Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
This article outlines how to use Copy Activity in Azure Data Factory or Synapse pipelines to copy data from and to Azure Synapse Analytics, and use Data Flow to transform data in Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2. To learn about Azure Data Factory, read the introductory article.
Supported capabilities
This Azure Synapse Analytics connector is supported for the following capabilities:
| Supported capabilities | IR | Managed private endpoint |
|---|---|---|
| Copy activity (source/sink) | ① ② | ✓ |
| Mapping data flow (source/sink) | ① | ✓ |
| Lookup activity | ① ② | ✓ |
| GetMetadata activity | ① ② | ✓ |
| Script activity | ① ② | ✓ |
| Stored procedure activity | ① ② | ✓ |
① Azure integration runtime ② Self-hosted integration runtime
For Copy activity, this Azure Synapse Analytics connector supports these functions:
- Copy data by using SQL authentication and Microsoft Entra Application token authentication with a service principal or managed identities for Azure resources.
- As a source, retrieve data by using a SQL query or stored procedure. You can also choose to parallel copy from an Azure Synapse Analytics source, see the Parallel copy from Azure Synapse Analytics section for details.
- As a sink, load data by using COPY statement or PolyBase or bulk insert. We recommend COPY statement or PolyBase for better copy performance. The connector also supports automatically creating destination table with DISTRIBUTION = ROUND_ROBIN if not exists based on the source schema.
Important
If you copy data by using an Azure Integration Runtime, configure a server-level firewall rule so that Azure services can access the logical SQL server. If you copy data by using a self-hosted integration runtime, configure the firewall to allow the appropriate IP range. This range includes the machine's IP that is used to connect to Azure Synapse Analytics.
Get started
Tip
To achieve best performance, use PolyBase or COPY statement to load data into Azure Synapse Analytics. The Use PolyBase to load data into Azure Synapse Analytics and Use COPY statement to load data into Azure Synapse Analytics sections have details. For a walkthrough with a use case, see Load 1 TB into Azure Synapse Analytics under 15 minutes with Azure Data Factory.
To perform the copy activity with a pipeline, you can use one of the following tools or SDKs:
- Copy Data tool
- Azure portal
- .NET SDK
- Python SDK
- Azure PowerShell
- REST API
- Azure Resource Manager template
Create an Azure Synapse Analytics linked service using UI
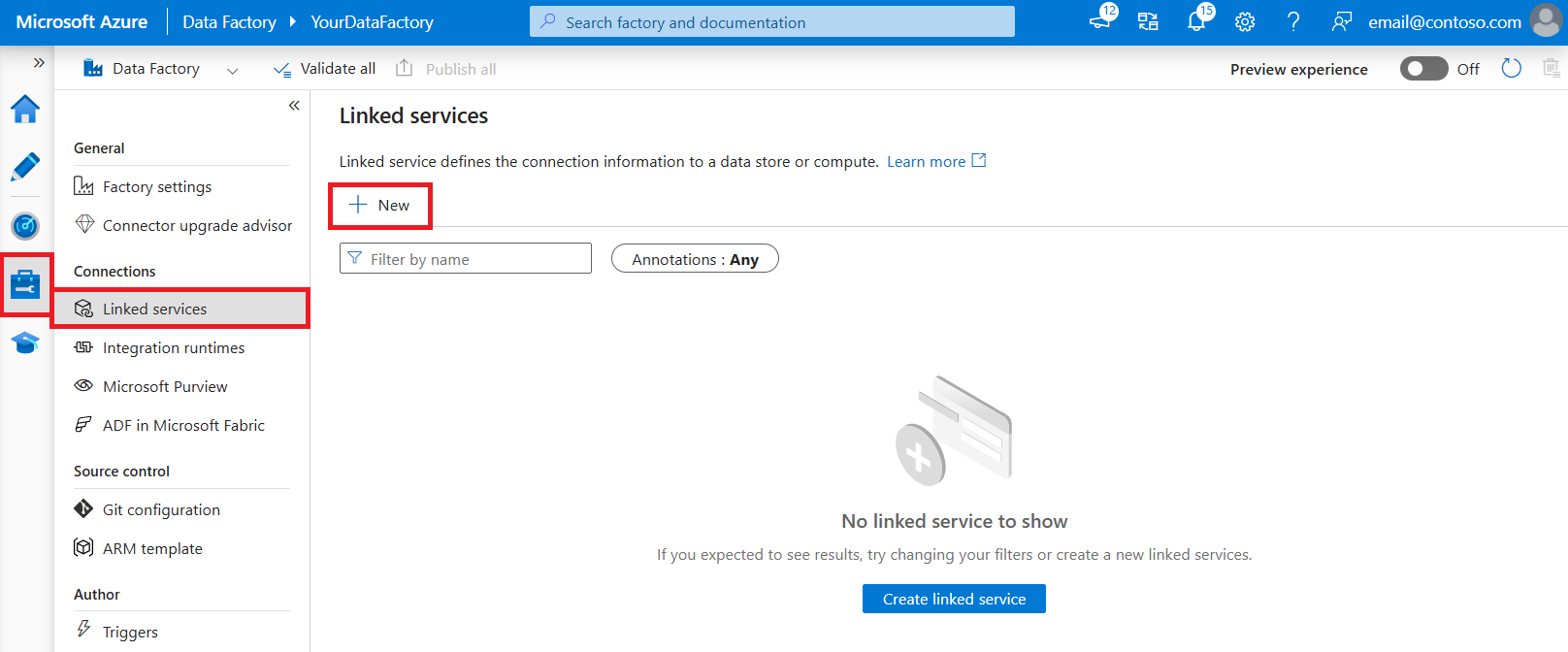
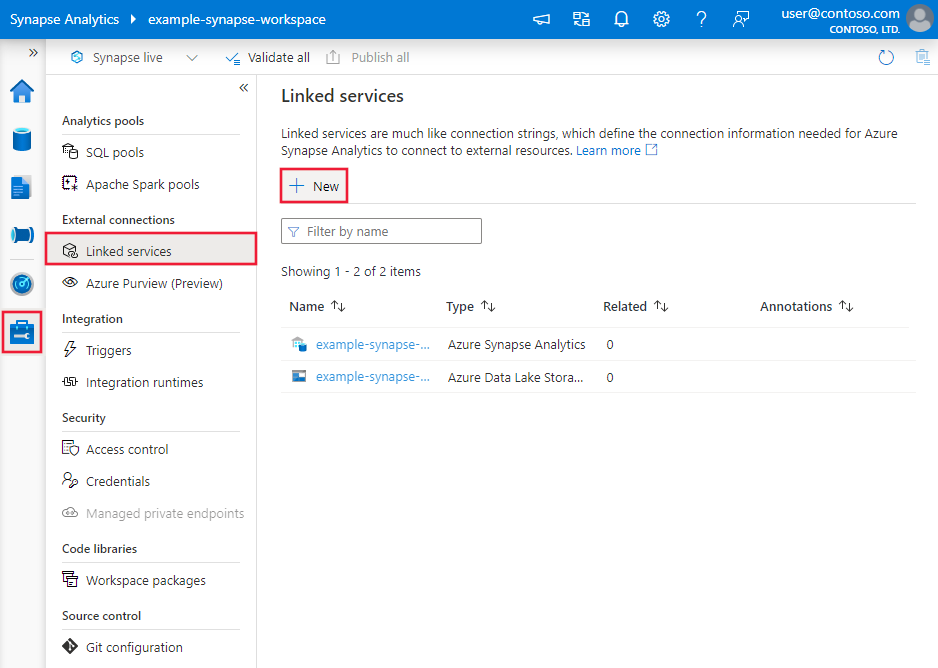
Use the following steps to create an Azure Synapse Analytics linked service in the Azure portal UI.
