本文将介绍一种缩放工具,该工具使用 Azure 自动化运行手册和 Azure 逻辑应用程序来自动缩放您 Azure 虚拟桌面环境中的会话主机虚拟机。 若要了解有关缩放工具的详细信息,请参阅使用 Azure 自动化和 Azure Logic 应用缩放会话主机。
注释
先决条件
在开始设置缩放工具之前,请确保准备好以下各项:
- Azure 虚拟桌面主机池。
- 已配置并注册到 Azure 虚拟桌面服务的会话主机池虚拟机。
- 在 Azure 订阅上分配有基于角色的访问控制 (RBAC) 参与者角色的用户,用来创建资源。 您还需要应用程序管理员和/或所有者的 RBAC 角色,以创建托管标识。
- Log Analytics 工作区(可选)。
用于部署该工具的计算机必须具有:
- PowerShell 5.1 或更高版本
- Azure Az PowerShell 模块
如果一切准备就绪,让我们开始吧。
创建或更新 Azure 自动化帐户
注释
如果您已有一个 Azure 自动化帐户,并且其中的运行簿运行旧版的缩放脚本,只需按照以下说明进行操作,以确保它已更新。
首先,需要一个 Azure 自动化帐户来运行 PowerShell Runbook。 本部分介绍的过程是有效的,即使你有一个想要用于设置 PowerShell Runbook 的现有 Azure 自动化帐户。 设置方式如下:
打开 PowerShell。
运行以下 cmdlet 登录到 Azure 帐户。
Connect-AzAccount -Environment AzureChinaCloud注释
你的帐户必须在要部署缩放工具的 Azure 订阅上具有贡献者权限。
运行以下 cmdlet,下载用于创建 Azure 自动化帐户的脚本:
New-Item -ItemType Directory -Path "C:\Temp" -Force Set-Location -Path "C:\Temp" $Uri = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/RDS-Templates/master/wvd-templates/wvd-scaling-script/CreateOrUpdateAzAutoAccount.ps1" # Download the script Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $Uri -OutFile ".\CreateOrUpdateAzAutoAccount.ps1"运行以下 cmdlet 以执行脚本并创建 Azure 自动化帐户。 可以填写参数的值,也可以对其进行注释以使用其默认值。
$Params = @{ "AADTenantId" = "<Azure_Active_Directory_tenant_ID>" # Optional. If not specified, it will use the current Azure context "SubscriptionId" = "<Azure_subscription_ID>" # Optional. If not specified, it will use the current Azure context "UseARMAPI" = $true "ResourceGroupName" = "<Resource_group_name>" # Optional. Default: "WVDAutoScaleResourceGroup" "AutomationAccountName" = "<Automation_account_name>" # Optional. Default: "WVDAutoScaleAutomationAccount" "Location" = "<Azure_region_for_deployment>" "WorkspaceName" = "<Log_analytics_workspace_name>" # Optional. If specified, Log Analytics will be used to configure the custom log table that the runbook PowerShell script can send logs to } .\CreateOrUpdateAzAutoAccount.ps1 @Params注释
