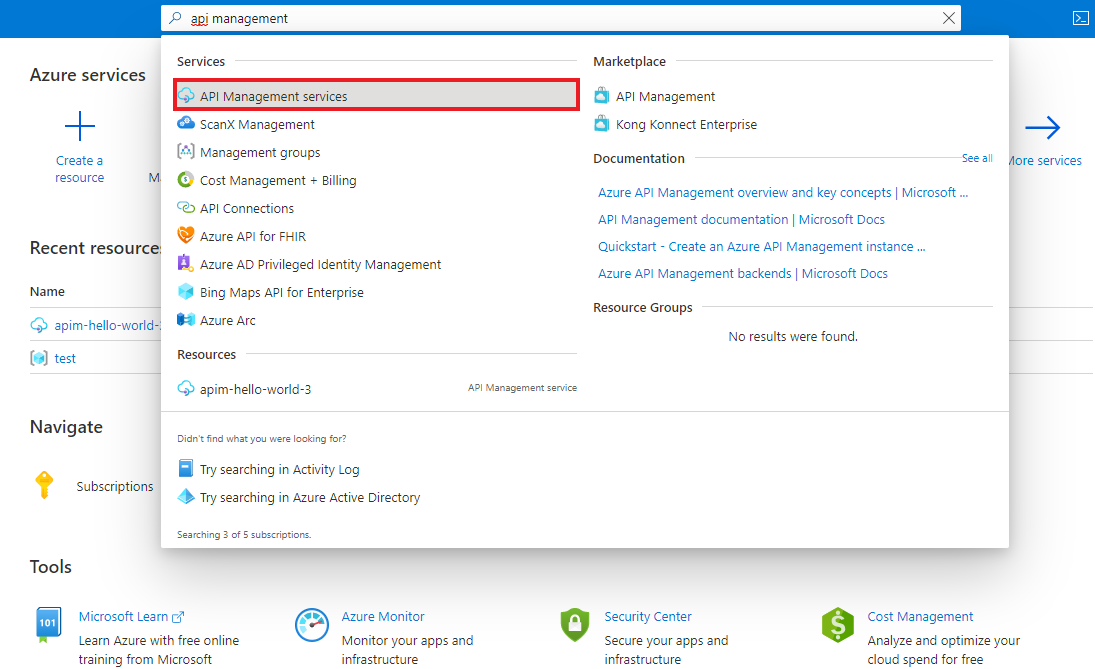
In the Azure portal, search for and select API Management services:
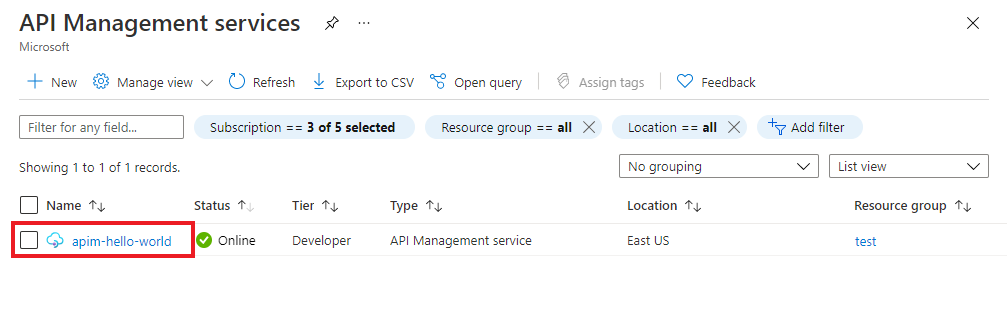
On the API Management services page, select your API Management instance:
Create an API
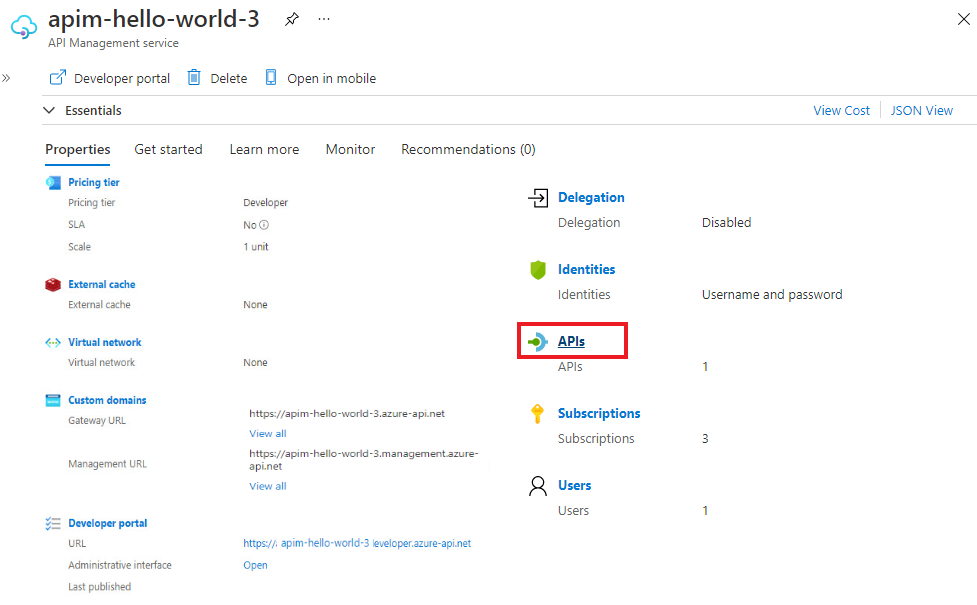
Under APIs in the left menu, select APIs.
Select + Add API.
Select the HTTP tile:

Enter the backend Web service URL (for example,
https://httpbin.org) and other settings for the API. The settings are explained in the Import and publish your first API tutorial.Select Create.
At this point, you have no operations in API Management that map to the operations in your backend API. If you call an operation that's exposed through the backend but not through API Management, you get a 404 error.
Note
By default, when you add an API, even if it's connected to a backend service, API Management won't expose any operations until you allow them. To allow an operation of your backend service, create an API Management operation that maps to the backend operation.
Add and test an operation
This section shows how to add a /get operation to map it to the backend http://httpbin.org/get operation.
Add an operation
- Select the API you created in the previous step.
- Select + Add operation.
- In URL, select GET and enter /get in the text box.
- In Display name, enter FetchData.
- Select Save.
Test the operation
Test the operation in the Azure portal. (You can also test it in the developer portal.)
- Select the Test tab.
- Select FetchData.
- Select Send.
The response that the http://httpbin.org/get operation generates appears in the HTTP response section. If you want to transform your operations, see Transform and protect your API.
Add and test a parameterized operation