Browse to the Manage tab in your Azure Data Factory or Synapse workspace and select Linked Services, then click New:
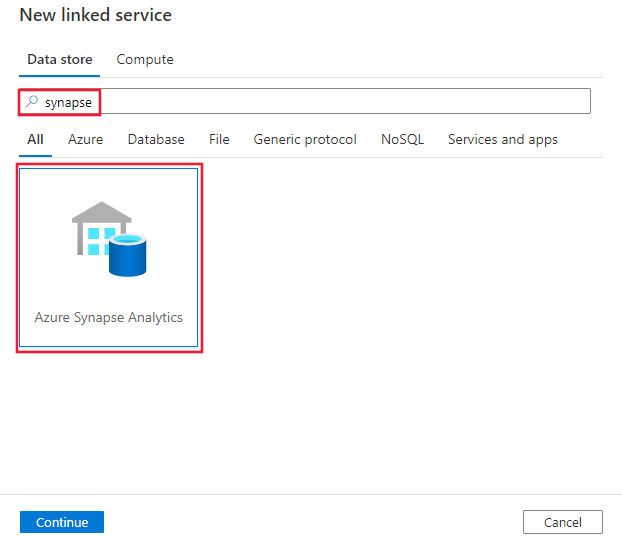
Search for Synapse and select the Azure Synapse Analytics connector.
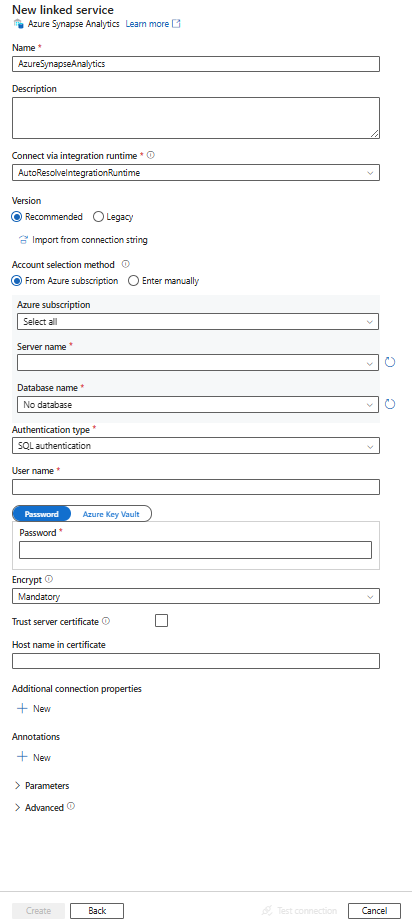
Configure the service details, test the connection, and create the new linked service.
Connector configuration details
The following sections provide details about properties that define Data Factory and Synapse pipeline entities specific to an Azure Synapse Analytics connector.
Linked service properties
The Azure Synapse Analytics connector Recommended version supports TLS 1.3. Refer to this section to upgrade your Azure Synapse Analytics connector version from Legacy one. For the property details, see the corresponding sections.
Tip
When creating linked service for a serverless SQL pool in Azure Synapse from the Azure portal:
- For Account Selection Method, choose Enter manually.
- Paste the fully qualified domain name of the serverless endpoint. You can find this in the Azure portal Overview page for your Synapse workspace, in the properties under Serverless SQL endpoint. For example,
myserver-ondemand.sql-azuresynapse.azure.cn. - For Database name, provide the database name in the serverless SQL pool.
Tip
If you hit error with error code as "UserErrorFailedToConnectToSqlServer" and message like "The session limit for the database is XXX and has been reached.", add Pooling=false to your connection string and try again.
Recommended version
These generic properties are supported for an Azure Synapse Analytics linked service when you apply Recommended version:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to AzureSqlDW. | Yes |
| server | The name or network address of the SQL server instance you want to connect to. | Yes |
| database | The name of the database. | Yes |
| authenticationType | The type used for authentication. Allowed values are SQL (default), ServicePrincipal, SystemAssignedManagedIdentity, UserAssignedManagedIdentity. Go to the relevant authentication section on specific properties and prerequisites. | Yes |
| encrypt | Indicate whether TLS encryption is required for all data sent between the client and server. Options: mandatory (for true, default)/optional (for false)/strict. | No |
| trustServerCertificate | Indicate whether the channel will be encrypted while bypassing the certificate chain to validate trust. | No |
| hostNameInCertificate | The host name to use when validating the server certificate for the connection. When not specified, the server name is used for certificate validation. | No |
| connectVia | The integration runtime to be used to connect to the data store. You can use Azure Integration Runtime or a self-hosted integration runtime (if your data store is located in a private network). If not specified, it uses the default Azure Integration Runtime. | No |
For additional connection properties, see the table below:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| applicationIntent | The application workload type when connecting to a server. Allowed values are ReadOnly and ReadWrite. |
No |
| connectTimeout | The length of time (in seconds) to wait for a connection to the server before terminating the attempt and generating an error. | No |
| connectRetryCount | The number of reconnections attempted after identifying an idle connection failure. The value should be an integer between 0 and 255. | No |
| connectRetryInterval | The amount of time (in seconds) between each reconnection attempt after identifying an idle connection failure. The value should be an integer between 1 and 60. | No |
| loadBalanceTimeout | The minimum time (in seconds) for the connection to live in the connection pool before the connection being destroyed. | No |
| commandTimeout | The default wait time (in seconds) before terminating the attempt to execute a command and generating an error. | No |
| integratedSecurity | The allowed values are true or false. When specifying false, indicate whether userName and password are specified in the connection. When specifying true, indicates whether the current Windows account credentials are used for authentication. |
No |
| failoverPartner | The name or address of the partner server to connect to if the primary server is down. | No |
| maxPoolSize | The maximum number of connections allowed in the connection pool for the specific connection. | No |
| minPoolSize | The minimum number of connections allowed in the connection pool for the specific connection. | No |
| multipleActiveResultSets | The allowed values are true or false. When you specify true, an application can maintain multiple active result sets (MARS). When you specify false, an application must process or cancel all result sets from one batch before it can execute any other batches on that connection. |
No |
| multiSubnetFailover | The allowed values are true or false. If your application is connecting to an AlwaysOn availability group (AG) on different subnets, setting this property to true provides faster detection of and connection to the currently active server. |
No |
| packetSize | The size in bytes of the network packets used to communicate with an instance of server. | No |
| pooling | The allowed values are true or false. When you specify true, the connection will be pooled. When you specify false, the connection will be explicitly opened every time the connection is requested. |
No |
SQL authentication
To use SQL authentication, in addition to the generic properties that are described in the preceding section, specify the following properties:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| userName | The user name used to connect to the server. | Yes |
| password | The password for the user name. Mark this field as SecureString to store it securely. Or, you can reference a secret stored in Azure Key Vault. | Yes |
Example: using SQL authentication
{
"name": "AzureSqlDWLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "AzureSqlDW",
"typeProperties": {
"server": "<name or network address of the SQL server instance>",
"database": "<database name>",
"encrypt": "<encrypt>",
"trustServerCertificate": false,
"authenticationType": "SQL",
"userName": "<user name>",
"password": {
"type": "SecureString",
"value": "<password>"
}
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Example: password in Azure Key Vault
{
"name": "AzureSqlDWLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "AzureSqlDW",
"typeProperties": {
"server": "<name or network address of the SQL server instance>",
"database": "<database name>",
"encrypt": "<encrypt>",
"trustServerCertificate": false,
"authenticationType": "SQL",
"userName": "<user name>",
"password": {
"type": "AzureKeyVaultSecret",
"store": {
"referenceName": "<Azure Key Vault linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"secretName": "<secretName>"
}
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Service principal authentication
To use service principal authentication, in addition to the generic properties that are described in the preceding section, specify the following properties:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| servicePrincipalId | Specify the application's client ID. | Yes |
| servicePrincipalCredential | The service principal credential. Specify the application's key. Mark this field as SecureString to store it securely, or reference a secret stored in Azure Key Vault. | Yes |
| tenant | Specify the tenant information (domain name or tenant ID) under which your application resides. You can retrieve it by hovering the mouse in the top-right corner of the Azure portal. | Yes |
| azureCloudType | For service principal authentication, specify the type of Azure cloud environment to which your Microsoft Entra application is registered. By default, the data factory or Synapse pipeline's cloud environment is used. |
No |
You also need to follow the steps below:
Create a Microsoft Entra application from the Azure portal. Make note of the application name and the following values that define the linked service:
- Application ID
- Application key
- Tenant ID
Provision a Microsoft Entra administrator for your server in the Azure portal if you haven't already done so. The Microsoft Entra administrator can be a Microsoft Entra user or Microsoft Entra group. If you grant the group with managed identity an admin role, skip steps 3 and 4. The administrator will have full access to the database.
