本文介绍如何在 Azure Databricks 中创建和使用按需功能。
若要使用按需特征,必须为 Unity Catalog 启用工作区,并且必须使用 Databricks Runtime 13.3 LTS ML 或更高版本。
什么是按需特征?
“按需”是指其值不是提前已知的,而是在推断时计算的特征。 在 Azure Databricks 中,使用 Python 用户定义的函数 (UDF) 来指定如何计算按需特征。 这些函数由 Unity Catalog 管理,并可通过目录资源管理器发现。
要求
- 若要使用用户定义的函数(UDF)创建训练集,或创建功能服务终结点,您必须对 Unity 目录中的
USE CATALOGsystem架构拥有USE SCHEMA目录和system.information_schema权限。
Workflow
若要计算按需特征,需要指定一个 Python 用户定义的函数 (UDF),该函数描述如何计算特征值。
- 在训练期间,可以在
feature_lookupsAPI 的create_training_set参数中提供此函数及其输入绑定。 - 必须使用特征存储方法
log_model记录训练的模型。 这样可以确保模型在用于推理时自动评估按需特征。 - 对于批量评分,
score_batchAPI 会自动计算并返回所有特征值,包括按需特征。
创建 Python UDF
可以使用 SQL 或 Python 代码创建 Python UDF。 以下示例在目录 main 和架构 default中创建 Python UDF。
Python
若要使用 Python,必须先安装 databricks-sdk[openai] 包。 按如下所示使用 %pip install:
%pip install unitycatalog-ai[databricks]
dbutils.library.restartPython()
然后,使用类似于下面的代码创建 Python UDF:
from unitycatalog.ai.core.databricks import DatabricksFunctionClient
client = DatabricksFunctionClient()
CATALOG = "main"
SCHEMA = "default"
def add_numbers(number_1: float, number_2: float) -> float:
"""
A function that accepts two floating point numbers, adds them,
and returns the resulting sum as a float.
Args:
number_1 (float): The first of the two numbers to add.
number_2 (float): The second of the two numbers to add.
Returns:
float: The sum of the two input numbers.
"""
return number_1 + number_2
function_info = client.create_python_function(
func=add_numbers,
catalog=CATALOG,
schema=SCHEMA,
replace=True
)
Databricks SQL
以下代码演示如何使用 Databricks SQL 创建 Python UDF:
%sql
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION main.default.add_numbers(x INT, y INT)
RETURNS INT
LANGUAGE PYTHON
COMMENT 'add two numbers'
AS $$
def add_numbers(n1: int, n2: int) -> int:
return n1 + n2
return add_numbers(x, y)
$$
运行代码后,可以在目录资源管理器中浏览三级命名空间以查看函数定义:
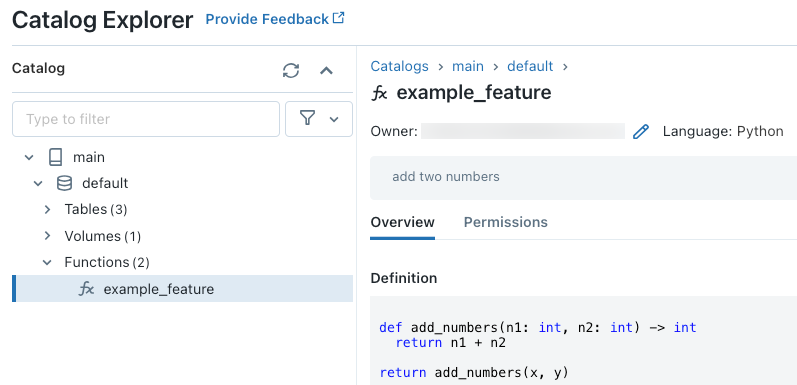
有关创建 Python UDF 的更多详细信息,请参阅将 Python UDF 注册到 Unity Catalog 和 SQL 语言手册。
如何处理缺失特征值
当 Python UDF 依赖于 FeatureLookup 的结果时,如果找不到请求的查找键,则返回的值由环境决定。 使用 score_batch 时,返回的值为 None。 实现联机服务时,返回的值为 float("nan")。
以下代码是关于如何处理这两种情况的示例。
%sql
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION square(x INT)
RETURNS INT
LANGUAGE PYTHON AS
$$
import numpy as np
if x is None or np.isnan(x):
return 0
return x * x
$$
使用按需特征训练模型
若要训练模型,请使用传递给 FeatureFunction 参数中 create_training_set API 的 feature_lookups。
以下示例代码使用上一节中定义的 Python UDF main.default.example_feature。
# Install databricks-feature-engineering first with:
# %pip install databricks-feature-engineering
# dbutils.library.restartPython()
from databricks.feature_engineering import FeatureEngineeringClient
from databricks.feature_engineering import FeatureFunction, FeatureLookup
from sklearn import linear_model
fe = FeatureEngineeringClient()