如果您的策略不允许您在特定区域创建缩放脚本资源,请更新策略分配,并将您希望添加的区域加入到允许区域的列表中。
如果以前尚未创建自动化帐户,cmdlet 的输出将在自动化帐户变量中包含加密的 Webhook URI。 请务必保留一份 URI 的记录,因为在为 Azure 逻辑应用设置执行计划时需要使用它作为参数。 如果要更新现有自动化帐户,可以使用 PowerShell 检索 Webhook URI 来访问变量。
如果为 Log Analytics 指定了参数 WorkspaceName,则 cmdlet 的输出还将包含 Log Analytics 工作区 ID 及其主键。 记下工作区 ID 和主密钥,因为在为 Azure 逻辑应用设置执行计划时,稍后需要将它们与参数一起使用。
设置 Azure 自动化帐户后,登录到 Azure 订阅,并检查以确保 Azure 自动化帐户和相关 runbook 已显示在指定的资源组中,如下图所示:
图像显示了 Azure 概述页,其中包含新建的 Azure 自动化帐户和 Runbook。
若要检查 webhook 是否位于其预期位置,请选择 runbook 的名称。 接下来,转到 Runbook 的“资源”部分,然后选择 Webhooks。
创建管理标识
拥有Azure 自动化帐户后,还需要设置托管标识(如果尚未设置)。 托管标识将帮助 Runbook 访问其他与 Microsoft Entra 相关的资源,并对重要的自动化过程进行身份验证。
若要设置托管标识,请按照为Azure 自动化帐户使用系统分配的托管标识中的说明进行作。 创建托管标识后,请向 Azure 虚拟桌面资源(例如主机池、VM 等)分配相应的参与者权限。完成后,返回到本文并 创建 Azure 逻辑应用和执行计划 以完成初始设置过程。
创建 Azure 逻辑应用和执行计划
最后,需要创建 Azure 逻辑应用并为新的缩放工具设置执行计划。 首先,下载并导入 桌面虚拟化 PowerShell 模块 ,以在 PowerShell 会话中使用(如果尚未这样做)。
打开 PowerShell。
运行以下 cmdlet 登录到 Azure 帐户。
Connect-AzAccount -Environment AzureChinaCloud运行以下 cmdlet 以下载用于创建 Azure 逻辑应用的脚本。
New-Item -ItemType Directory -Path "C:\Temp" -Force Set-Location -Path "C:\Temp" $Uri = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/RDS-Templates/master/wvd-templates/wvd-scaling-script/CreateOrUpdateAzLogicApp.ps1" # Download the script Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $Uri -OutFile ".\CreateOrUpdateAzLogicApp.ps1"运行以下 PowerShell 脚本,为主机池创建 Azure 逻辑应用和执行计划
注释
需要为每个要自动缩放的主机池运行此脚本,但只需要一个Azure 自动化帐户。