Create contained database users for the service principal. Connect to the data warehouse from or to which you want to copy data by using tools like SSMS, with a Microsoft Entra identity that has at least ALTER ANY USER permission. Run the following T-SQL:
CREATE USER [your_application_name] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;Grant the service principal needed permissions as you normally do for SQL users or others. Run the following code, or refer to more options here. If you want to use PolyBase to load the data, learn the required database permission.
EXEC sp_addrolemember db_owner, [your application name];Configure an Azure Synapse Analytics linked service in an Azure Data Factory or Synapse workspace.
Linked service example that uses service principal authentication
{
"name": "AzureSqlDWLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "AzureSqlDW",
"typeProperties": {
"connectionString": "Server=tcp:<servername>.database.chinacloudapi.cn,1433;Database=<databasename>;Connection Timeout=30",
"servicePrincipalId": "<service principal id>",
"servicePrincipalCredential": {
"type": "SecureString",
"value": "<application key>"
},
"tenant": "<tenant info, e.g. microsoft.partner.onmschina.cn>"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
System-assigned managed identities for Azure resources authentication
A data factory or Synapse workspace can be associated with a system-assigned managed identity for Azure resources that represents the resource. You can use this managed identity for Azure Synapse Analytics authentication. The designated resource can access and copy data from or to your data warehouse by using this identity.
To use system-assigned managed identity authentication, specify the generic properties that are described in the preceding section, and follow these steps.
Provision a Microsoft Entra administrator for your server on the Azure portal if you haven't already done so. The Microsoft Entra administrator can be a Microsoft Entra user or Microsoft Entra group. If you grant the group with system-assigned managed identity an admin role, skip steps 3 and 4. The administrator will have full access to the database.
Create contained database users for the system-assigned managed identity. Connect to the data warehouse from or to which you want to copy data by using tools like SSMS, with a Microsoft Entra identity that has at least ALTER ANY USER permission. Run the following T-SQL.
CREATE USER [your_resource_name] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;Grant the system-assigned managed identity needed permissions as you normally do for SQL users and others. Run the following code, or refer to more options here. If you want to use PolyBase to load the data, learn the required database permission.
EXEC sp_addrolemember db_owner, [your_resource_name];Configure an Azure Synapse Analytics linked service.
Example:
{
"name": "AzureSqlDWLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "AzureSqlDW",
"typeProperties": {
"server": "<name or network address of the SQL server instance>",
"database": "<database name>",
"encrypt": "<encrypt>",
"trustServerCertificate": false,
"authenticationType": "SystemAssignedManagedIdentity"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
User-assigned managed identity authentication
A data factory or Synapse workspace can be associated with a user-assigned managed identities that represents the resource. You can use this managed identity for Azure Synapse Analytics authentication. The designated resource can access and copy data from or to your data warehouse by using this identity.
To use user-assigned managed identity authentication, in addition to the generic properties that are described in the preceding section, specify the following properties:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| credentials | Specify the user-assigned managed identity as the credential object. | Yes |
You also need to follow the steps below:
Provision a Microsoft Entra administrator for your server on the Azure portal if you haven't already done so. The Microsoft Entra administrator can be a Microsoft Entra user or Microsoft Entra group. If you grant the group with user-assigned managed identity an admin role, skip steps 3. The administrator will have full access to the database.
Create contained database users for the user-assigned managed identity. Connect to the data warehouse from or to which you want to copy data by using tools like SSMS, with a Microsoft Entra identity that has at least ALTER ANY USER permission. Run the following T-SQL.
CREATE USER [your_resource_name] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;Create one or multiple user-assigned managed identities and grant the user-assigned managed identity needed permissions as you normally do for SQL users and others. Run the following code, or refer to more options here. If you want to use PolyBase to load the data, learn the required database permission.
EXEC sp_addrolemember db_owner, [your_resource_name];Assign one or multiple user-assigned managed identities to your data factory and create credentials for each user-assigned managed identity.
Configure an Azure Synapse Analytics linked service.
Example
{
"name": "AzureSqlDWLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "AzureSqlDW",
"typeProperties": {
"server": "<name or network address of the SQL server instance>",
"database": "<database name>",
"encrypt": "<encrypt>",
"trustServerCertificate": false,
"authenticationType": "UserAssignedManagedIdentity",
"credential": {
"referenceName": "credential1",
"type": "CredentialReference"
}
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Legacy version
These generic properties are supported for an Azure Synapse Analytics linked service when you apply Legacy version:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to AzureSqlDW. | Yes |
| connectionString | Specify the information needed to connect to the Azure Synapse Analytics instance for the connectionString property. Mark this field as a SecureString to store it securely. You can also put password/service principal key in Azure Key Vault and if it's SQL authentication pull the password configuration out of the connection string. See Store credentials in Azure Key Vault article with more details. |
Yes |
| connectVia | The integration runtime to be used to connect to the data store. You can use Azure Integration Runtime or a self-hosted integration runtime (if your data store is located in a private network). If not specified, it uses the default Azure Integration Runtime. | No |
For different authentication types, refer to the following sections on specific properties and prerequisites respectively:
- SQL authentication for the legacy version
- Service principal authentication for the legacy version
- System-assigned managed identity authentication for the legacy version
- User-assigned managed identity authentication for the legacy version
SQL authentication for the legacy version
To use SQL authentication, specify the generic properties that are described in the preceding section.
Service principal authentication for the legacy version
To use service principal authentication, in addition to the generic properties that are described in the preceding section, specify the following properties:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| servicePrincipalId | Specify the application's client ID. | Yes |
| servicePrincipalKey | Specify the application's key. Mark this field as a SecureString to store it securely, or reference a secret stored in Azure Key Vault. | Yes |
| tenant | Specify the tenant information, like the domain name or tenant ID, under which your application resides. Retrieve it by hovering the mouse in the upper-right corner of the Azure portal. | Yes |
| azureCloudType | For service principal authentication, specify the type of Azure cloud environment to which your Microsoft Entra application is registered. By default, the data factory or Synapse pipeline's cloud environment is used. |
No |
You also need to follow the steps in Service principal authentication to grant the corresponding permission.
System-assigned managed identity authentication for the legacy version
To use system-assigned managed identity authentication, follow the same step for the recommended version in System-assigned managed identity authentication.
User-assigned managed identity authentication for legacy version
To use user-assigned managed identity authentication, follow the same step for the recommended version in User-assigned managed identity authentication.
Dataset properties
For a full list of sections and properties available for defining datasets, see the Datasets article.
The following properties are supported for Azure Synapse Analytics dataset:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the dataset must be set to AzureSqlDWTable. | Yes |
| schema | Name of the schema. | No for source, Yes for sink |
| table | Name of the table/view. | No for source, Yes for sink |
| tableName | Name of the table/view with schema. This property is supported for backward compatibility. For new workload, use schema and table. |
No for source, Yes for sink |
Dataset properties example
{
"name": "AzureSQLDWDataset",
"properties":
{
"type": "AzureSqlDWTable",
"linkedServiceName": {
"referenceName": "<Azure Synapse Analytics linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"schema": [ < physical schema, optional, retrievable during authoring > ],
"typeProperties": {
"schema": "<schema_name>",
"table": "<table_name>"
}
}
}
Copy Activity properties
For a full list of sections and properties available for defining activities, see the Pipelines article. This section provides a list of properties supported by the Azure Synapse Analytics source and sink.
Azure Synapse Analytics as the source
Tip
To load data from Azure Synapse Analytics efficiently by using data partitioning, learn more from Parallel copy from Azure Synapse Analytics.