features = [
# The feature 'on_demand_feature' is computed as the sum of the input value 'new_source_input'
# and the pre-materialized feature 'materialized_feature_value'.
# - 'new_source_input' must be included in base_df and also provided at inference time.
# - For batch inference, it must be included in the DataFrame passed to 'FeatureEngineeringClient.score_batch'.
# - For real-time inference, it must be included in the request.
# - 'materialized_feature_value' is looked up from a feature table.
FeatureFunction(
udf_name="main.default.example_feature", # UDF must be in Unity Catalog so uses a three-level namespace
input_bindings={
"x": "new_source_input",
"y": "materialized_feature_value"
},
output_name="on_demand_feature",
),
# retrieve the prematerialized feature
FeatureLookup(
table_name = 'main.default.table',
feature_names = ['materialized_feature_value'],
lookup_key = 'id'
)
]
# base_df includes the columns 'id', 'new_source_input', and 'label'
training_set = fe.create_training_set(
df=base_df,
feature_lookups=features,
label='label',
exclude_columns=['id', 'new_source_input', 'materialized_feature_value'] # drop the columns not used for training
)
# The training set contains the columns 'on_demand_feature' and 'label'.
training_df = training_set.load_df().toPandas()
# training_df columns ['materialized_feature_value', 'label']
X_train = training_df.drop(['label'], axis=1)
y_train = training_df.label
model = linear_model.LinearRegression().fit(X_train, y_train)
指定默认值
若要指定功能的默认值,请使用 default_values .. 中的 FeatureLookup参数。
FeatureLookup(
table_name = 'main.default.table',
feature_names = ['materialized_feature_value'],
lookup_key = 'id',
default_values={
"materialized_feature_value": 0
}
)
如果使用 rename_outputs 参数重命名特征列,则 default_values 必须使用重命名后的特征名称。
FeatureLookup(
table_name = 'main.default.table',
feature_names = ['materialized_feature_value'],
lookup_key = 'id',
rename_outputs={"materialized_feature_value": "feature_value"},
default_values={
"feature_value": 0
}
)
记录模型并将其注册到 Unity Catalog
使用特征元数据打包的模型可以注册到 Unity Catalog。 用于创建模型的特征表必须存储在 Unity Catalog 中。
为了确保模型在用于推理时自动评估按需特征,必须设置注册表 URI,然后记录模型,如下所示:
import mlflow
mlflow.set_registry_uri("databricks-uc")
fe.log_model(
model=model,
artifact_path="main.default.model",
flavor=mlflow.sklearn,
training_set=training_set,
registered_model_name="main.default.recommender_model"
)
如果定义按需特征的 Python UDF 导入任何 Python 包,则必须使用参数 extra_pip_requirements 指定这些包。 例如:
import mlflow
mlflow.set_registry_uri("databricks-uc")
fe.log_model(
model=model,
artifact_path="model",
flavor=mlflow.sklearn,
training_set=training_set,
registered_model_name="main.default.recommender_model",
extra_pip_requirements=["scikit-learn==1.20.3"]
)
限制
按需特征可以输出特征存储支持的所有数据类型(MapType 和 ArrayType 除外)。
Notebook 示例:按需特征
以下笔记本演示一个示例,说明如何培训使用按需特征的模型并对其进行评分。
基本按需特征演示笔记本
以下笔记本演示了一个餐厅推荐模型示例。 餐馆的位置是从 Databricks 在线表查找的。 用户的当前位置会作为评分请求的一部分发送。 该模型使用按需特征来计算用户到餐厅的实时距离。 然后,该距离用作模型的输入。