$AADTenantId = (Get-AzContext).Tenant.Id $AzSubscription = Get-AzSubscription | Out-GridView -OutputMode:Single -Title "Select your Azure Subscription" Select-AzSubscription -Subscription $AzSubscription.Id $ResourceGroup = Get-AzResourceGroup | Out-GridView -OutputMode:Single -Title "Select the resource group for the new Azure Logic App" $WVDHostPool = Get-AzResource -ResourceType "Microsoft.DesktopVirtualization/hostpools" | Out-GridView -OutputMode:Single -Title "Select the host pool you'd like to scale" $LogAnalyticsWorkspaceId = Read-Host -Prompt "If you want to use Log Analytics, enter the Log Analytics Workspace ID returned by when you created the Azure Automation account, otherwise leave it blank" $LogAnalyticsPrimaryKey = Read-Host -Prompt "If you want to use Log Analytics, enter the Log Analytics Primary Key returned by when you created the Azure Automation account, otherwise leave it blank" $RecurrenceInterval = Read-Host -Prompt "Enter how often you'd like the job to run in minutes, e.g. '15'" $BeginPeakTime = Read-Host -Prompt "Enter the start time for peak hours in local time, e.g. 9:00" $EndPeakTime = Read-Host -Prompt "Enter the end time for peak hours in local time, e.g. 18:00" $TimeDifference = Read-Host -Prompt "Enter the time difference between local time and UTC in hours, e.g. +5:30" $SessionThresholdPerCPU = Read-Host -Prompt "Enter the maximum number of sessions per CPU that will be used as a threshold to determine when new session host VMs need to be started during peak hours" $MinimumNumberOfRDSH = Read-Host -Prompt "Enter the minimum number of session host VMs to keep running during off-peak hours" $MaintenanceTagName = Read-Host -Prompt "Enter the name of the Tag associated with VMs you don't want to be managed