To copy data from Azure Synapse Analytics, set the type property in the Copy Activity source to SqlDWSource. The following properties are supported in the Copy Activity source section:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the Copy Activity source must be set to SqlDWSource. | Yes |
| sqlReaderQuery | Use the custom SQL query to read data. Example: select * from MyTable. |
No |
| sqlReaderStoredProcedureName | The name of the stored procedure that reads data from the source table. The last SQL statement must be a SELECT statement in the stored procedure. | No |
| storedProcedureParameters | Parameters for the stored procedure. Allowed values are name or value pairs. Names and casing of parameters must match the names and casing of the stored procedure parameters. |
No |
| isolationLevel | Specifies the transaction locking behavior for the SQL source. The allowed values are: ReadCommitted, ReadUncommitted, RepeatableRead, Serializable, Snapshot. If not specified, the database's default isolation level is used. For more information, see system.data.isolationlevel. | No |
| partitionOptions | Specifies the data partitioning options used to load data from Azure Synapse Analytics. Allowed values are: None (default), PhysicalPartitionsOfTable, and DynamicRange. When a partition option is enabled (that is, not None), the degree of parallelism to concurrently load data from an Azure Synapse Analytics is controlled by the parallelCopies setting on the copy activity. |
No |
| partitionSettings | Specify the group of the settings for data partitioning. Apply when the partition option isn't None. |
No |
Under partitionSettings: |
||
| partitionColumnName | Specify the name of the source column in integer or date/datetime type (int, smallint, bigint, date, smalldatetime, datetime, datetime2, or datetimeoffset) that will be used by range partitioning for parallel copy. If not specified, the index or the primary key of the table is detected automatically and used as the partition column.Apply when the partition option is DynamicRange. If you use a query to retrieve the source data, hook ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition in the WHERE clause. For an example, see the Parallel copy from SQL database section. |
No |
| partitionUpperBound | The maximum value of the partition column for partition range splitting. This value is used to decide the partition stride, not for filtering the rows in table. All rows in the table or query result will be partitioned and copied. If not specified, copy activity auto detect the value. Apply when the partition option is DynamicRange. For an example, see the Parallel copy from SQL database section. |
No |
| partitionLowerBound | The minimum value of the partition column for partition range splitting. This value is used to decide the partition stride, not for filtering the rows in table. All rows in the table or query result will be partitioned and copied. If not specified, copy activity auto detect the value. Apply when the partition option is DynamicRange. For an example, see the Parallel copy from SQL database section. |
No |
Note the following point:
- When using stored procedure in source to retrieve data, note if your stored procedure is designed as returning different schema when different parameter value is passed in, you may encounter failure or see unexpected result when importing schema from UI or when copying data to SQL database with auto table creation.
Example: using SQL query
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyFromAzureSQLDW",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<Azure Synapse Analytics input dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<output dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "SqlDWSource",
"sqlReaderQuery": "SELECT * FROM MyTable"
},
"sink": {
"type": "<sink type>"
}
}
}
]
Example: using stored procedure
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyFromAzureSQLDW",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<Azure Synapse Analytics input dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<output dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "SqlDWSource",
"sqlReaderStoredProcedureName": "CopyTestSrcStoredProcedureWithParameters",
"storedProcedureParameters": {
"stringData": { "value": "str3" },
"identifier": { "value": "$$Text.Format('{0:yyyy}', <datetime parameter>)", "type": "Int"}
}
},
"sink": {
"type": "<sink type>"
}
}
}
]
Sample stored procedure:
CREATE PROCEDURE CopyTestSrcStoredProcedureWithParameters
(
@stringData varchar(20),
@identifier int
)
AS
SET NOCOUNT ON;
BEGIN
select *
from dbo.UnitTestSrcTable
where dbo.UnitTestSrcTable.stringData != stringData
and dbo.UnitTestSrcTable.identifier != identifier
END
GO
Azure Synapse Analytics as sink
Azure Data Factory and Synapse pipelines support three ways to load data into Azure Synapse Analytics.
- Use COPY statement
- Use PolyBase
- Use bulk insert
The fastest and most scalable way to load data is through the COPY statement or the PolyBase.
To copy data to Azure Synapse Analytics, set the sink type in Copy Activity to SqlDWSink. The following properties are supported in the Copy Activity sink section:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the Copy Activity sink must be set to SqlDWSink. | Yes |
| allowPolyBase | Indicates whether to use PolyBase to load data into Azure Synapse Analytics. allowCopyCommand and allowPolyBase cannot be both true. See Use PolyBase to load data into Azure Synapse Analytics section for constraints and details. Allowed values are True and False (default). |
No. Apply when using PolyBase. |
| polyBaseSettings | A group of properties that can be specified when the allowPolybase property is set to true. |
No. Apply when using PolyBase. |
| allowCopyCommand | Indicates whether to use COPY statement to load data into Azure Synapse Analytics. allowCopyCommand and allowPolyBase cannot be both true. See Use COPY statement to load data into Azure Synapse Analytics section for constraints and details. Allowed values are True and False (default). |
No. Apply when using COPY. |
| copyCommandSettings | A group of properties that can be specified when allowCopyCommand property is set to TRUE. |
No. Apply when using COPY. |
| writeBatchSize | Number of rows to inserts into the SQL table per batch. The allowed value is integer (number of rows). By default, the service dynamically determines the appropriate batch size based on the row size. |
No. Apply when using bulk insert. |
| writeBatchTimeout | The wait time for the insert, upsert and stored procedure operation to complete before it times out. Allowed values are for the timespan. An example is "00:30:00" for 30 minutes. If no value is specified, the time-out defaults to "00:30:00". |
No. Apply when using bulk insert. |
| preCopyScript | Specify a SQL query for Copy Activity to run before writing data into Azure Synapse Analytics in each run. Use this property to clean up the preloaded data. | No |
| tableOption | Specifies whether to automatically create the sink table, if it does not exist, based on the source schema. Allowed values are: none (default), autoCreate. |
No |
| disableMetricsCollection | The service collects metrics such as Azure Synapse Analytics DWUs for copy performance optimization and recommendations, which introduce additional master DB access. If you are concerned with this behavior, specify true to turn it off. |
No (default is false) |
| maxConcurrentConnections | The upper limit of concurrent connections established to the data store during the activity run. Specify a value only when you want to limit concurrent connections. | No |
| WriteBehavior | Specify the write behavior for copy activity to load data into Azure Synapse Analytics. The allowed value is Insert and Upsert. By default, the service uses insert to load data. |
No |
| upsertSettings | Specify the group of the settings for write behavior. Apply when the WriteBehavior option is Upsert. |
No |
Under upsertSettings: |
||
| keys | Specify the column names for unique row identification. Either a single key or a series of keys can be used. If not specified, the primary key is used. | No |
| interimSchemaName | Specify the interim schema for creating interim table. Note: user need to have the permission for creating and deleting table. By default, interim table will share the same schema as sink table. | No |
Example 1: Azure Synapse Analytics sink
"sink": {
"type": "SqlDWSink",
"allowPolyBase": true,
"polyBaseSettings":
{
"rejectType": "percentage",
"rejectValue": 10.0,
"rejectSampleValue": 100,
"useTypeDefault": true
}
}
Example 2: Upsert data
"sink": {
"type": "SqlDWSink",
"writeBehavior": "Upsert",
"upsertSettings": {
"keys": [
"<column name>"
],
"interimSchemaName": "<interim schema name>"
},
}
Parallel copy from Azure Synapse Analytics
The Azure Synapse Analytics connector in copy activity provides built-in data partitioning to copy data in parallel. You can find data partitioning options on the Source tab of the copy activity.