This section shows how to add an operation that takes a parameter. In this example, you map the operation to http://httpbin.org/status/200.
Add an operation
- Select the API that you created earlier.
- On the Design tab, select + Add operation.
- In URL, select GET and enter /status/{code} in the text box.
- In Display name, enter GetStatus.
- Select Save.
Test the operation
Test the operation in the Azure portal. (You can also test it in the developer portal.)
Select the Test tab.
Select GetStatus. In code, enter 200.
Select Send.
The response that the
http://httpbin.org/status/200operation generates appears in the HTTP response section. If you want to transform your operations, see Transform and protect your API.
Add and test a wildcard operation
This section shows how to add a wildcard operation. A wildcard operation enables you to pass an arbitrary value with an API request. Instead of creating separate GET operations as shown in the previous sections, you could create a wildcard GET operation.
Caution
Be cautious when you configure a wildcard operation. This configuration might make an API more vulnerable to certain API security threats.
Add an operation
- Select the API you created earlier.
- On the Design tab, select + Add operation.
- In URL, select GET and enter /* in the text box.
- In Display name, enter WildcardGet.
- Select Save.
Test the operation
Test the operation in the Azure portal. (You can also test it in the developer portal.)
Select the Test tab.
Select WildcardGet. Try the GET operations that you tested in previous sections, or try a different supported GET operation.
For example, in Template parameters, change the value next to the wildcard (*) name to headers. The operation returns the incoming request's HTTP headers.
Select Send.