by this scaling tool" $LimitSecondsToForceLogOffUser = Read-Host -Prompt "Enter the number of seconds to wait before automatically signing out users. If set to 0, any session host VM that has user sessions, will be left untouched" $LogOffMessageTitle = Read-Host -Prompt "Enter the title of the message sent to the user before they are forced to sign out" $LogOffMessageBody = Read-Host -Prompt "Enter the body of the message sent to the user before they are forced to sign out" $WebhookURI = Read-Host -Prompt "Enter the webhook URI that has already been generated for this Azure Automation account. The URI is stored as encrypted in the above Automation Account variable. To retrieve the value, see https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/automation/shared-resources/variables?tabs=azure-powershell#powershell-cmdlets-to-access-variables" $Params = @{ "AADTenantId" = $AADTenantId # Optional. If not specified, it will use the current Azure context "SubscriptionID" = $AzSubscription.Id # Optional. If not specified, it will use the current Azure context "ResourceGroupName" = $ResourceGroup.ResourceGroupName # Optional. Default: "WVDAutoScaleResourceGroup" "Location" = $ResourceGroup.Location # Optional. Default: "China North 2" "UseARMAPI" = $true "HostPoolName" = $WVDHostPool.Name "HostPoolResourceGroupName" = $WVDHostPool.ResourceGroupName # Optional. Default: same as ResourceGroupName param value "LogAnalyticsWorkspaceId" = $LogAnalyticsWorkspaceId # Optional. If not specified, script will not log to the Log Analytics "LogAnalyticsPrimaryKey" = $LogAnalyticsPrimaryKey # Optional. If not specified, script will not log to the Log Analytics "RecurrenceInterval" = $RecurrenceInterval # Optional. Default: 15 "BeginPeakTime" = $BeginPeakTime # Optional. Default: "09:00" "EndPeakTime" = $EndPeakTime # Optional. Default: "17:00" "TimeDifference" = $TimeDifference # Optional. Default: "-7:00" "SessionThresholdPerCPU" = $SessionThresholdPerCPU # Optional. Default: 1 "MinimumNumberOfRDSH" = $MinimumNumberOfRDSH # Optional. Default: 1 "MaintenanceTagName" = $MaintenanceTagName # Optional. "LimitSecondsToForceLogOffUser" = $LimitSecondsToForceLogOffUser # Optional. Default: 1 "LogOffMessageTitle" = $LogOffMessageTitle # Optional. Default: "Machine is about to shutdown." "LogOffMessageBody" = $LogOffMessageBody # Optional. Default: "Your session will be logged off. Please save and close everything." "WebhookURI" = $WebhookURI } .\CreateOrUpdateAzLogicApp.ps1 @Params运行脚本后,Azure 逻辑应用应出现在资源组中,如下图所示。
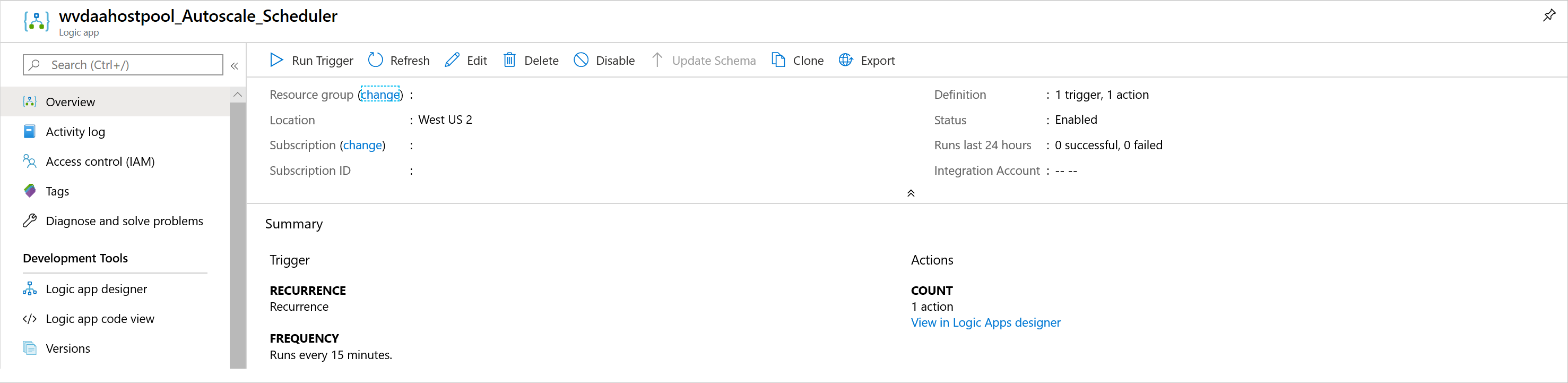
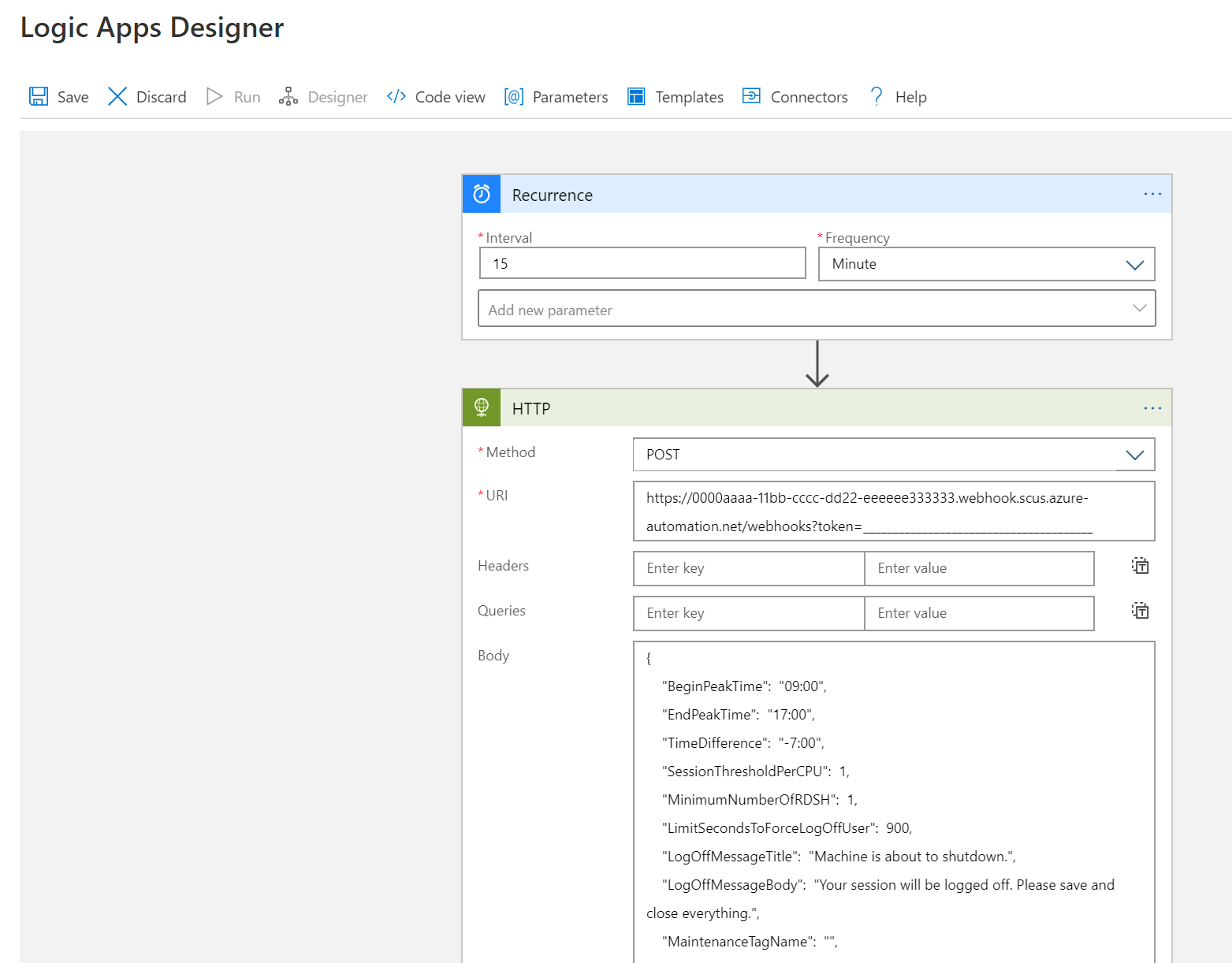
若要更改执行计划(例如更改重复间隔或时区),请转到 Azure 逻辑应用自动缩放计划程序,然后选择 “编辑 ”转到 Azure 逻辑应用设计器。
管理缩放工具
创建缩放工具后,即可访问其输出。 本部分介绍你可能会发现一些有用的功能。
查看作业状态
可以在 Azure 门户中查看所有 Runbook 作业的汇总状态,或查看特定 Runbook 作业的更深入的状态。
在所选 Azure 自动化帐户右侧的“作业统计信息”下,可以查看所有 Runbook 作业摘要的列表。 打开窗口左侧的 “作业 ”页会显示当前作业状态、开始时间和完成时间。
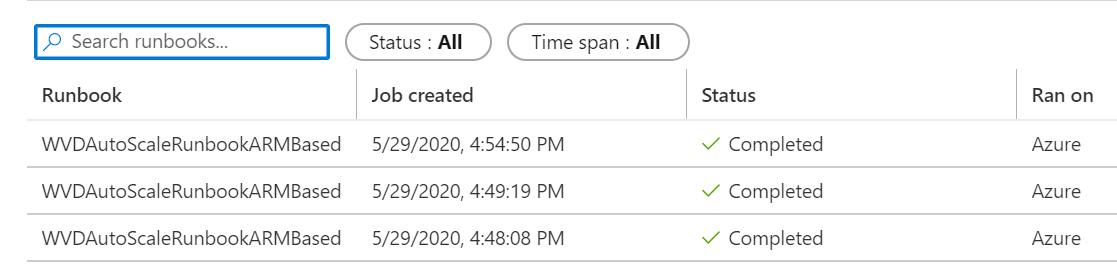
查看日志和缩放工具输出
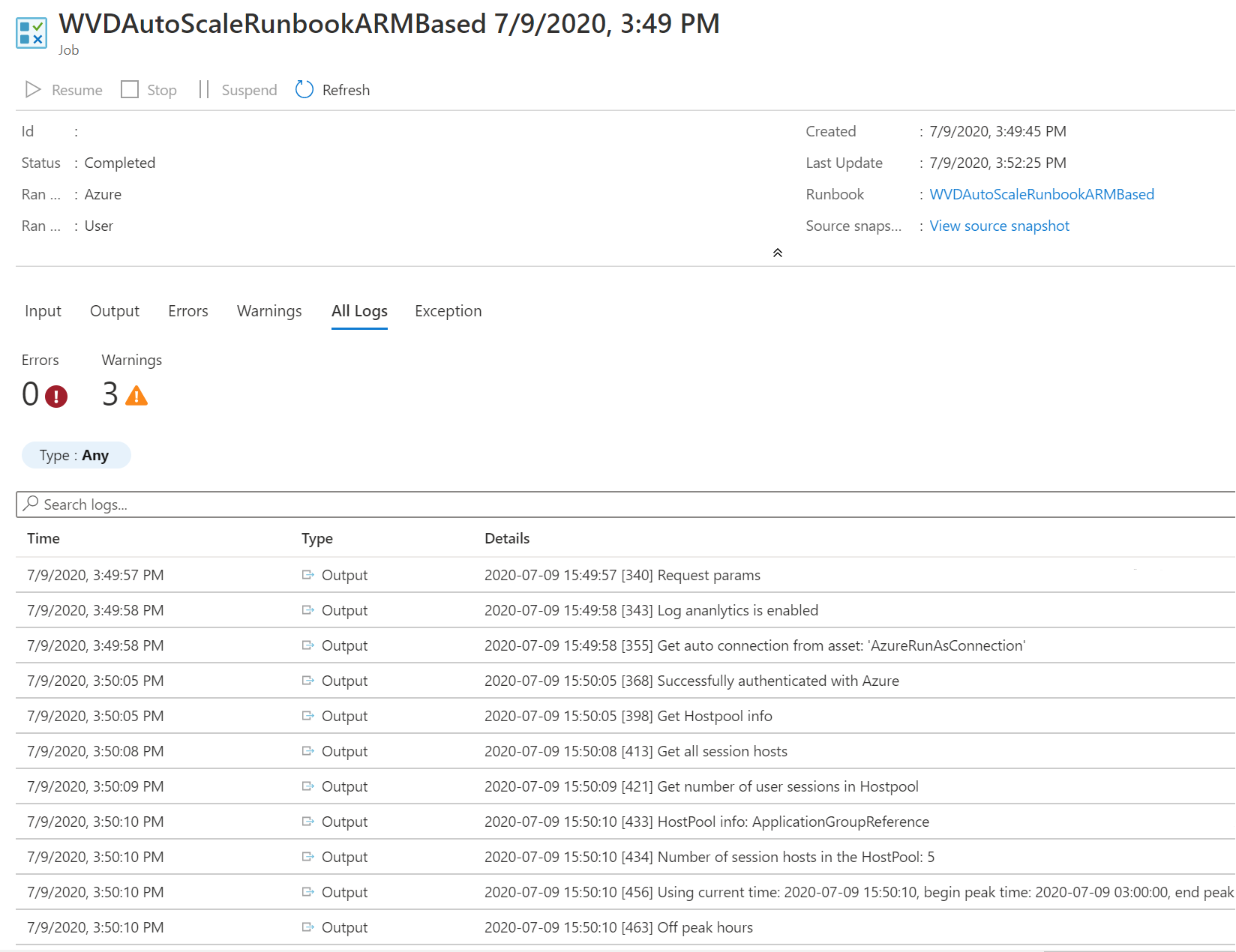
可以通过打开 runbook 并选择作业来查看横向扩展和横向缩减操作的日志。
导航到承载 Azure 自动化帐户的资源组中的运行手册,然后选择概述。 在概述页上,选择“ 最近作业 ”下的作业以查看其缩放工具输出,如下图所示。
检查运行手册脚本版本号
可以通过在 Azure 自动化帐户中打开 Runbook 文件并选择 “查看”来检查正在使用的 Runbook 脚本版本。 运行手册的脚本将显示在屏幕右侧。 在脚本中,你将在v#.#.#部分中看到格式为SYNOPSIS的版本号。 可 在此处找到最新的版本号。 如果在 Runbook 脚本中看不到版本号,这意味着你运行的是脚本的早期版本,应该立即更新它。 如果需要更新 Runbook 脚本,请按照 创建或更新 Azure 自动化帐户中的说明进行作。
报告问题
报告问题时,需要提供以下信息来帮助我们进行故障排除:
引起该问题的作业中的完整日志,位于 所有日志 选项卡下。 若要了解如何获取日志,请按照 查看日志和缩放工具输出中的说明进行作。 如果日志中有任何敏感信息或私有信息,可以在向我们提交问题之前将其删除。