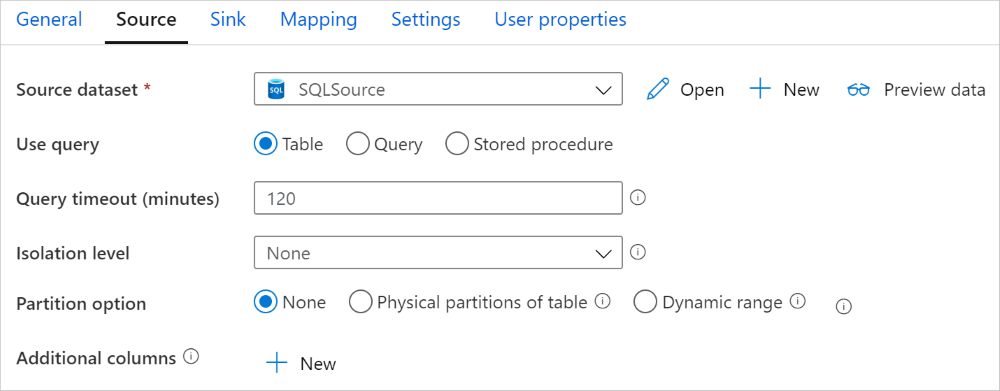
When you enable partitioned copy, copy activity runs parallel queries against your Azure Synapse Analytics source to load data by partitions. The parallel degree is controlled by the parallelCopies setting on the copy activity. For example, if you set parallelCopies to four, the service concurrently generates and runs four queries based on your specified partition option and settings, and each query retrieves a portion of data from your Azure Synapse Analytics.
You are suggested to enable parallel copy with data partitioning especially when you load large amount of data from your Azure Synapse Analytics. The following are suggested configurations for different scenarios. When copying data into file-based data store, it's recommended to write to a folder as multiple files (only specify folder name), in which case the performance is better than writing to a single file.
| Scenario | Suggested settings |
|---|---|
| Full load from large table, with physical partitions. | Partition option: Physical partitions of table. During execution, the service automatically detects the physical partitions, and copies data by partitions. To check if your table has physical partition or not, you can refer to this query. |
| Full load from large table, without physical partitions, while with an integer or datetime column for data partitioning. | Partition options: Dynamic range partition. Partition column (optional): Specify the column used to partition data. If not specified, the index or primary key column is used. Partition upper bound and partition lower bound (optional): Specify if you want to determine the partition stride. This is not for filtering the rows in table, all rows in the table will be partitioned and copied. If not specified, copy activity auto detect the values. For example, if your partition column "ID" has values range from 1 to 100, and you set the lower bound as 20 and the upper bound as 80, with parallel copy as 4, the service retrieves data by 4 partitions - IDs in range <=20, [21, 50], [51, 80], and >=81, respectively. |
| Load a large amount of data by using a custom query, without physical partitions, while with an integer or date/datetime column for data partitioning. | Partition options: Dynamic range partition. Query: SELECT * FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition AND <your_additional_where_clause>.Partition column: Specify the column used to partition data. Partition upper bound and partition lower bound (optional): Specify if you want to determine the partition stride. This is not for filtering the rows in table, all rows in the query result will be partitioned and copied. If not specified, copy activity auto detect the value. For example, if your partition column "ID" has values range from 1 to 100, and you set the lower bound as 20 and the upper bound as 80, with parallel copy as 4, the service retrieves data by 4 partitions- IDs in range <=20, [21, 50], [51, 80], and >=81, respectively. Here are more sample queries for different scenarios: 1. Query the whole table: SELECT * FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition2. Query from a table with column selection and additional where-clause filters: SELECT <column_list> FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition AND <your_additional_where_clause>3. Query with subqueries: SELECT <column_list> FROM (<your_sub_query>) AS T WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition AND <your_additional_where_clause>4. Query with partition in subquery: SELECT <column_list> FROM (SELECT <your_sub_query_column_list> FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition) AS T |
Best practices to load data with partition option:
- Choose distinctive column as partition column (like primary key or unique key) to avoid data skew.
- If the table has built-in partition, use partition option "Physical partitions of table" to get better performance.
- If you use Azure Integration Runtime to copy data, you can set larger "Data Integration Units (DIU)" (>4) to utilize more computing resource. Check the applicable scenarios there.
- "Degree of copy parallelism" control the partition numbers, setting this number too large sometime hurts the performance, recommend setting this number as (DIU or number of Self-hosted IR nodes) * (2 to 4).
- Note Azure Synapse Analytics can execute a maximum of 32 queries at a moment, setting "Degree of copy parallelism" too large may cause a Synapse throttling issue.
Example: full load from large table with physical partitions
"source": {
"type": "SqlDWSource",
"partitionOption": "PhysicalPartitionsOfTable"
}
Example: query with dynamic range partition
"source": {
"type": "SqlDWSource",
"query": "SELECT * FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition AND <your_additional_where_clause>",
"partitionOption": "DynamicRange",
"partitionSettings": {
"partitionColumnName": "<partition_column_name>",
"partitionUpperBound": "<upper_value_of_partition_column (optional) to decide the partition stride, not as data filter>",
"partitionLowerBound": "<lower_value_of_partition_column (optional) to decide the partition stride, not as data filter>"
}
}
Sample query to check physical partition
SELECT DISTINCT s.name AS SchemaName, t.name AS TableName, c.name AS ColumnName, CASE WHEN c.name IS NULL THEN 'no' ELSE 'yes' END AS HasPartition
FROM sys.tables AS t
LEFT JOIN sys.objects AS o ON t.object_id = o.object_id
LEFT JOIN sys.schemas AS s ON o.schema_id = s.schema_id
LEFT JOIN sys.indexes AS i ON t.object_id = i.object_id
LEFT JOIN sys.index_columns AS ic ON ic.partition_ordinal > 0 AND ic.index_id = i.index_id AND ic.object_id = t.object_id
LEFT JOIN sys.columns AS c ON c.object_id = ic.object_id AND c.column_id = ic.column_id
LEFT JOIN sys.types AS y ON c.system_type_id = y.system_type_id
WHERE s.name='[your schema]' AND t.name = '[your table name]'
If the table has physical partition, you would see "HasPartition" as "yes".
Use COPY statement to load data into Azure Synapse Analytics
Using COPY statement is a simple and flexible way to load data into Azure Synapse Analytics with high throughput. To learn more details, check Bulk load data using the COPY statement
- If your source data is in Azure Blob or Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2, and the format is COPY statement compatible, you can use copy activity to directly invoke COPY statement to let Azure Synapse Analytics pull the data from source. For details, see Direct copy by using COPY statement.
- If your source data store and format isn't originally supported by COPY statement, use the Staged copy by using COPY statement feature instead. The staged copy feature also provides you better throughput. It automatically converts the data into COPY statement compatible format, stores the data in Azure Blob storage, then calls COPY statement to load data into Azure Synapse Analytics.
Tip
When using COPY statement with Azure Integration Runtime, effective Data Integration Units (DIU) is always 2. Tuning the DIU doesn't impact the performance, as loading data from storage is powered by the Azure Synapse engine.
Direct copy by using COPY statement
Azure Synapse Analytics COPY statement directly supports Azure Blob and Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2. If your source data meets the criteria described in this section, use COPY statement to copy directly from the source data store to Azure Synapse Analytics. Otherwise, use Staged copy by using COPY statement. The service checks the settings and fails the copy activity run if the criteria is not met.
The source linked service and format are with the following types and authentication methods:
Supported source data store type Supported format Supported source authentication type Azure Blob Delimited text Account key authentication, shared access signature authentication, service principal authentication (using ServicePrincipalKey), system-assigned managed identity authentication Parquet Account key authentication, shared access signature authentication ORC Account key authentication, shared access signature authentication Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 Delimited text
Parquet
ORCAccount key authentication, service principal authentication (using ServicePrincipalKey), shared access signature authentication, system-assigned managed identity authentication Important
- When you use managed identity authentication for your storage linked service, learn the needed configurations for Azure Blob and Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 respectively.
- If your Azure Storage is configured with VNet service endpoint, you must use managed identity authentication with "allow trusted Microsoft service" enabled on storage account, refer to Impact of using VNet Service Endpoints with Azure storage.
Format settings are with the following:
- For Parquet:
compressioncan be no compression, Snappy, orGZip. - For ORC:
compressioncan be no compression,zlib, or Snappy. - For Delimited text:
rowDelimiteris explicitly set as single character or "\r\n", the default value is not supported.nullValueis left as default or set to empty string ("").encodingNameis left as default or set to utf-8 or utf-16.escapeCharmust be same asquoteChar, and is not empty.skipLineCountis left as default or set to 0.compressioncan be no compression orGZip.