The response that the
http://httpbin.org/headersoperation generates appears in the HTTP response section. If you want to transform your operations, see Transform and protect your API.
Note
It can be important to understand how the host for the backend API you're integrating with handles trailing slashes on an operation URL. For more information, see this API Management FAQ.
Append other APIs
You can compose an API out of APIs that are exposed by different services, including:
- An OpenAPI specification
- A SOAP API
- A GraphQL API
- A Web App that's hosted in Azure App Service
- Azure Functions
- Azure Logic Apps
- Azure Service Fabric
Note
When you import an API, the operations are appended to your current API.
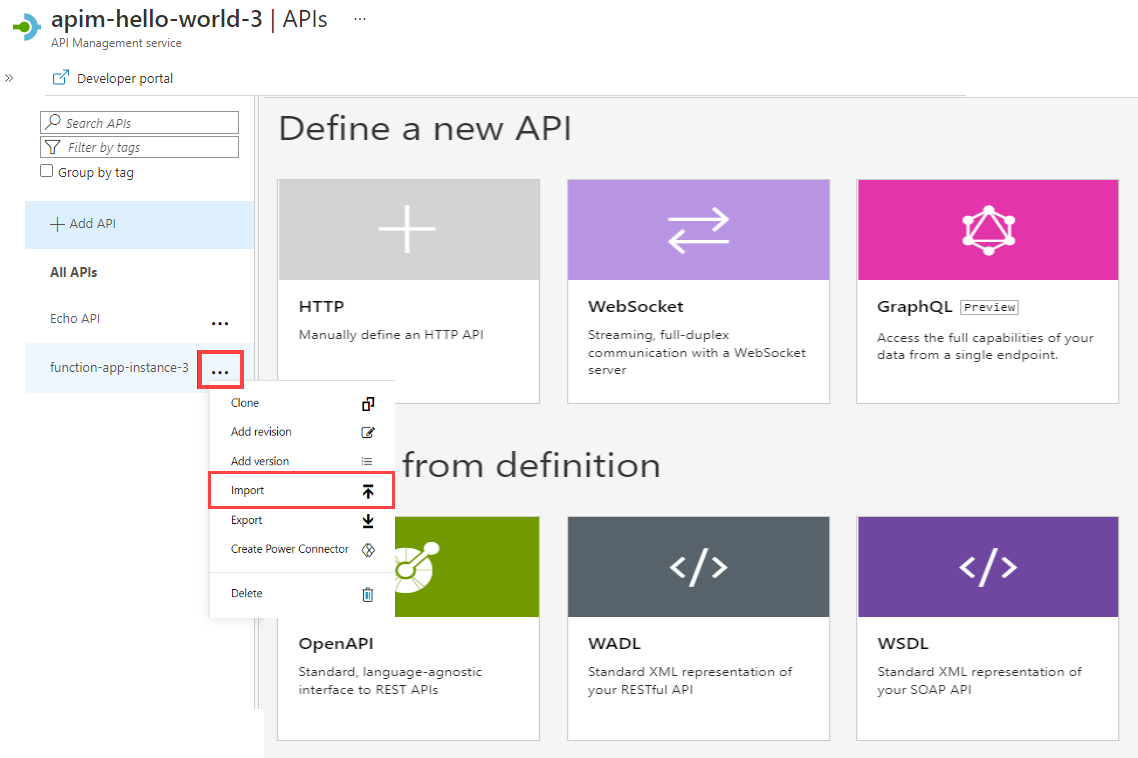
To append an API to an existing API:
Go to your Azure API Management instance in the Azure portal:
Select APIs on the Overview page or select APIs > APIs in the menu on the left.
Select the ellipsis (...) next to the API that you want to append another API to.
Select Import from the drop-down menu:
Select a service from which to import an API.
Related content
- API import limitations
- Import an OpenAPI specification
- Import a SOAP API
- Import a SOAP API and convert it to REST
- Import an App Service API
- Import a WebSocket API
- Import a GraphQL API
- Import a function app API
- Import a logic app API
- Import a Service Fabric service
- Import SAP OData metadata
- Edit an API