正在使用的 Runbook 脚本的版本。 若要了解如何获取版本号,请参阅 检查 Runbook 脚本版本号
在 Azure 自动化帐户中安装的以下每个 PowerShell 模块的版本号。 若要查找这些模块,请打开 Azure 自动化帐户,在窗口左侧窗格中的“共享资源”部分下选择“模块”,然后搜索模块的名称。
- Az.Accounts
- Az.Compute
- Az.Resources
- Az.Automation
- OMSIngestionAPI
- Az.桌面虚拟化
Log Analytics
如果决定使用 Log Analytics,可以在 Log Analytics 工作区的“日志”视图中的“自定义日志”下查看名为WVDTenantScale_CL的自定义日志中的所有日志数据。 我们列出了你可能会发现有用的一些示例查询。
若要查看主机池的所有日志,请输入以下查询:
WVDTenantScale_CL | where hostpoolName_s == "<host_pool_name>" | project TimeStampUTC = TimeGenerated, TimeStampLocal = TimeStamp_s, HostPool = hostpoolName_s, LineNumAndMessage = logmessage_s, AADTenantId = TenantId若要查看主机池中当前正在运行的会话主机 VM 和活动用户会话总数,请输入以下查询:
WVDTenantScale_CL | where logmessage_s contains "Number of running session hosts:" or logmessage_s contains "Number of user sessions:" or logmessage_s contains "Number of user sessions per Core:" | where hostpoolName_s == "<host_pool_name>" | project TimeStampUTC = TimeGenerated, TimeStampLocal = TimeStamp_s, HostPool = hostpoolName_s, LineNumAndMessage = logmessage_s, AADTenantId = TenantId若要查看主机池中所有会话主机 VM 的状态,请输入以下查询:
WVDTenantScale_CL | where logmessage_s contains "Session host:" | where hostpoolName_s == "<host_pool_name>" | project TimeStampUTC = TimeGenerated, TimeStampLocal = TimeStamp_s, HostPool = hostpoolName_s, LineNumAndMessage = logmessage_s, AADTenantId = TenantId若要查看任何错误和警告,请输入以下查询:
WVDTenantScale_CL | where logmessage_s contains "ERROR:" or logmessage_s contains "WARN:" | project TimeStampUTC = TimeGenerated, TimeStampLocal = TimeStamp_s, HostPool = hostpoolName_s, LineNumAndMessage = logmessage_s, AADTenantId = TenantId
局限性
以下是使用此扩展脚本对会话主机虚拟机进行扩展的一些限制:
- 缩放脚本不考虑标准与夏令时之间的时间更改。