- For Parquet:
If your source is a folder,
recursivein copy activity must be set to true, andwildcardFilenameneed to be*or*.*.wildcardFolderPath,wildcardFilename(other than*or*.*),modifiedDateTimeStart,modifiedDateTimeEnd,prefix,enablePartitionDiscoveryandadditionalColumnsare not specified.
The following COPY statement settings are supported under allowCopyCommand in copy activity:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| defaultValues | Specifies the default values for each target column in Azure Synapse Analytics. The default values in the property overwrite the DEFAULT constraint set in the data warehouse, and identity column cannot have a default value. | No |
| additionalOptions | Additional options that will be passed to an Azure Synapse Analytics COPY statement directly in "With" clause in COPY statement. Quote the value as needed to align with the COPY statement requirements. | No |
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyFromAzureBlobToSQLDataWarehouseViaCOPY",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "ParquetDataset",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "AzureSQLDWDataset",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "ParquetSource",
"storeSettings":{
"type": "AzureBlobStorageReadSettings",
"recursive": true
}
},
"sink": {
"type": "SqlDWSink",
"allowCopyCommand": true,
"copyCommandSettings": {
"defaultValues": [
{
"columnName": "col_string",
"defaultValue": "DefaultStringValue"
}
],
"additionalOptions": {
"MAXERRORS": "10000",
"DATEFORMAT": "'ymd'"
}
}
},
"enableSkipIncompatibleRow": true
}
}
]
Staged copy by using COPY statement
When your source data is not natively compatible with COPY statement, enable data copying via an interim staging Azure Blob or Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 (it can't be Azure Premium Storage). In this case, the service automatically converts the data to meet the data format requirements of COPY statement. Then it invokes COPY statement to load data into Azure Synapse Analytics. Finally, it cleans up your temporary data from the storage. See Staged copy for details about copying data via a staging.
To use this feature, create an Azure Blob Storage linked service or Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 linked service with account key or system-managed identity authentication that refers to the Azure storage account as the interim storage.
Important
- When you use managed identity authentication for your staging linked service, learn the needed configurations for Azure Blob and Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 respectively. You also need to grant permissions to your Azure Synapse Analytics workspace managed identity in your staging Azure Blob Storage or Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account. To learn how to grant this permission, see Grant permissions to workspace managed identity.
- If your staging Azure Storage is configured with VNet service endpoint, you must use managed identity authentication with "allow trusted Microsoft service" enabled on storage account, refer to Impact of using VNet Service Endpoints with Azure storage.
Important
If your staging Azure Storage is configured with Managed Private Endpoint and has the storage firewall enabled, you must use managed identity authentication and grant Storage Blob Data Reader permissions to the Synapse SQL Server to ensure it can access the staged files during the COPY statement load.
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyFromSQLServerToSQLDataWarehouseViaCOPYstatement",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "SQLServerDataset",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "AzureSQLDWDataset",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "SqlSource",
},
"sink": {
"type": "SqlDWSink",
"allowCopyCommand": true
},
"stagingSettings": {
"linkedServiceName": {
"referenceName": "MyStagingStorage",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
}
}
}
}
]
Use PolyBase to load data into Azure Synapse Analytics
Using PolyBase is an efficient way to load a large amount of data into Azure Synapse Analytics with high throughput. You'll see a large gain in the throughput by using PolyBase instead of the default BULKINSERT mechanism.
- If your source data is in Azure Blob or Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2, and the format is PolyBase compatible, you can use copy activity to directly invoke PolyBase to let Azure Synapse Analytics pull the data from source. For details, see Direct copy by using PolyBase.
- If your source data store and format isn't originally supported by PolyBase, use the Staged copy by using PolyBase feature instead. The staged copy feature also provides you better throughput. It automatically converts the data into PolyBase-compatible format, stores the data in Azure Blob storage, then calls PolyBase to load data into Azure Synapse Analytics.
Tip
Learn more on Best practices for using PolyBase. When using PolyBase with Azure Integration Runtime, effective Data Integration Units (DIU) for direct or staged storage-to-Synapse is always 2. Tuning the DIU doesn't impact the performance, as loading data from storage is powered by Synapse engine.
The following PolyBase settings are supported under polyBaseSettings in copy activity:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| rejectValue | Specifies the number or percentage of rows that can be rejected before the query fails. Learn more about PolyBase's reject options in the Arguments section of CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE (Transact-SQL). Allowed values are 0 (default), 1, 2, etc. |
No |
| rejectType | Specifies whether the rejectValue option is a literal value or a percentage. Allowed values are Value (default) and Percentage. |
No |
| rejectSampleValue | Determines the number of rows to retrieve before PolyBase recalculates the percentage of rejected rows. Allowed values are 1, 2, etc. |
Yes, if the rejectType is percentage. |
| useTypeDefault | Specifies how to handle missing values in delimited text files when PolyBase retrieves data from the text file. Learn more about this property from the Arguments section in CREATE EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT (Transact-SQL). Allowed values are True and False (default). |
No |
Direct copy by using PolyBase
Azure Synapse Analytics PolyBase directly supports Azure Blob and Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2. If your source data meets the criteria described in this section, use PolyBase to copy directly from the source data store to Azure Synapse Analytics. Otherwise, use Staged copy by using PolyBase.
If the requirements aren't met, the service checks the settings and automatically falls back to the BULKINSERT mechanism for the data movement.
The source linked service is with the following types and authentication methods:
Supported source data store type Supported source authentication type Azure Blob Account key authentication, system-assigned managed identity authentication Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 Account key authentication, system-assigned managed identity authentication Important
- When you use managed identity authentication for your storage linked service, learn the needed configurations for Azure Blob and Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 respectively.
- If your Azure Storage is configured with VNet service endpoint, you must use managed identity authentication with "allow trusted Microsoft service" enabled on storage account, refer to Impact of using VNet Service Endpoints with Azure storage.
The source data format is of Parquet, ORC, or Delimited text, with the following configurations:
- Folder path doesn't contain wildcard filter.
- File name is empty, or points to a single file. If you specify wildcard file name in copy activity, it can only be
*or*.*. rowDelimiteris default, \n, \r\n, or \r.nullValueis left as default or set to empty string (""), andtreatEmptyAsNullis left as default or set to true.encodingNameis left as default or set to utf-8.quoteChar,escapeChar, andskipLineCountaren't specified. PolyBase support skip header row, which can be configured asfirstRowAsHeader.compressioncan be no compression,GZip, or Deflate.
If your source is a folder,
recursivein copy activity must be set to true.wildcardFolderPath,wildcardFilename,modifiedDateTimeStart,modifiedDateTimeEnd,prefix,enablePartitionDiscovery, andadditionalColumnsare not specified.
Note
If your source is a folder, note PolyBase retrieves files from the folder and all of its subfolders, and it doesn't retrieve data from files for which the file name begins with an underline (_) or a period (.), as documented here - LOCATION argument.
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyFromAzureBlobToSQLDataWarehouseViaPolyBase",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "ParquetDataset",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "AzureSQLDWDataset",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "ParquetSource",
"storeSettings":{
"type": "AzureBlobStorageReadSettings",
"recursive": true
}
},
"sink": {
"type": "SqlDWSink",
"allowPolyBase": true
}
}
}
]
Staged copy by using PolyBase
When your source data is not natively compatible with PolyBase, enable data copying via an interim staging Azure Blob or Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 (it can't be Azure Premium Storage). In this case, the service automatically converts the data to meet the data format requirements of PolyBase. Then it invokes PolyBase to load data into Azure Synapse Analytics. Finally, it cleans up your temporary data from the storage. See Staged copy for details about copying data via a staging.
To use this feature, create an Azure Blob Storage linked service or Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 linked service with account key or managed identity authentication that refers to the Azure storage account as the interim storage.
Important
- When you use managed identity authentication for your staging linked service, learn the needed configurations for Azure Blob and Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 respectively. You also need to grant permissions to your Azure Synapse Analytics workspace managed identity in your staging Azure Blob Storage or Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account. To learn how to grant this permission, see Grant permissions to workspace managed identity.
- If your staging Azure Storage is configured with VNet service endpoint, you must use managed identity authentication with "allow trusted Microsoft service" enabled on storage account, refer to Impact of using VNet Service Endpoints with Azure storage.
Important
If your staging Azure Storage is configured with Managed Private Endpoint and has the storage firewall enabled, you must use managed identity authentication and grant Storage Blob Data Reader permissions to the Synapse SQL Server to ensure it can access the staged files during the PolyBase load.
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyFromSQLServerToSQLDataWarehouseViaPolyBase",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "SQLServerDataset",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "AzureSQLDWDataset",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "SqlSource",
},
"sink": {
"type": "SqlDWSink",
"allowPolyBase": true
},
"enableStaging": true,
"stagingSettings": {
"linkedServiceName": {
"referenceName": "MyStagingStorage",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
}
}
}
}
]
Best practices for using PolyBase
The following sections provide best practices in addition to those practices mentioned in Best practices for Azure Synapse Analytics.
Required database permission
To use PolyBase, the user that loads data into Azure Synapse Analytics must have "CONTROL" permission on the target database. One way to achieve that is to add the user as a member of the db_owner role. Learn how to do that in the Azure Synapse Analytics overview.
Row size and data type limits
PolyBase loads are limited to rows smaller than 1 MB. It cannot be used to load to VARCHR(MAX), NVARCHAR(MAX), or VARBINARY(MAX). For more information, see Azure Synapse Analytics service capacity limits.
When your source data has rows greater than 1 MB, you might want to vertically split the source tables into several small ones. Make sure that the largest size of each row doesn't exceed the limit. The smaller tables can then be loaded by using PolyBase and merged together in Azure Synapse Analytics.
Alternatively, for data with such wide columns, you can use non-PolyBase to load the data by turning off "allow PolyBase" setting.
Azure Synapse Analytics resource class
To achieve the best possible throughput, assign a larger resource class to the user that loads data into Azure Synapse Analytics via PolyBase.
PolyBase troubleshooting
Loading to Decimal column
If your source data is in text format or other non-PolyBase compatible stores (using staged copy and PolyBase), and it contains empty value to be loaded into Azure Synapse Analytics Decimal column, you may get the following error:
ErrorCode=FailedDbOperation, ......HadoopSqlException: Error converting data type VARCHAR to DECIMAL.....Detailed Message=Empty string can't be converted to DECIMAL.....
The solution is to unselect "Use type default" option (as false) in copy activity sink -> PolyBase settings. "USE_TYPE_DEFAULT" is a PolyBase native configuration, which specifies how to handle missing values in delimited text files when PolyBase retrieves data from the text file.
Check the tableName property in Azure Synapse Analytics
The following table gives examples of how to specify the tableName property in the JSON dataset. It shows several combinations of schema and table names.
| DB Schema | Table name | tableName JSON property |
|---|---|---|
| dbo | MyTable | MyTable or dbo.MyTable or [dbo].[MyTable] |
| dbo1 | MyTable | dbo1.MyTable or [dbo1].[MyTable] |
| dbo | My.Table | [My.Table] or [dbo].[My.Table] |
| dbo1 | My.Table | [dbo1].[My.Table] |
If you see the following error, the problem might be the value you specified for the tableName property. See the preceding table for the correct way to specify values for the tableName JSON property.
Type=System.Data.SqlClient.SqlException,Message=Invalid object name 'stg.Account_test'.,Source=.Net SqlClient Data Provider
Columns with default values
Currently, the PolyBase feature accepts only the same number of columns as in the target table. An example is a table with four columns where one of them is defined with a default value. The input data still needs to have four columns. A three-column input dataset yields an error similar to the following message:
All columns of the table must be specified in the INSERT BULK statement.
The NULL value is a special form of the default value. If the column is nullable, the input data in the blob for that column might be empty. But it can't be missing from the input dataset. PolyBase inserts NULL for missing values in Azure Synapse Analytics.
External file access failed
If you receive the following error, ensure that you are using managed identity authentication and have granted Storage Blob Data Reader permissions to the Azure Synapse workspace's managed identity.
Job failed due to reason: at Sink '[SinkName]': shaded.msdataflow.com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerException: External file access failed due to internal error: 'Error occurred while accessing HDFS: Java exception raised on call to HdfsBridge_IsDirExist. Java exception message:\r\nHdfsBridge::isDirExist
For more information, see Grant permissions to managed identity after workspace creation.
Mapping data flow properties
When transforming data in mapping data flow, you can read and write to tables from Azure Synapse Analytics. For more information, see the source transformation and sink transformation in mapping data flows.
Source transformation
Settings specific to Azure Synapse Analytics are available in the Source Options tab of the source transformation.
Input Select whether you point your source at a table (equivalent of Select * from <table-name>) or enter a custom SQL query.
Enable Staging It is highly recommended that you use this option in production workloads with Azure Synapse Analytics sources. When you execute a data flow activity with Azure Synapse Analytics sources from a pipeline, you will be prompted for a staging location storage account and will use that for staged data loading. It is the fastest mechanism to load data from Azure Synapse Analytics.
- When you use managed identity authentication for your storage linked service, learn the needed configurations for Azure Blob and Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 respectively.
- If your Azure Storage is configured with VNet service endpoint, you must use managed identity authentication with "allow trusted Microsoft service" enabled on storage account, refer to Impact of using VNet Service Endpoints with Azure storage.
- When you use Azure Synapse serverless SQL pool as source, enable staging is not supported.
Query: If you select Query in the input field, enter a SQL query for your source. This setting overrides any table that you've chosen in the dataset. Order By clauses aren't supported here, but you can set a full SELECT FROM statement. You can also use user-defined table functions. select * from udfGetData() is a UDF in SQL that returns a table. This query will produce a source table that you can use in your data flow. Using queries is also a great way to reduce rows for testing or for lookups.
SQL Example: Select * from MyTable where customerId > 1000 and customerId < 2000
Batch size: Enter a batch size to chunk large data into reads. In data flows, this setting will be used to set Spark columnar caching. This is an option field, which will use Spark defaults if it is left blank.
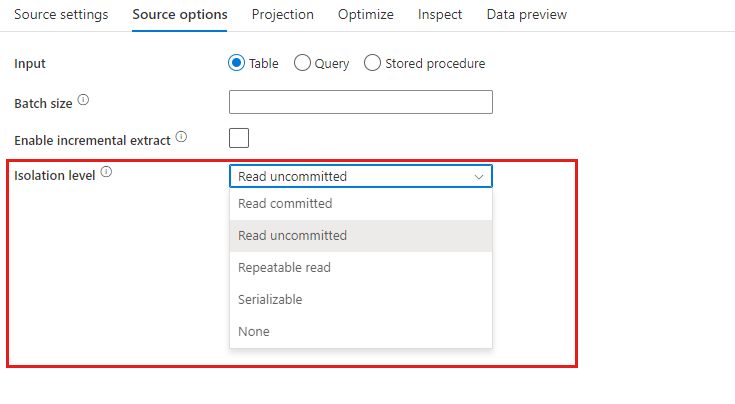
Isolation Level: The default for SQL sources in mapping data flow is read uncommitted. You can change the isolation level here to one of these values:
- Read Committed
- Read Uncommitted
- Repeatable Read
- Serializable
- None (ignore isolation level)
Sink transformation
Settings specific to Azure Synapse Analytics are available in the Settings tab of the sink transformation.
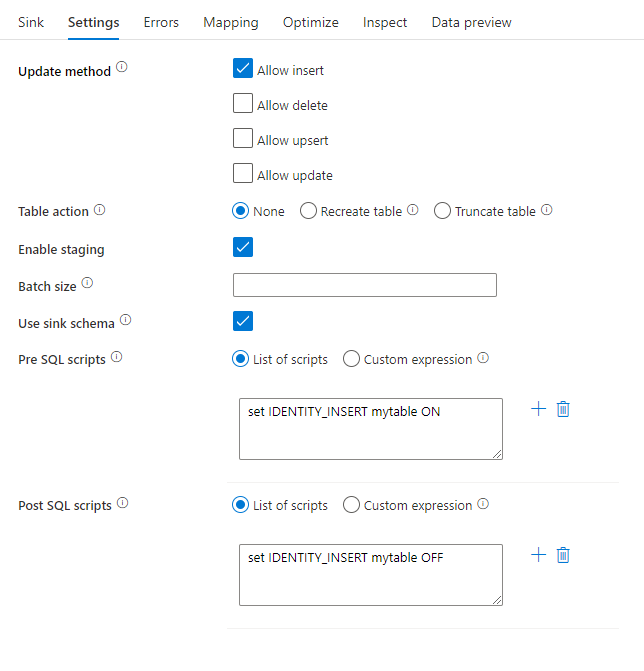
Update method: Determines what operations are allowed on your database destination. The default is to only allow inserts. To update, upsert, or delete rows, an alter-row transformation is required to tag rows for those actions. For updates, upserts and deletes, a key column or columns must be set to determine which row to alter.
Table action: Determines whether to recreate or remove all rows from the destination table prior to writing.
- None: No action will be done to the table.
- Recreate: The table will get dropped and recreated. Required if creating a new table dynamically.
- Truncate: All rows from the target table will get removed.
Enable staging: This enables loading into Azure Synapse Analytics SQL Pools using the copy command and is recommended for most Synapse sinks. The staging storage is configured in Execute Data Flow activity.
- When you use managed identity authentication for your storage linked service, learn the needed configurations for Azure Blob and Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 respectively.
- If your Azure Storage is configured with VNet service endpoint, you must use managed identity authentication with "allow trusted Microsoft service" enabled on storage account, refer to Impact of using VNet Service Endpoints with Azure storage.
Batch size: Controls how many rows are being written in each bucket. Larger batch sizes improve compression and memory optimization, but risk out of memory exceptions when caching data.
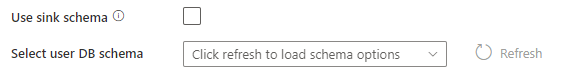
Use sink schema: By default, a temporary table will be created under the sink schema as staging. You can alternatively uncheck the Use sink schema option and instead, in Select user DB schema, specify a schema name under which Data Factory will create a staging table to load upstream data and automatically clean them up upon completion. Make sure you have create table permission in the database and alter permission on the schema.
Pre and Post SQL scripts: Enter multi-line SQL scripts that will execute before (pre-processing) and after (post-processing) data is written to your Sink database
Tip
- It's recommended to break single batch scripts with multiple commands into multiple batches.
- Only Data Definition Language (DDL) and Data Manipulation Language (DML) statements that return a simple update count can be run as part of a batch. Learn more from Performing batch operations
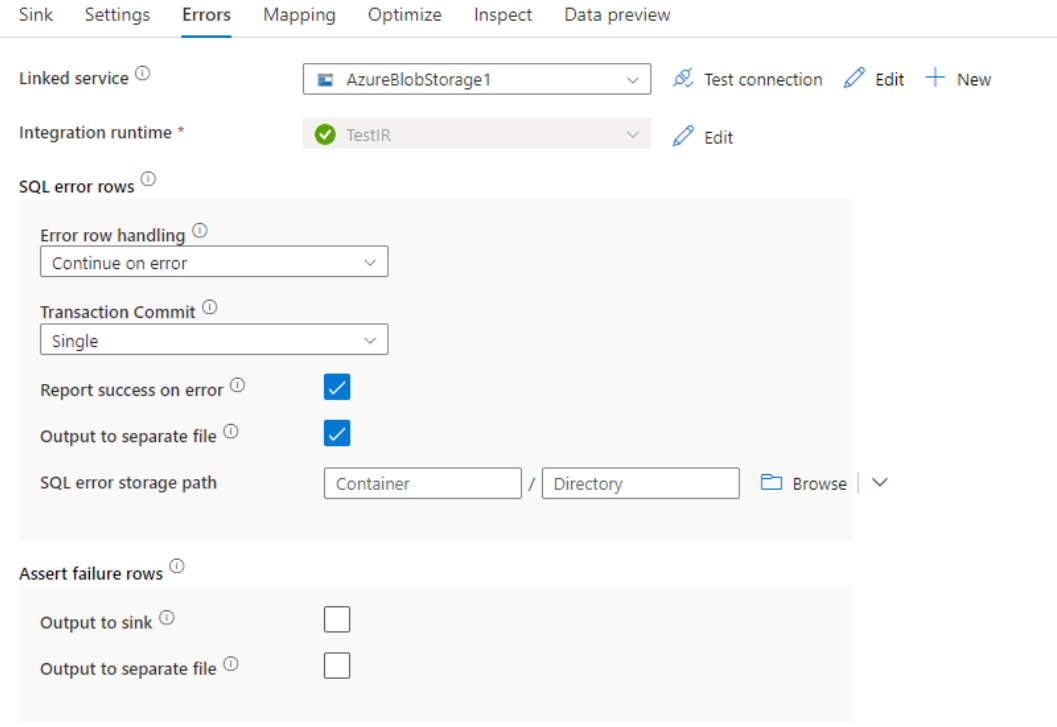
Error row handling
When writing to Azure Synapse Analytics, certain rows of data may fail due to constraints set by the destination. Some common errors include:
- String or binary data would be truncated in table
- Cannot insert the value NULL into column
- Conversion failed when converting the value to data type
By default, a data flow run will fail on the first error it gets. You can choose to Continue on error that allows your data flow to complete even if individual rows have errors. The service provides different options for you to handle these error rows.
Transaction Commit: Choose whether your data gets written in a single transaction or in batches. Single transaction will provide better performance and no data written will be visible to others until the transaction completes. Batch transactions have worse performance but can work for large datasets.
Output rejected data: If enabled, you can output the error rows into a csv file in Azure Blob Storage or an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account of your choosing. This will write the error rows with three additional columns: the SQL operation like INSERT or UPDATE, the data flow error code, and the error message on the row.
Report success on error: If enabled, the data flow will be marked as a success even if error rows are found.
Lookup activity properties
To learn details about the properties, check Lookup activity.
GetMetadata activity properties
To learn details about the properties, check GetMetadata activity
Data type mapping for Azure Synapse Analytics
When you copy data from or to Azure Synapse Analytics, the following mappings are used from Azure Synapse Analytics data types to Azure Data Factory interim data types. These mappings are also used when copying data from or to Azure Synapse Analytics using Synapse pipelines, since pipelines also implement Azure Data Factory within Azure Synapse. See schema and data type mappings to learn how Copy Activity maps the source schema and data type to the sink.
Tip
Refer to Table data types in Azure Synapse Analytics article on Azure Synapse Analytics supported data types and the workarounds for unsupported ones.
| Azure Synapse Analytics data type | Data Factory interim data type |
|---|---|
| bigint | Int64 |
| binary | Byte[] |
| bit | Boolean |
| char | String, Char[] |
| date | DateTime |
| Datetime | DateTime |
| datetime2 | DateTime |
| Datetimeoffset | DateTimeOffset |
| Decimal | Decimal |
| FILESTREAM attribute (varbinary(max)) | Byte[] |
| Float | Double |
| image | Byte[] |
| int | Int32 |
| money | Decimal |
| nchar | String, Char[] |
| numeric | Decimal |
| nvarchar | String, Char[] |
| real | Single |
| rowversion | Byte[] |
| smalldatetime | DateTime |
| smallint | Int16 |
| smallmoney | Decimal |
| time | TimeSpan |
| tinyint | Byte |
| uniqueidentifier | Guid |
| varbinary | Byte[] |
| varchar | String, Char[] |
Upgrade the Azure Synapse Analytics version
To upgrade the Azure Synapse Analytics version, in Edit linked service page, select Recommended under Version and configure the linked service by referring to Linked service properties for the recommended version.
Differences between the recommended and the legacy version
The table below shows the differences between Azure Synapse Analytics using the recommended and the legacy version.
| Recommended version | Legacy version |
|---|---|
Support TLS 1.3 via encrypt as strict. |
TLS 1.3 is not supported. |
Related content
For a list of data stores supported as sources and sinks by Copy Activity, see supported data stores and formats.